SQL developers are responsible for managing and organizing data in databases. They write and optimize SQL queries to ensure data is easily accessible and efficiently stored, playing a key role in data management and analysis.
SQL development skills include proficiency in SQL programming, understanding of database management systems, and the ability to troubleshoot and optimize queries. Additionally, skills like analytical thinking and attention to detail are important for success in this role.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job SQL Developer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 9 essential SQL Developer skills, 10 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
9 fundamental SQL Developer skills and traits
The best skills for SQL Developers include SQL Proficiency, Database Design, Data Modeling, Performance Tuning, Stored Procedures, Backup and Recovery, Security Management, ETL Processes and Version Control.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 essential skills of a SQL Developer.
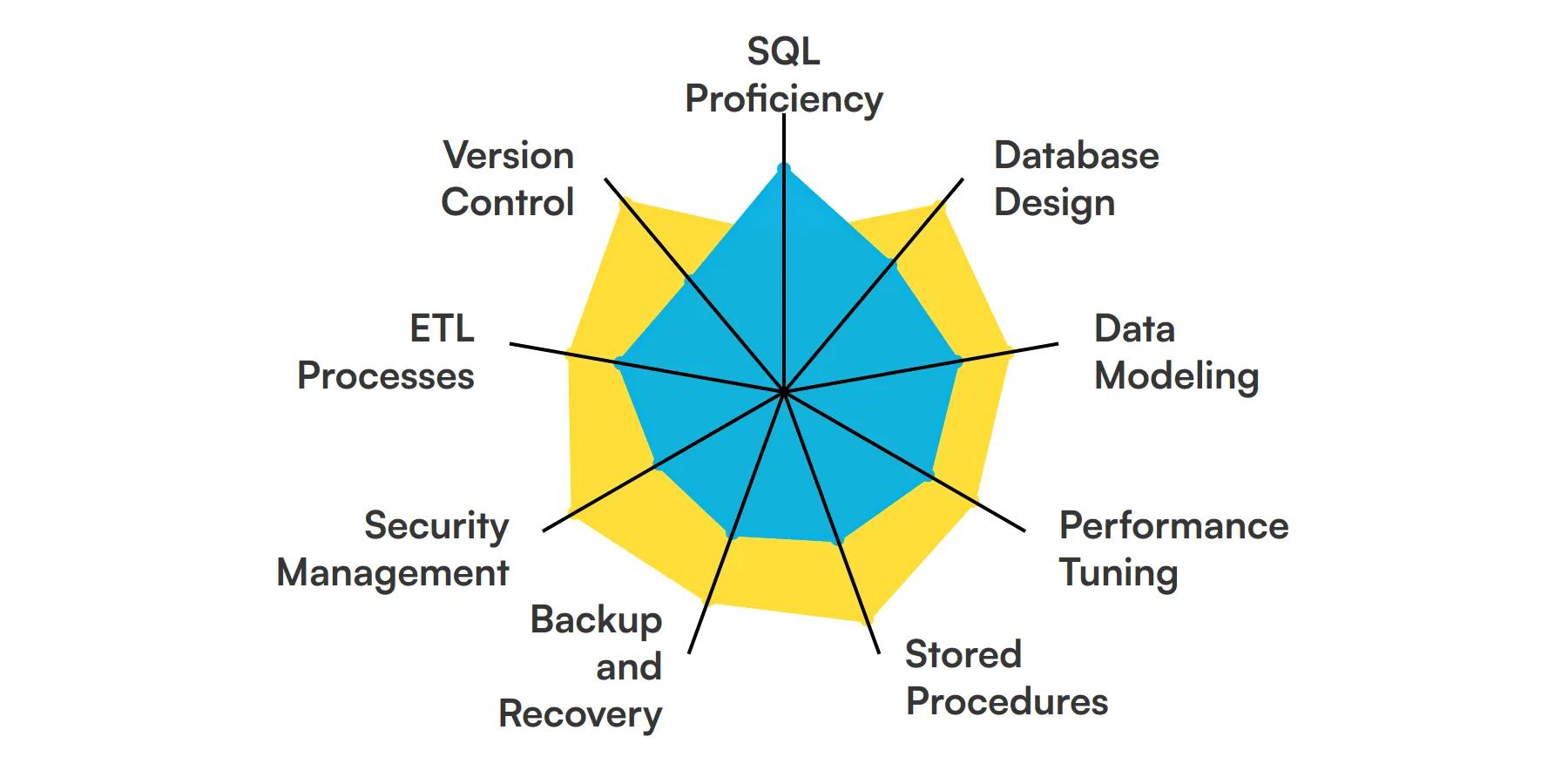
SQL Proficiency
A SQL Developer must have a strong command of SQL to write, optimize, and troubleshoot queries. This skill is fundamental for managing and manipulating databases effectively.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a SQL Developer Job Description.
