Visual designers are the creative minds behind the aesthetics of digital and print media. They focus on the look and feel of a product, ensuring it is visually appealing and aligned with the brand's identity.
Visual design skills encompass a range of abilities, including proficiency in design software like Adobe Creative Suite, a strong understanding of color theory and typography, and the ability to create compelling visual narratives.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Visual Designer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 9 essential Visual Designer skills, 11 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
9 fundamental Visual Designer skills and traits
The best skills for Visual Designers include Typography, Color Theory, Layout Design, Graphic Software, User Interface (UI) Design, Branding, Illustration, Responsive Design and Prototyping.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 essential skills of a Visual Designer.
Typography
Typography is the art of arranging text in a visually appealing way. A visual designer uses this skill to ensure that the text is readable and aesthetically pleasing, which helps in conveying the message effectively.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Graphic Designer Job Description.
Color Theory
Understanding color theory is crucial for creating visually harmonious designs. A visual designer uses this knowledge to choose color schemes that evoke the right emotions and ensure brand consistency.
Layout Design
Layout design involves arranging visual elements on a page. A visual designer uses this skill to create balanced and organized designs that guide the viewer's eye and enhance the overall user experience.
Graphic Software
Proficiency in graphic software like Adobe Creative Suite is essential. A visual designer uses these tools to create and manipulate visual elements, ensuring high-quality and professional designs.
User Interface (UI) Design
UI design focuses on the look and feel of a product's interface. A visual designer uses this skill to create intuitive and visually appealing interfaces that enhance user interaction.
Branding
Branding involves creating a cohesive visual identity for a brand. A visual designer ensures that all design elements align with the brand's values and message, maintaining consistency across all platforms.
Illustration
Illustration skills allow a visual designer to create custom graphics and visuals. This adds a unique touch to designs and helps in effectively communicating complex ideas.
Responsive Design
Responsive design ensures that visuals look good on all devices. A visual designer uses this skill to create flexible designs that provide a seamless user experience across different screen sizes.
Prototyping
Prototyping involves creating interactive mockups of designs. A visual designer uses this skill to test and refine design concepts before final implementation, ensuring functionality and usability.
11 secondary Visual Designer skills and traits
The best skills for Visual Designers include Animation, Photography, 3D Modeling, Print Design, Web Design, Video Editing, Data Visualization, Wireframing, Content Management Systems (CMS), SEO Basics and HTML/CSS.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 11 secondary skills of a Visual Designer.
Animation
Animation skills can bring static designs to life. A visual designer might use animation to create engaging and dynamic content that captures the audience's attention.
Photography
Basic photography skills can be useful for a visual designer. Understanding composition, lighting, and editing can help in creating or selecting high-quality images for designs.
3D Modeling
3D modeling skills allow a visual designer to create three-dimensional visuals. This can be particularly useful for product design, virtual reality, and other immersive experiences.
Print Design
Print design involves creating visuals for physical media like brochures, posters, and packaging. A visual designer uses this skill to ensure that designs are print-ready and visually appealing.
Web Design
Web design skills are important for creating visually appealing websites. A visual designer uses this knowledge to ensure that web pages are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Video Editing
Video editing skills can enhance a visual designer's ability to create compelling multimedia content. This is useful for marketing campaigns, social media, and other digital platforms.
Data Visualization
Data visualization involves presenting data in a graphical format. A visual designer uses this skill to create clear and informative charts, graphs, and infographics.
Wireframing
Wireframing is the process of creating a basic layout of a design. A visual designer uses this skill to plan the structure and functionality of a design before adding detailed visual elements.
Content Management Systems (CMS)
Knowledge of CMS platforms like WordPress can be beneficial. A visual designer might use this skill to manage and update website content efficiently.
SEO Basics
Understanding basic SEO principles can help a visual designer create search-friendly designs. This ensures that the visual content contributes to the overall visibility and ranking of a website.
