UI designers are responsible for crafting the visual elements of digital products, ensuring that users have an engaging and intuitive experience. They work closely with UX designers and developers to bring wireframes and prototypes to life, focusing on aesthetics, consistency, and usability.
UI design skills encompass a range of abilities, including proficiency in design tools like Sketch, Figma, and Adobe XD, as well as a strong understanding of color theory, typography, and layout principles. Additionally, soft skills such as creativity and attention to detail are crucial for success in this role.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job UI Designer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 7 essential UI Designer skills, 7 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
7 fundamental UI Designer skills and traits
The best skills for UI Designers include Visual Design, UX Principles, Prototyping, Interaction Design, Responsive Design, Typography and Color Theory.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 7 essential skills of a UI Designer.
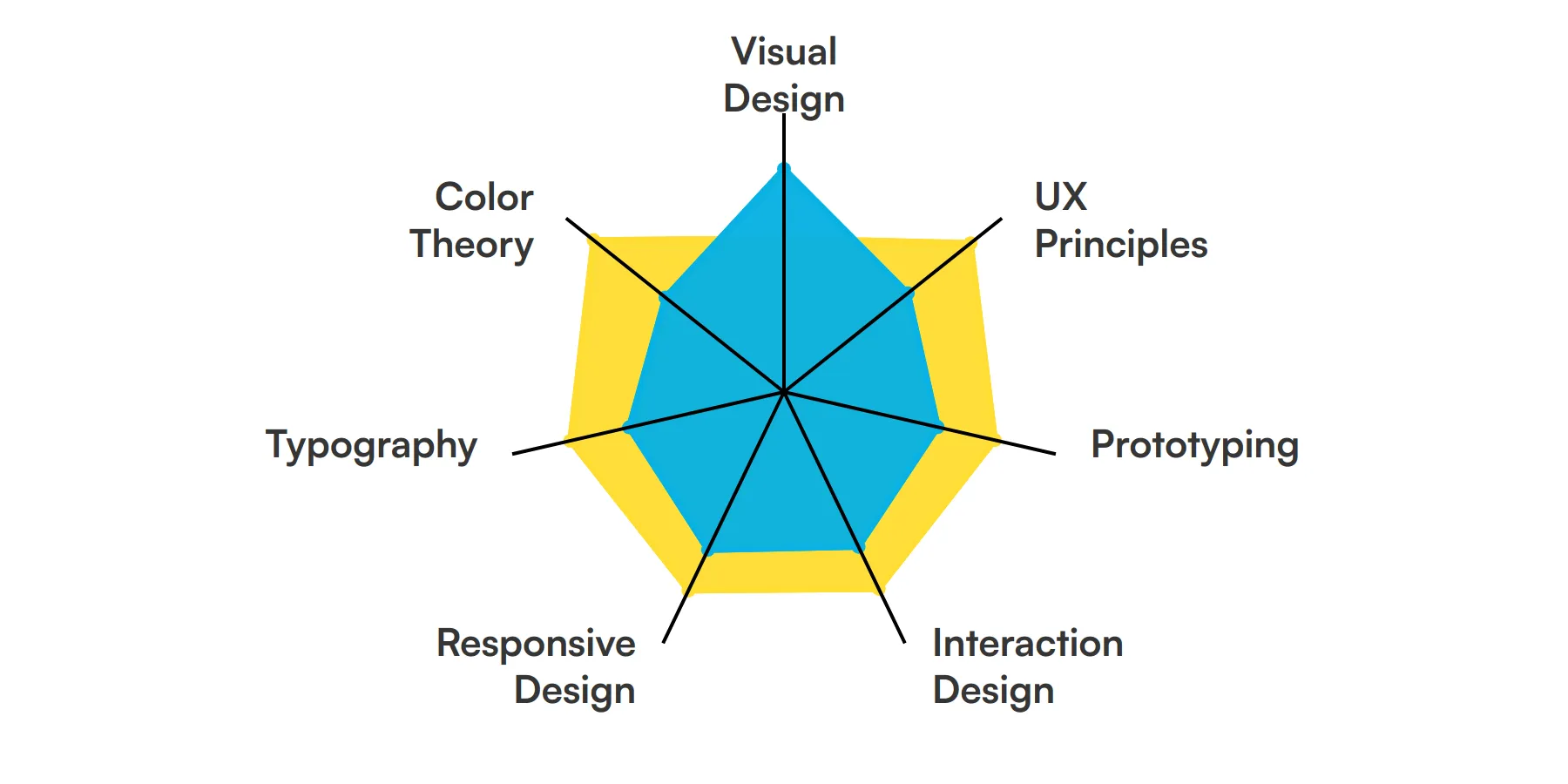
Visual Design
Visual design focuses on the aesthetics of a site and its related materials by strategically implementing images, colors, fonts, and other elements. A UI designer uses this skill to create a compelling layout that enhances the user's experience while ensuring the interface is attractive.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Visual Designer Job Description.