Database Design
Understanding database design principles is crucial for creating efficient and scalable databases. This includes knowledge of normalization, indexing, and relationships between tables.
Data Modeling
Data modeling involves creating visual representations of data structures. SQL Developers use this skill to ensure data is stored logically and can be retrieved efficiently.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Performance Tuning
Performance tuning is about optimizing database performance. SQL Developers need to identify bottlenecks and improve query execution times to ensure smooth database operations.
Stored Procedures
Writing and managing stored procedures allows SQL Developers to encapsulate complex business logic within the database. This helps in maintaining code consistency and reusability.
Backup and Recovery
Knowledge of backup and recovery strategies is essential for data protection. SQL Developers must ensure that data can be restored in case of corruption or loss.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Database Administrator (DBA) Job Description.
Security Management
Implementing security measures to protect data from unauthorized access is a key responsibility. SQL Developers need to manage user permissions and encryption techniques.
ETL Processes
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes are used to move data between systems. SQL Developers design and implement these processes to ensure data integrity and consistency.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Version Control
Using version control systems like Git helps SQL Developers manage changes to database schemas and scripts. This ensures that changes are tracked and can be rolled back if necessary.
10 secondary SQL Developer skills and traits
The best skills for SQL Developers include Scripting Languages, Cloud Platforms, Data Warehousing, Big Data Technologies, Reporting Tools, API Integration, NoSQL Databases, Data Governance, Agile Methodologies and Business Acumen.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 10 secondary skills of a SQL Developer.
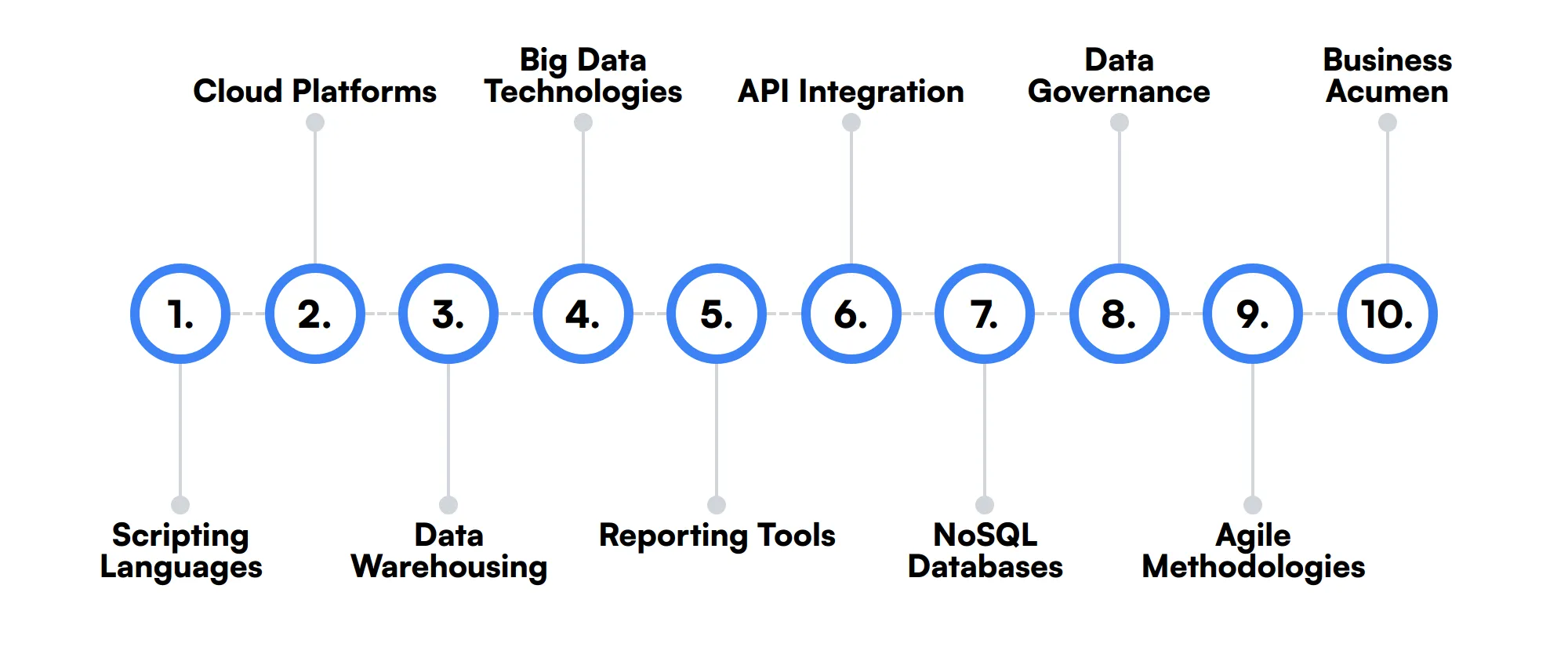
Scripting Languages
Familiarity with scripting languages like Python or PowerShell can be beneficial for automating database tasks and integrating with other systems.
Cloud Platforms
