Spring Boot developers are crucial in crafting robust back-end systems and microservices. Their role is pivotal in building applications that are not only efficient but also scalable and easy to maintain.
Essential skills for a Spring Boot developer include a deep understanding of the Spring framework, proficiency in Java, and familiarity with database management and microservices architecture. Additionally, they should possess strong problem-solving abilities and effective communication skills.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Spring Boot Developer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 9 essential Spring Boot Developer skills, 10 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
9 fundamental Spring Boot Developer skills and traits
The best skills for Spring Boot Developers include Java Programming, Spring Framework, RESTful APIs, Spring Security, JPA/Hibernate, Maven/Gradle, Unit Testing, Microservices and Docker/Kubernetes.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 essential skills of a Spring Boot Developer.
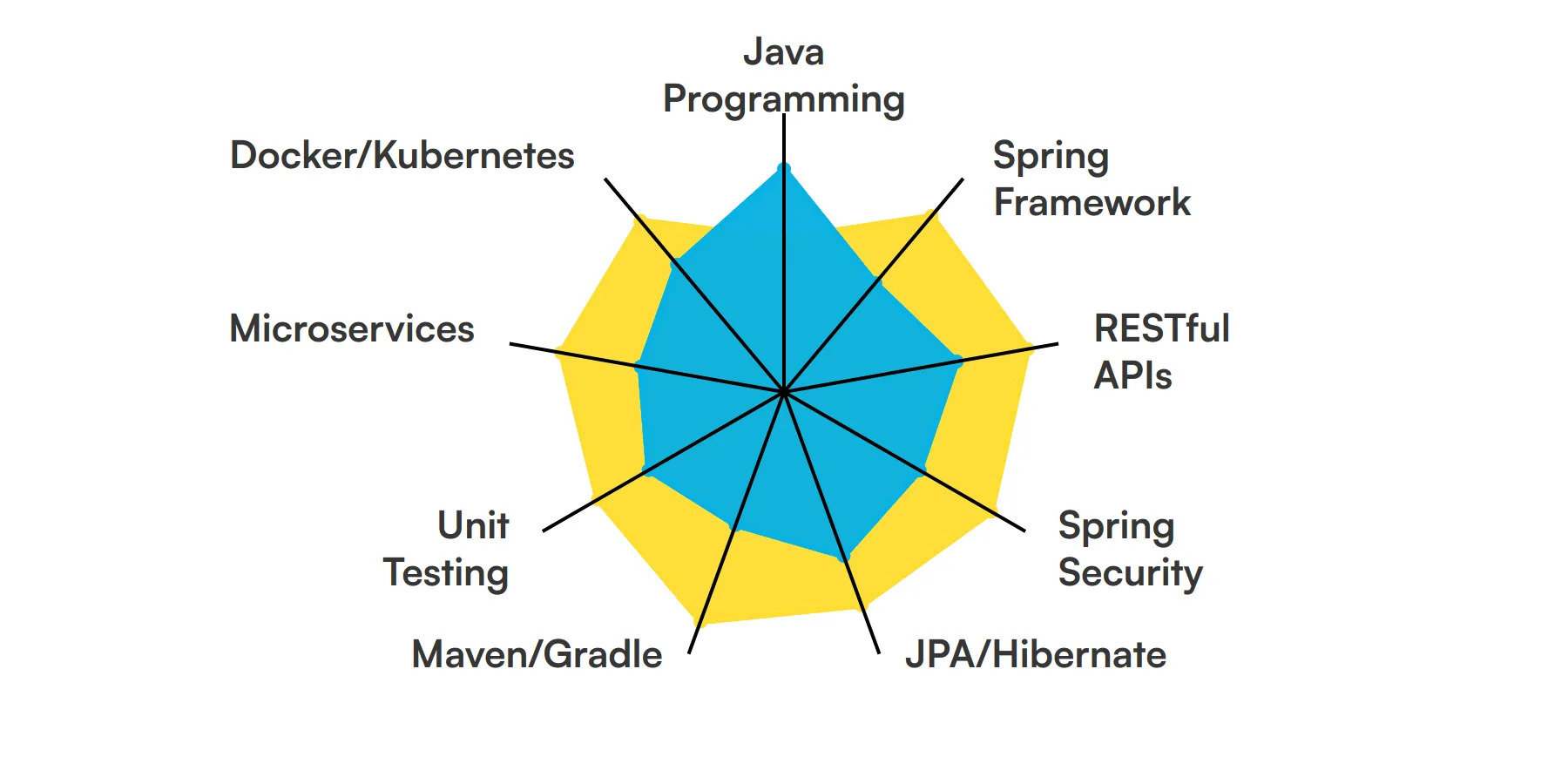
Java Programming
A Spring Boot developer must have a strong grasp of Java programming. This includes understanding object-oriented principles, data structures, and algorithms. Java is the backbone of Spring Boot applications, so proficiency in this language is non-negotiable.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Java Developer Job Description.