HTML/CSS
Basic knowledge of HTML and CSS can be useful for a visual designer. This allows for better collaboration with developers and ensures that designs are implemented accurately.
How to assess Visual Designer skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a Visual Designer goes beyond just glancing at their portfolio or resume. It involves a deep dive into their understanding and application of key design principles such as typography, color theory, and layout design, among others.
While portfolios can showcase a candidate's ability to use graphic software and create visually appealing designs, they don't always reveal the depth of their understanding of user interface design or their ability to adapt designs for responsive frameworks. This is where structured assessments come into play.
Using tailored assessments like those offered by Adaface can significantly streamline the hiring process. These tests are designed to measure a candidate's practical skills in areas like UI design, branding, and prototyping, ensuring that you're not just assessing their theoretical knowledge but also their ability to apply it in real-world scenarios. By integrating Adaface assessments, companies have reported a 85% reduction in screening time, making it easier to identify top talent quickly.
Let’s look at how to assess Visual Designer skills with these 1 talent assessments.
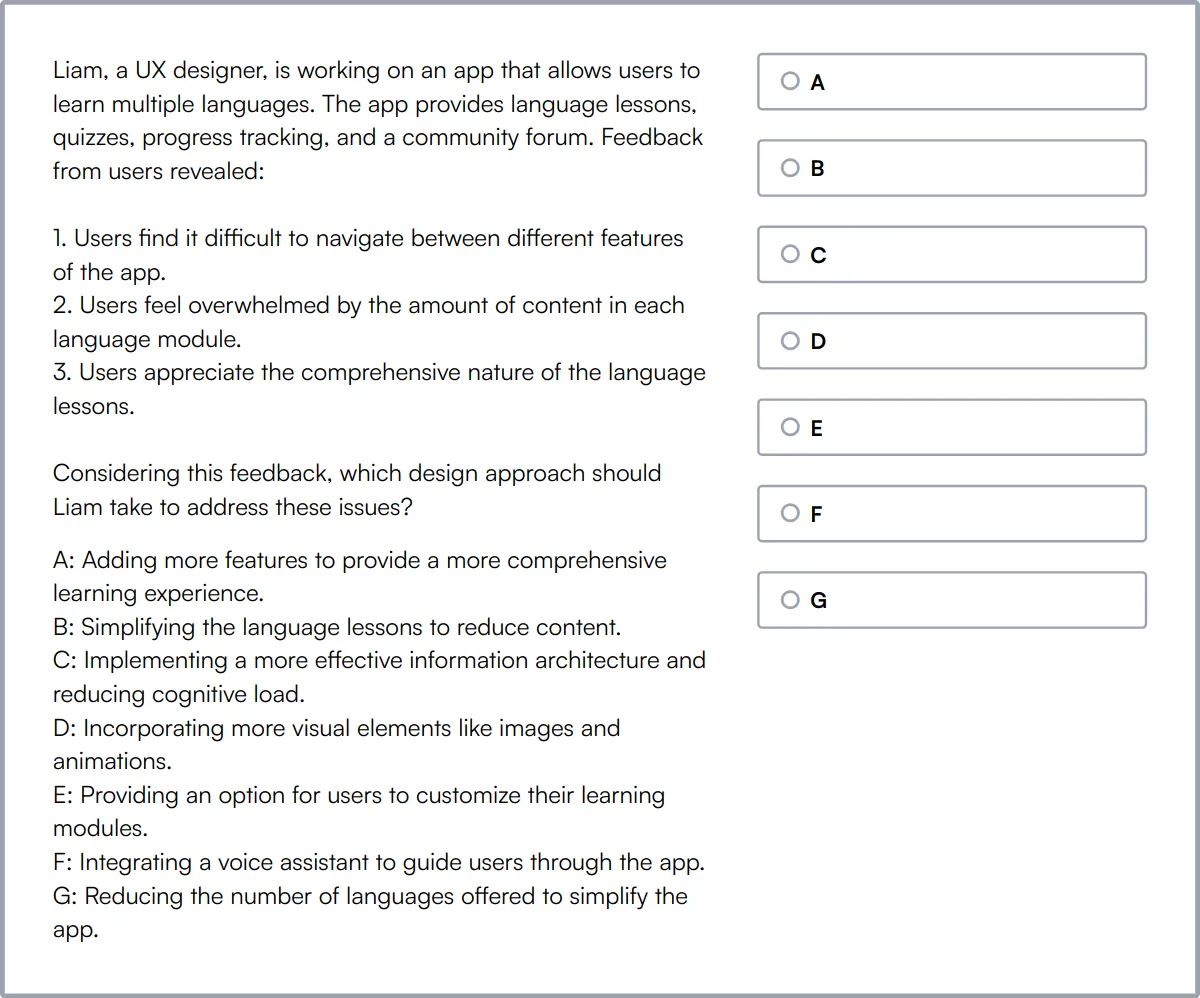
UI/UX Design Test
Our UI/UX Design Test focuses on testing concepts around wire-framing, prototyping, A/B testing, landing pages, and UI/UX design principles. It assesses a candidate's product designing skills and their ability to create useful designs for feature requirements via scenario-based questions.
The test assesses their understanding of design thinking, UX design principles, wire-framing, landing pages, and customer journey. It also covers UI fundamentals, A/B testing, user research techniques, and interaction design principles.
Successful candidates have a strong grasp of visual design principles, information architecture, and mobile app design considerations. They also demonstrate knowledge of accessibility guidelines and principles, UX writing and content strategy, and human-computer interaction (HCI) fundamentals.
Summary: The 9 key Visual Designer skills and how to test for them
| Visual Designer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Typography | Evaluate candidate's ability to use fonts to enhance readability and aesthetics. |