Knowledge of cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud is useful for managing databases in cloud environments. This includes understanding cloud-specific database services.
Data Warehousing
Experience with data warehousing concepts and tools can help SQL Developers in designing systems that support large-scale data analysis and reporting.
Big Data Technologies
Familiarity with big data technologies like Hadoop or Spark can be advantageous for handling large datasets and performing complex data processing tasks.
Reporting Tools
Knowledge of reporting tools like Tableau or Power BI allows SQL Developers to create visualizations and reports that help stakeholders make data-driven decisions.
API Integration
Understanding how to integrate databases with APIs can be useful for enabling data exchange between different systems and applications.
NoSQL Databases
Familiarity with NoSQL databases like MongoDB or Cassandra can be beneficial for projects that require flexible schema designs and horizontal scalability.
Data Governance
Knowledge of data governance practices helps ensure data quality, consistency, and compliance with regulations. SQL Developers may need to implement these practices in their work.
Agile Methodologies
Understanding agile methodologies can help SQL Developers work more effectively in teams that use iterative development processes and continuous integration.
Business Acumen
Having a good understanding of the business context in which the database operates can help SQL Developers design solutions that align with organizational goals.
How to assess SQL Developer skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of SQL Developers is a nuanced process that involves more than just glancing at a resume. While a resume might highlight a candidate's exposure to SQL Proficiency, Database Design, or Security Management, it doesn't provide a clear picture of their hands-on capabilities or problem-solving skills.
To truly understand whether a candidate will thrive in a SQL Developer role, employers must implement practical and targeted assessments. This approach ensures that the candidate not only knows the theory but can also apply their knowledge effectively in real-world scenarios. For instance, testing their skills in Performance Tuning or ETL Processes can reveal much about their ability to optimize and manage data workflows efficiently.