UX Principles
Understanding UX principles is key for a UI designer, as it involves creating a logical flow in the user interface that enhances usability and user satisfaction. This skill ensures that the design is not only visually pleasing but also functional and easy to navigate.
Prototyping
Prototyping is a crucial stage in UI design where ideas are brought to life. UI designers use tools like Sketch or Adobe XD to create mockups that simulate the final product, allowing for iterative testing and feedback to refine the interface.
Interaction Design
This skill involves designing engaging interfaces with logical interactions. It requires a deep understanding of how users and technology communicate, ensuring that the UI designer can create an intuitive interface that responds to user actions.
Responsive Design
Responsive design ensures that an application’s interface adjusts smoothly across different devices. A UI designer must master this skill to ensure a seamless user experience whether the user is on a desktop, tablet, or mobile phone.
Typography
Typography in UI design involves choosing and arranging typefaces to make the text not only readable but also visually appealing. This skill is important for UI designers as text is a primary communication tool in user interfaces.
Color Theory
Color theory is essential for UI designers as it influences user perception and actions within the interface. A UI designer uses this skill to create a color palette that aligns with brand identity and enhances user experience.
7 secondary UI Designer skills and traits
The best skills for UI Designers include User Research, Information Architecture, Graphic Design, Web Development, Animation, Accessibility Standards and Software Proficiency.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 7 secondary skills of a UI Designer.
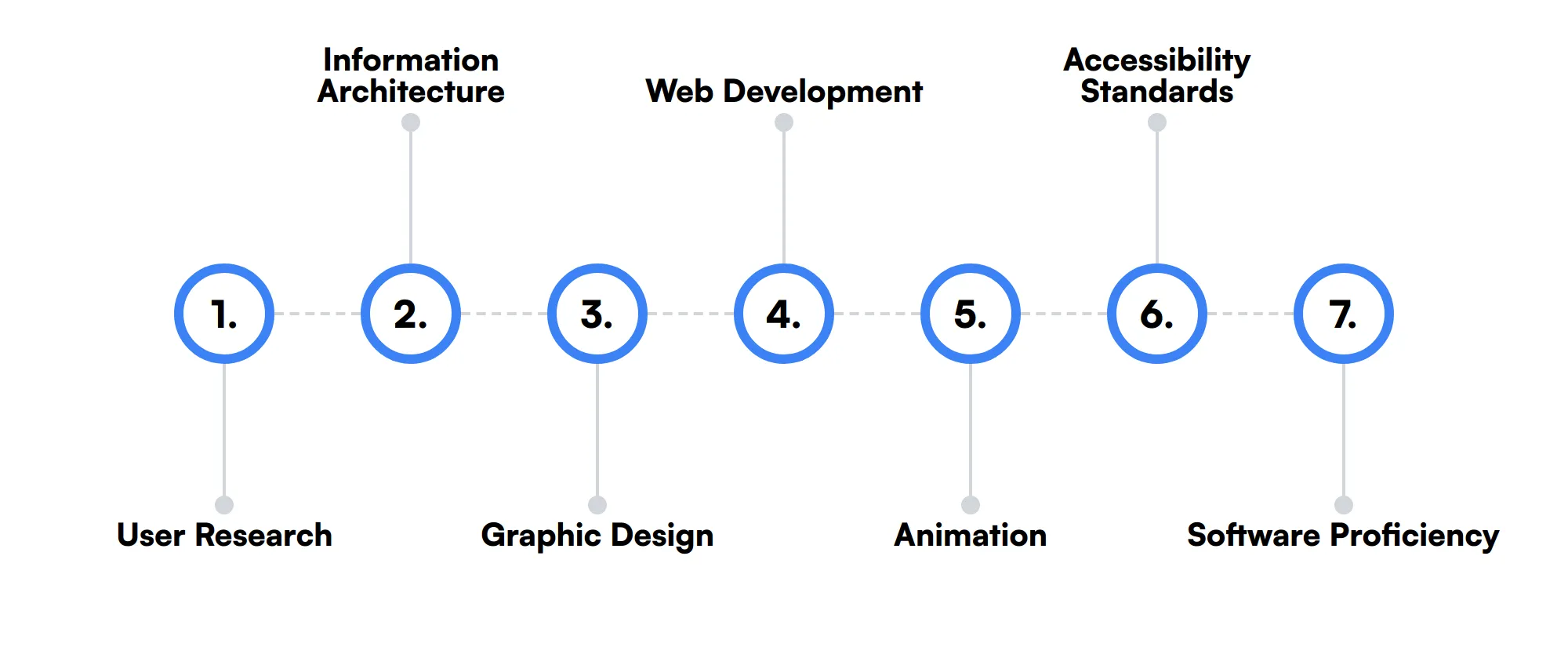
User Research
User research involves gathering insights about the target users' behaviors, needs, and motivations through observation techniques, task analysis, and other feedback methodologies. This skill helps inform the design process.