| 2. Color Theory | Assess understanding of color interactions and their impact on design. |
| 3. Layout Design | Review effectiveness in organizing content for optimal user engagement. |
| 4. Graphic Software | Test proficiency in tools like Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator. |
| 5. User Interface (UI) Design | Examine designs for functionality, aesthetic appeal, and user friendliness. |
| 6. Branding | Check ability to create cohesive identities that resonate with audiences. |
| 7. Illustration | Assess skill in creating visual representations for various media. |
| 8. Responsive Design | Evaluate designs that adapt well to different screen sizes. |
| 9. Prototyping | Test ability to create functional previews of projects. |
Visual Reasoning Test
Visual Designer skills FAQs
What is the importance of typography in visual design?
Typography sets the tone and readability of a design. It involves choosing fonts, sizes, and spacing to create a visually appealing and readable text layout.
How can I assess a candidate's knowledge of color theory?
Ask for a portfolio showcasing their use of color. Discuss their choices and reasoning behind color schemes in their projects.
What should I look for in a candidate's layout design skills?
Evaluate their ability to organize elements in a visually pleasing and functional manner. Check for balance, alignment, and consistency in their work.
Which graphic software should a visual designer be proficient in?
Common tools include Adobe Creative Suite (Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign), Sketch, and Figma. Proficiency in these tools is often expected.
Why is user interface (UI) design important for a visual designer?
UI design focuses on the look and feel of a product. It ensures that the interface is visually appealing and user-friendly.
How can I evaluate a candidate's branding skills?
Review their portfolio for consistency in brand elements like logos, color schemes, and typography. Discuss their approach to creating a cohesive brand identity.
What is responsive design and why is it important?
Responsive design ensures that a website or application looks good on all devices. It involves flexible layouts and scalable images to provide a seamless user experience.
How can I test a candidate's prototyping skills?
Ask them to create a prototype for a given project. Evaluate their ability to translate ideas into interactive models using tools like Figma, Sketch, or Adobe XD.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