Using specialized assessment tools like Adaface can significantly streamline the hiring process. Adaface assessments are designed to mirror actual job tasks, allowing employers to see candidates in action. By integrating these assessments, companies have reported an 85% reduction in screening time, making it easier to identify top talent swiftly. For more details on how Adaface can enhance your hiring process, visit Adaface assessments.
Let’s look at how to assess SQL Developer skills with these 5 talent assessments.
SQL Online Test
SQL Online Test evaluates a candidate's ability to design and build relational databases and tables from scratch, apply CRUD options, write efficient queries and subqueries to filter data, and create efficient indexes for faster SQL queries.
The test assesses their understanding of creating databases, CRUD operations, joins, subqueries, conditional expressions, views, indexes, string functions, mathematical functions, timestamps, locks, transactions, scale, and security.
Successful candidates demonstrate proficiency in database creation, table management, and query optimization.
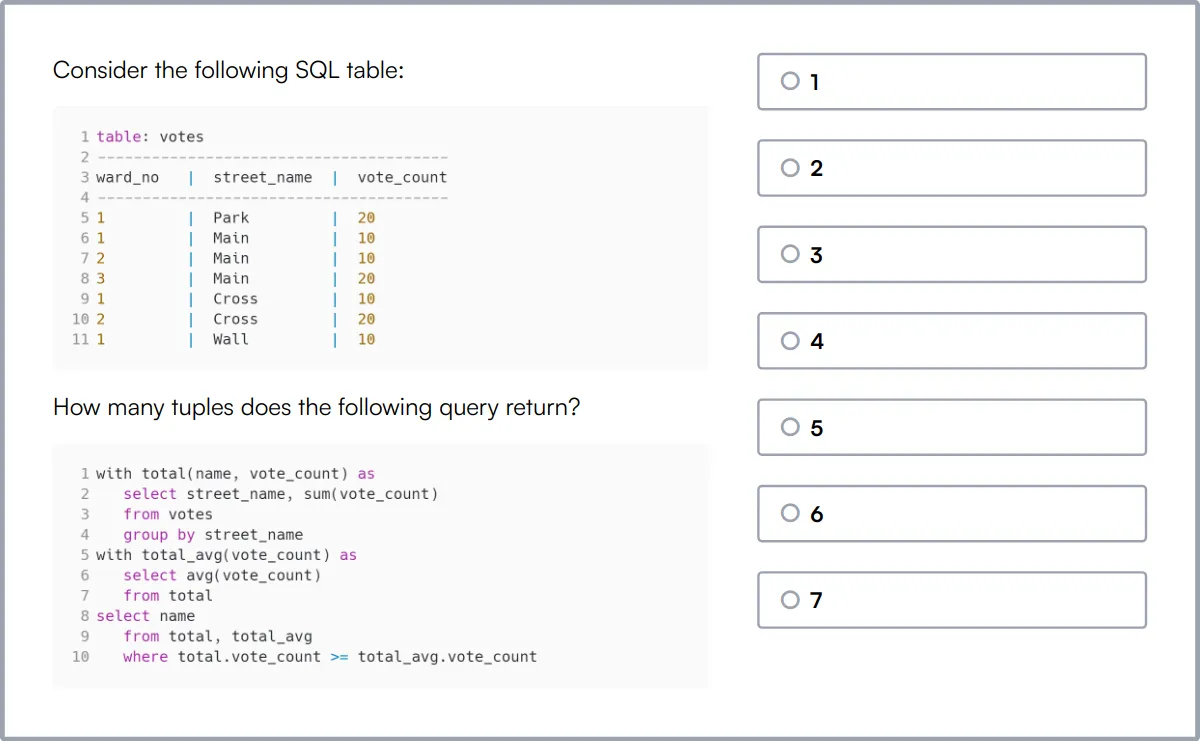
Data Modeling Skills Test
Data Modeling Skills Test evaluates a candidate's knowledge and abilities in database design, SQL, ER diagrams, normalization, relational schema, data integrity, data mapping, data warehousing, data manipulation, data validation, and data transformation.