Information Architecture
Information architecture is the skill of structuring and organizing content in a way that users can navigate intuitively. It's crucial for ensuring that users find information they need efficiently.
Graphic Design
Graphic design skills are useful for UI designers to create visual elements such as icons and images that are both attractive and supportive of the user experience.
Web Development
Basic knowledge of web development, including HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, allows UI designers to understand the constraints and possibilities of web platforms when designing interfaces.
Animation
Animation can enhance the user experience by providing visual feedback and creating a dynamic interface. UI designers use this skill to guide users through their interaction with the product.
Accessibility Standards
Knowledge of accessibility standards ensures that UI designs are usable by people with a wide range of physical and cognitive abilities. This skill is important for creating inclusive products.
Software Proficiency
Proficiency in design software like Adobe Suite, Figma, and Sketch is necessary for creating high-fidelity designs and effective prototypes.
How to assess UI Designer skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a UI Designer can be a nuanced process. While resumes and portfolios provide a glimpse into a designer's capabilities, they often fall short of revealing the depth of their proficiency in key areas such as Visual Design, UX Principles, Prototyping, Interaction Design, Responsive Design, Typography, and Color Theory. To truly understand a candidate's competencies, a more hands-on approach is necessary.
Skills-based assessments offer a reliable way to evaluate a UI Designer's abilities. These assessments can simulate real-world tasks and challenges, providing insights into how a designer thinks and solves problems. Adaface on-the-job skill tests are an excellent tool for this purpose, helping you achieve 2x improved quality of hires and an 85% reduction in screening time. By focusing on practical skills, you can ensure that your candidates are not only qualified but also a great fit for your specific needs.
Let’s look at how to assess UI Designer skills with these 1 talent assessments.
UI/UX Design Test
Our UI/UX Design Test evaluates a candidate's ability to create user-friendly and visually appealing designs. It covers a wide range of skills necessary for effective UI/UX design.
The test assesses their understanding of design thinking, UX design principles, wire-framing, and landing pages. It also evaluates their knowledge of customer journey, UI fundamentals, and A/B testing. Candidates are tested on their ability to conduct user research, apply interaction and visual design principles, and consider mobile app design.
High-scoring candidates demonstrate proficiency in information architecture, accessibility guidelines, UX writing, and human-computer interaction fundamentals. They show a strong ability to create designs that meet feature requirements through scenario-based questions.
Summary: The 7 key UI Designer skills and how to test for them
| UI Designer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Visual Design | Evaluate the candidate’s ability to create aesthetically pleasing interfaces. |
| 2. UX Principles | Assess understanding of user-centered design and usability principles. |
| 3. Prototyping | Check proficiency in creating interactive mockups and wireframes. |
| 4. Interaction Design | Determine skills in designing intuitive user interactions. |
| 5. Responsive Design | Evaluate ability to create designs that adapt to various devices. |
| 6. Typography | Assess knowledge of font selection and text layout. |
| 7. Color Theory | Evaluate understanding of color usage and combinations. |
UI/UX Design Test
UI Designer skills FAQs
What are the key skills to look for in a UI Designer?
Key skills include Visual Design, UX Principles, Prototyping, Interaction Design, Responsive Design, Typography, Color Theory, User Research, Information Architecture, Graphic Design, Web Development, Animation, Accessibility Standards, and Software Proficiency.
How can I assess a candidate's proficiency in Visual Design?
Review their portfolio for design aesthetics, attention to detail, and creativity. Look for consistency in style and the ability to create visually appealing interfaces.
What is the importance of UX Principles in UI Design?
UX Principles ensure that the design is user-centered, providing a seamless and intuitive experience. Assess this by discussing their approach to user research and usability testing.
How do I evaluate a UI Designer's prototyping skills?
Ask for examples of prototypes they have created. Evaluate their ability to use prototyping tools and how effectively they communicate design ideas through prototypes.
Why is Responsive Design important and how can I test it?
Responsive Design ensures that interfaces work well on various devices. Assess this by reviewing their portfolio for designs that adapt to different screen sizes and asking about their approach to responsive design.
What should I look for in a candidate's understanding of Typography?
Evaluate their knowledge of font pairing, readability, and hierarchy. Review their portfolio to see how they use typography to enhance the user experience.
How can I assess a UI Designer's knowledge of Accessibility Standards?
Discuss their understanding of accessibility guidelines and ask for examples of how they have implemented accessible design in their projects.
What software proficiency should a UI Designer have?
Look for proficiency in design tools like Adobe XD, Sketch, Figma, and prototyping tools. Assess their ability to use these tools effectively through their portfolio and practical tests.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