Spring Framework
Knowledge of the Spring Framework is crucial for a Spring Boot developer. This includes understanding core concepts like dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, and Spring MVC. These skills are necessary to build scalable and maintainable applications.
RESTful APIs
Creating and consuming RESTful APIs is a key skill for a Spring Boot developer. This involves designing endpoints, handling HTTP requests and responses, and ensuring secure and efficient data exchange between client and server.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Spring Security
Understanding Spring Security is essential for implementing authentication and authorization in Spring Boot applications. This skill helps in securing applications against common threats and ensuring that only authorized users can access certain resources.
JPA/Hibernate
Proficiency in Java Persistence API (JPA) and Hibernate is important for managing database interactions. A Spring Boot developer uses these tools to map Java objects to database tables and perform CRUD operations efficiently.
Maven/Gradle
Knowledge of build tools like Maven or Gradle is necessary for managing project dependencies and build configurations. These tools help in automating the build process, making it easier to manage and deploy Spring Boot applications.
Unit Testing
A Spring Boot developer should be skilled in writing unit tests using frameworks like JUnit and Mockito. This ensures that the code is reliable and helps in catching bugs early in the development process.
Microservices
Understanding microservices architecture is important for building scalable and modular applications. A Spring Boot developer often works with microservices to break down large applications into smaller, manageable services.
Docker/Kubernetes
Familiarity with containerization tools like Docker and orchestration platforms like Kubernetes is beneficial. These skills help in deploying and managing Spring Boot applications in a cloud environment.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Kubernetes Engineer Job Description.
10 secondary Spring Boot Developer skills and traits
The best skills for Spring Boot Developers include Thymeleaf, Spring Cloud, Kafka/RabbitMQ, Git, SQL/NoSQL, CI/CD, OAuth2/JWT, API Documentation, Linux and Reactive Programming.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 10 secondary skills of a Spring Boot Developer.