The test assesses their understanding of data modeling, database design, SQL, ER diagrams, normalization, relational schema, data integrity, data mapping, data validation, and data transformation.
Candidates who excel in this test show strong skills in database design and data integrity.
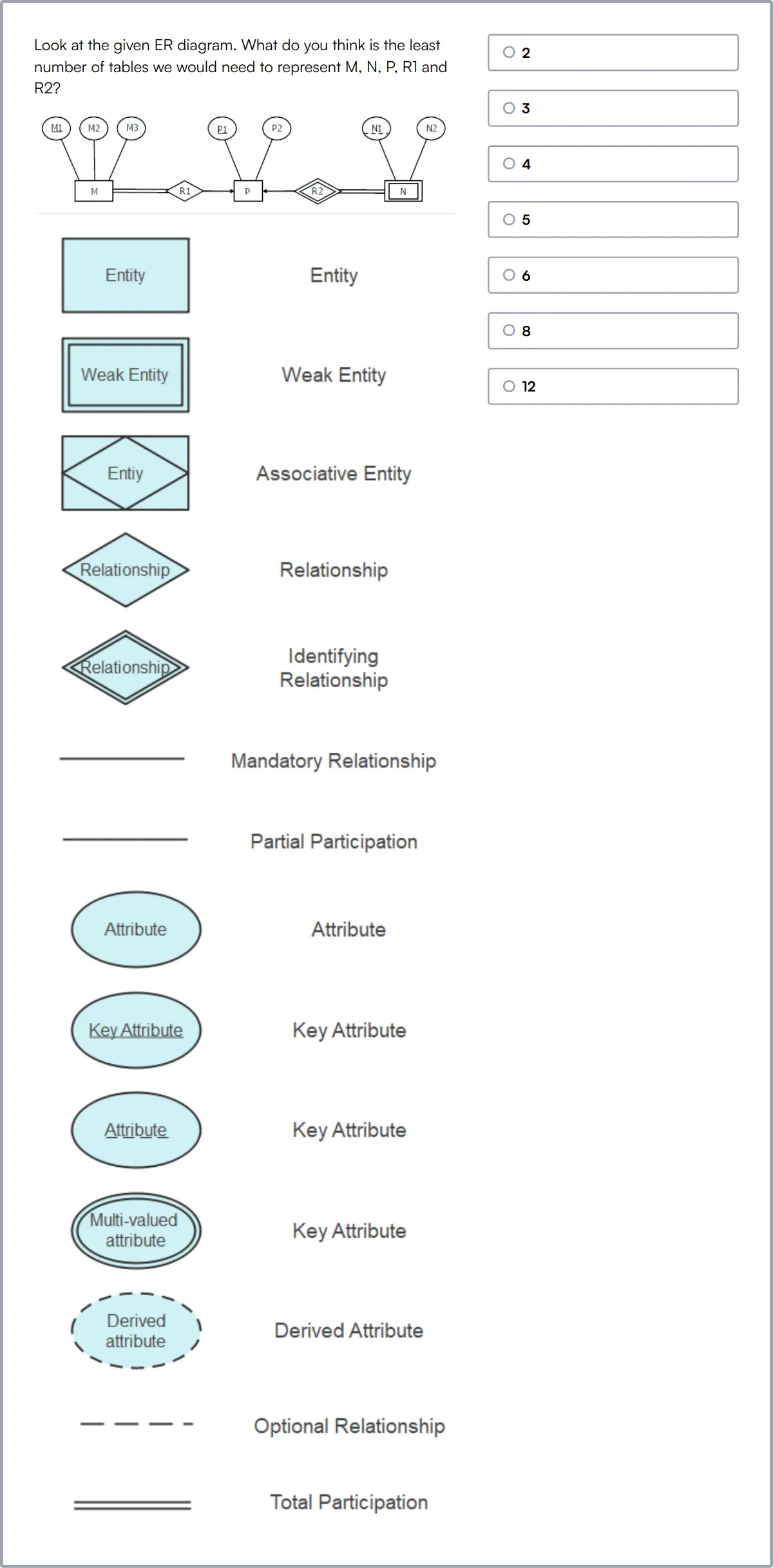
SQL Server Online Test
SQL Server Online Test uses scenario-based MCQs to evaluate candidates on their knowledge of SQL Server, including their proficiency in writing complex SQL queries, administering SQL Server instances, and managing data.
The test assesses their understanding of transactional and relational databases, configurations, database objects, installation, synchronization, transaction logs, database monitoring, maintenance, backup, recovery, SQL Server security, troubleshooting, and SAN.
High-scoring candidates demonstrate strong skills in SQL Server administration and performance optimization.
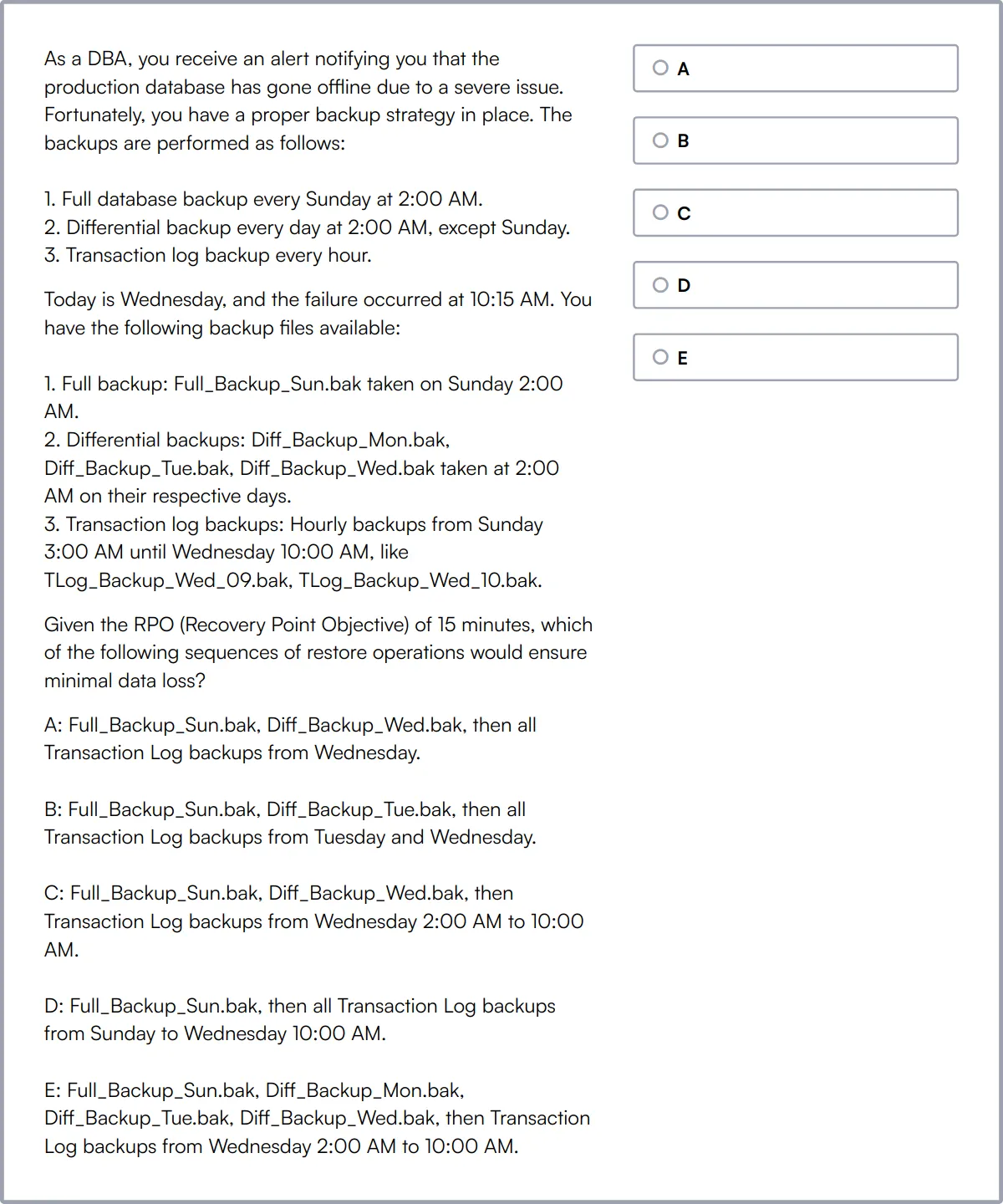
SQL Coding Test
SQL Coding Test evaluates a candidate's ability to design and build relational databases and tables from scratch, apply CRUD options, write efficient queries and subqueries to filter data, and create efficient indexes for faster SQL queries.