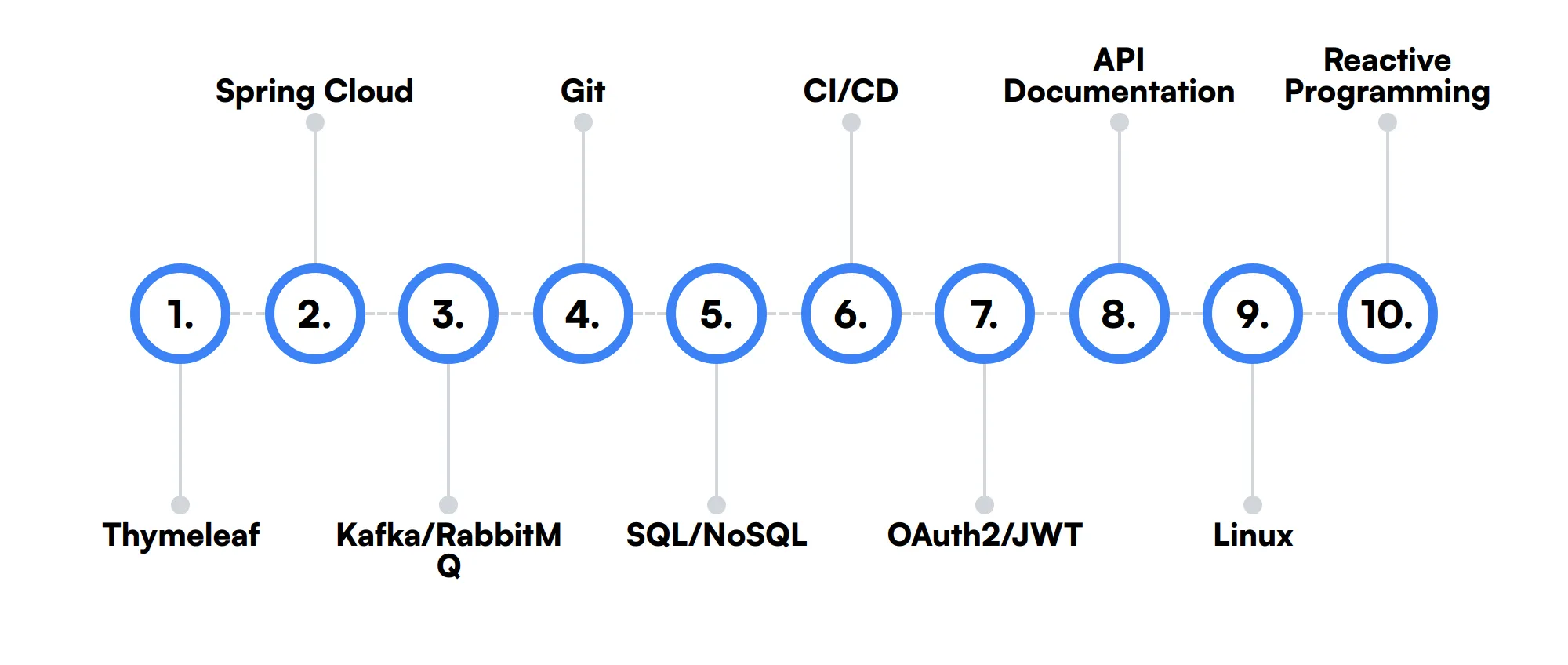
Thymeleaf
Knowledge of Thymeleaf is useful for creating dynamic web pages in Spring Boot applications. It integrates seamlessly with Spring MVC, making it easier to develop server-side rendered views.
Spring Cloud
Understanding Spring Cloud can be beneficial for a Spring Boot developer working with distributed systems. It provides tools for configuration management, service discovery, and circuit breakers, which are essential for building resilient microservices.
Kafka/RabbitMQ
Experience with messaging systems like Kafka or RabbitMQ is useful for building event-driven applications. These tools help in decoupling services and ensuring reliable message delivery.
Git
Proficiency in version control systems like Git is important for managing code changes and collaborating with other developers. It helps in tracking changes, resolving conflicts, and maintaining a clean codebase.
SQL/NoSQL
Knowledge of both SQL and NoSQL databases is beneficial for a Spring Boot developer. This includes understanding how to design schemas, write queries, and optimize database performance.
CI/CD
Familiarity with Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines is useful for automating the deployment process. Tools like Jenkins, Travis CI, or GitLab CI help in ensuring that code changes are tested and deployed efficiently.
OAuth2/JWT
Understanding OAuth2 and JWT is important for implementing secure authentication and authorization mechanisms. These skills help in managing user identities and securing API endpoints.
API Documentation
Experience with tools like Swagger or OpenAPI is useful for documenting RESTful APIs. This helps in creating clear and comprehensive API documentation, making it easier for other developers to understand and use the APIs.
Linux
Basic knowledge of Linux is beneficial for a Spring Boot developer, especially when deploying applications on Linux servers. This includes understanding shell commands, file permissions, and basic server management.
Reactive Programming
Familiarity with reactive programming concepts and tools like Project Reactor can be useful for building non-blocking, asynchronous applications. This helps in improving the performance and scalability of Spring Boot applications.