The test assesses their understanding of creating databases, CRUD operations, joins, subqueries, conditional expressions, views, indexes, string functions, and mathematical functions.
Candidates who perform well in this test show strong SQL coding skills and query optimization abilities.
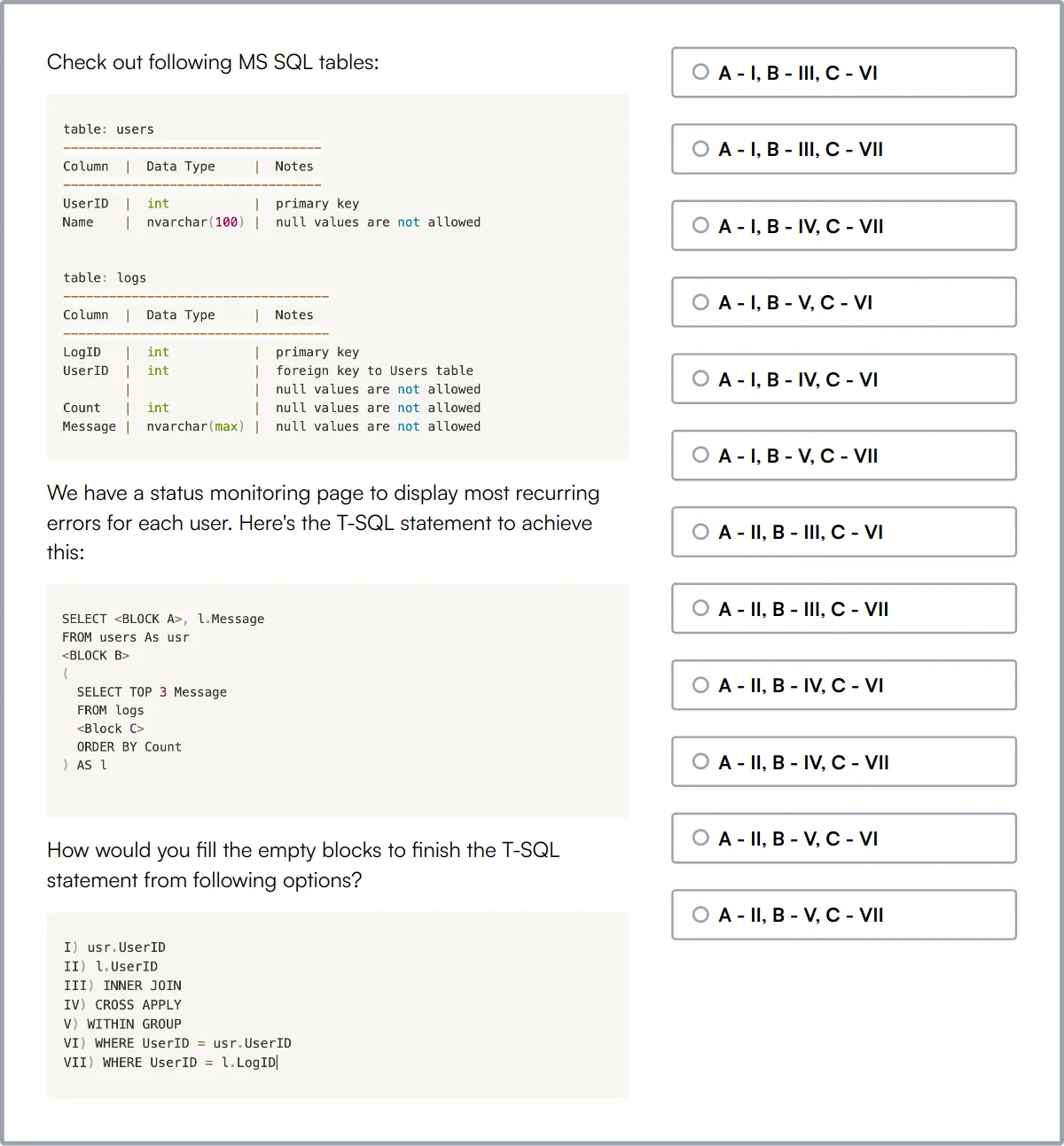
MS SQL Server Online Test
MS SQL Server Online Test uses scenario-based MCQs to evaluate candidates on their proficiency in working with Microsoft SQL Server, a popular relational database management system.
The test assesses their understanding of MS SQL Server, SQL querying, database management, indexes, normalization, database constraints, transactions, stored procedures, triggers, and views.
Successful candidates demonstrate strong skills in SQL Server database design, management, and optimization.
Summary: The 9 key SQL Developer skills and how to test for them
| SQL Developer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. SQL Proficiency | Evaluate candidate's ability to write and optimize complex SQL queries. |
| 2. Database Design | Assess understanding of logical schema structuring and normalization. |
| 3. Data Modeling | Check ability to create accurate data models for business needs. |
| 4. Performance Tuning | Review skills in optimizing database speed and efficiency. |
| 5. Stored Procedures | Test knowledge in writing and managing stored procedures. |
| 6. Backup and Recovery | Verify ability to implement reliable data backup and recovery strategies. |
| 7. Security Management | Examine expertise in enforcing data security and compliance standards. |
| 8. ETL Processes | Assess proficiency in designing and managing ETL workflows. |
| 9. Version Control | Evaluate use of version control systems for database code management. |
SQL Online Test
SQL Developer skills FAQs
What are the key skills to look for in an SQL Developer?
Key skills include SQL proficiency, database design, data modeling, performance tuning, and experience with stored procedures. Additionally, knowledge of ETL processes, version control, and scripting languages is beneficial.