How to assess Spring Boot Developer skills and traits
When it comes to hiring a Spring Boot Developer, understanding the breadth and depth of their skills is more than just a checklist of technologies mastered. It involves a nuanced approach to evaluating how well they can integrate Java programming with the dynamic functionalities of the Spring ecosystem, including Spring Framework, Spring Security, and more.
Traditional methods like reviewing resumes and conducting technical interviews can provide some insights, but they often fall short in painting a complete picture of a candidate's capabilities in real-world scenarios. To truly assess the practical skills of a Spring Boot Developer, a hands-on evaluation is necessary.
This is where Adaface assessments come into play, offering a tailored approach to testing candidates on key areas such as RESTful APIs, JPA/Hibernate, Maven/Gradle, and their ability to work with Docker/Kubernetes in a microservices architecture. By incorporating these assessments into your hiring process, you can achieve an 85% reduction in screening time while ensuring a high-quality addition to your team.
Let’s look at how to assess Spring Boot Developer skills with these 6 talent assessments.
Java Online Test
Our Java Online Test evaluates a candidate's proficiency in core Java concepts, including OOP, classes, exceptions, collections, and advanced topics like concurrent programming and database handling.
The test assesses knowledge of Java syntax and semantics, web application programming, object-oriented programming, working with databases, data structures, collections framework, exception handling, multi-threading, functional programming with Lambdas & Streams API, and SOLID principles.
Successful candidates demonstrate a strong understanding of Java's core interfaces and implementations, such as List, Set, and Map, and show proficiency in coding through scenario-based and code-tracing questions.
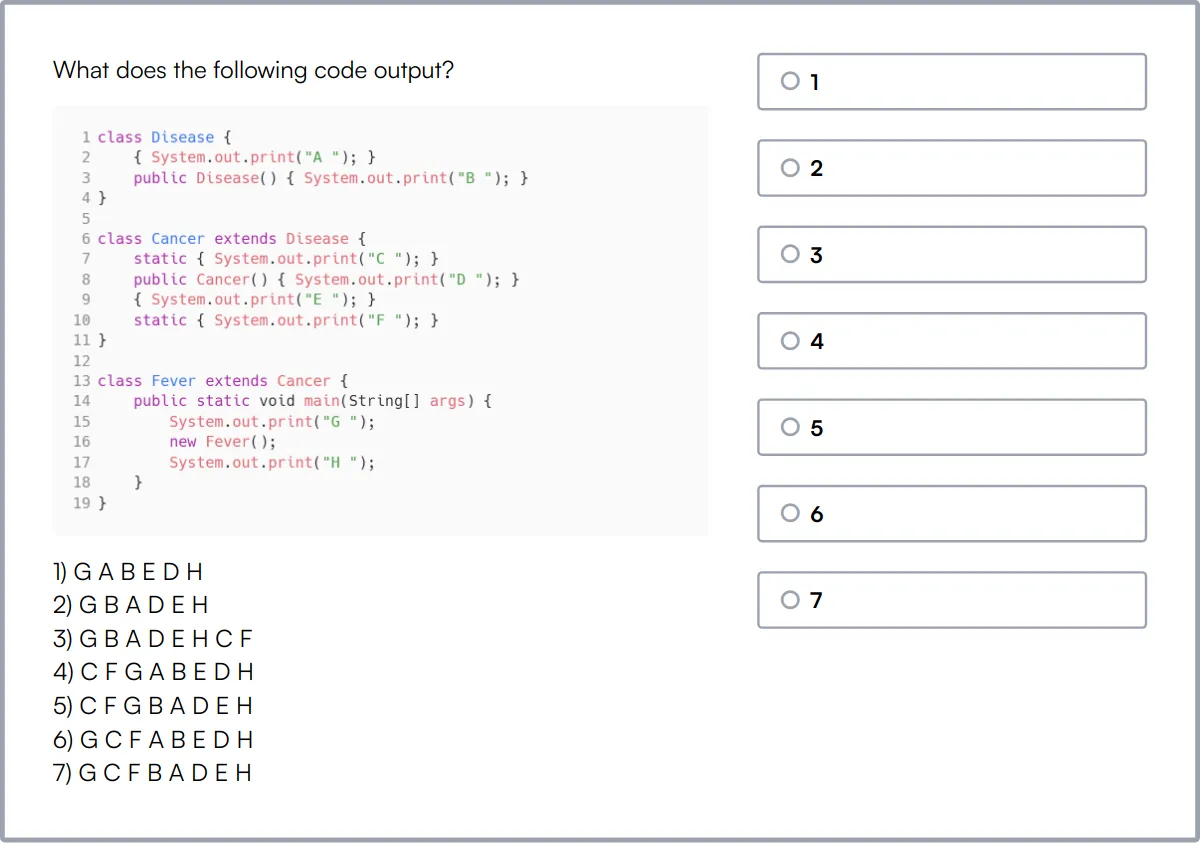
Java & Spring Online Test
Our Java & Spring Online Test assesses a candidate's ability to work with Spring modules, including Core, MVC, Security, and Boot, as well as their understanding of Java programming.