How can I assess an SQL Developer's proficiency in SQL?
You can assess SQL proficiency through technical interviews, coding tests, and practical assignments that require writing complex queries, optimizing existing queries, and understanding database schemas.
What is the importance of database design in an SQL Developer role?
Database design is crucial for creating efficient, scalable, and maintainable databases. It involves structuring data, defining relationships, and ensuring data integrity, which are essential for optimal database performance.
How do you evaluate an SQL Developer's performance tuning skills?
Evaluate performance tuning skills by asking candidates to identify and resolve performance issues in sample queries or databases. Look for their ability to use indexing, query optimization, and database profiling tools.
Why is knowledge of ETL processes important for an SQL Developer?
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes are important for data integration and migration. SQL Developers should be able to design and implement ETL workflows to ensure data is accurately and efficiently moved between systems.
What role does version control play in SQL development?
Version control helps manage changes to database schemas, scripts, and code. It allows SQL Developers to track revisions, collaborate with team members, and revert to previous versions if needed.
How can an SQL Developer contribute to data security management?
SQL Developers can contribute to data security by implementing access controls, encryption, and auditing mechanisms. They should also be aware of best practices for protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with regulations.
What is the significance of business acumen for an SQL Developer?
Business acumen helps SQL Developers understand the context and impact of their work. It enables them to align database solutions with business goals, improve decision-making, and communicate effectively with stakeholders.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