The test evaluates skills in Java syntax and basics, OOP, working with databases, Spring framework basics, Spring bean lifecycle, Spring Security, and Java programming.
Candidates are tested on their ability to handle dependency injection, AOP, RESTful web services, and database integration, along with their proficiency in design patterns, testing, debugging, and software architecture.
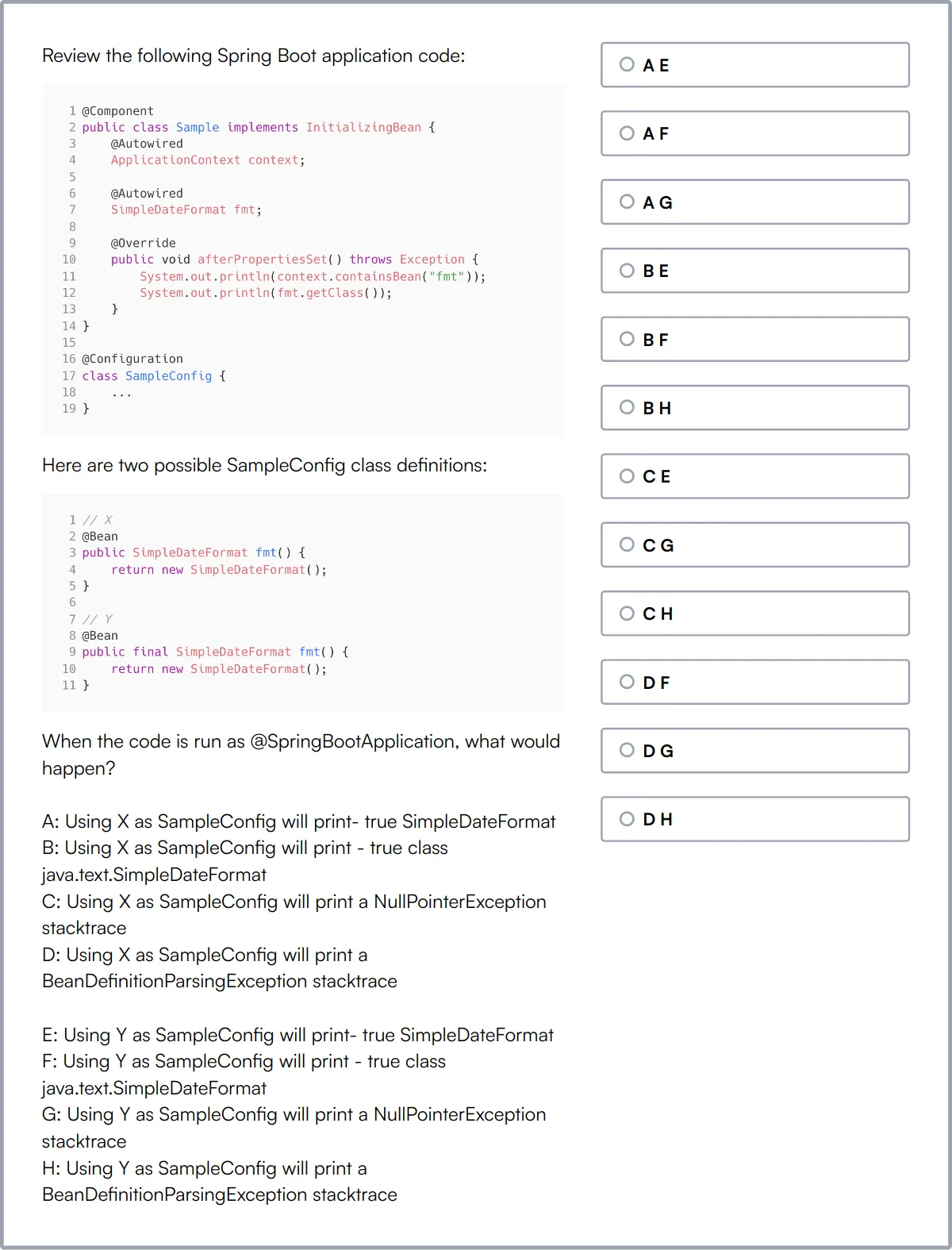
REST API Test
Our REST API Test evaluates a candidate's understanding of RESTful APIs and their ability to create, interact, and test them.
The test covers REST principles, HTTP methods, status codes, authentication, serialization formats, and best practices.
Candidates are assessed on their ability to design backend services and integrate APIs, with a focus on coding and technical aptitude.
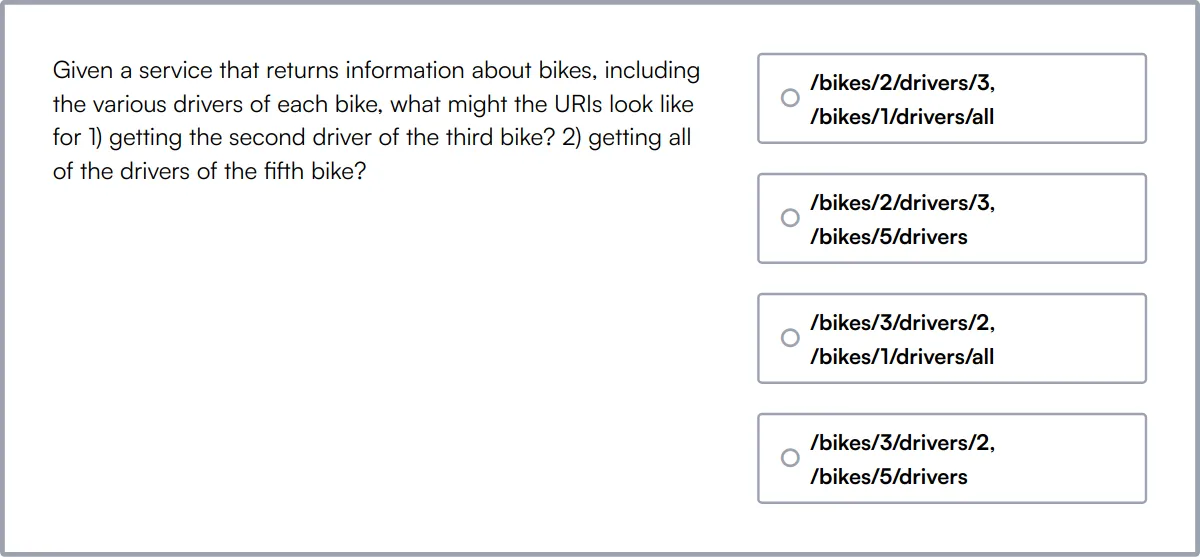
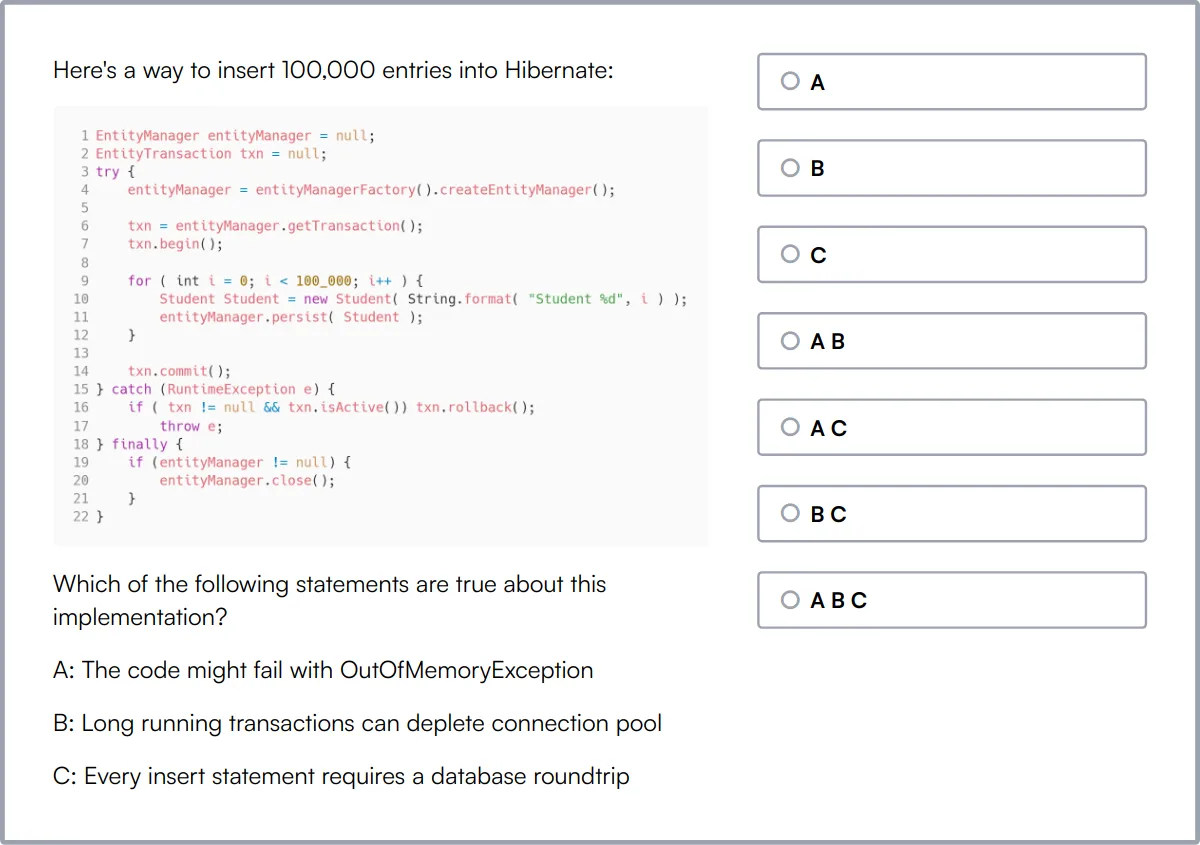
Hibernate Online Test
Our Hibernate Online Test evaluates a candidate's knowledge of Hibernate ORM, including mappings, associations, transactions, and HQL.
The test covers Hibernate basics, configuration, mapping entities, HQL, Criteria API, caching, transactions, annotations, inheritance, integration, and performance optimization.
Candidates are tested on their ability to design and develop Java applications that utilize Hibernate for data persistence effectively.
Elasticsearch Test
Our Elasticsearch Test evaluates a candidate's ability to design and deploy Elasticsearch clusters, configure and optimize search queries, and manage data ingestion and indexing.
The test covers data indexing, search queries, document retrieval, aggregations, cluster management, data modeling, performance optimization, monitoring and troubleshooting, security, scaling and distribution, and integration with other systems.
Candidates are assessed on their ability to handle Elasticsearch's core functionalities and ensure efficient data management and retrieval.
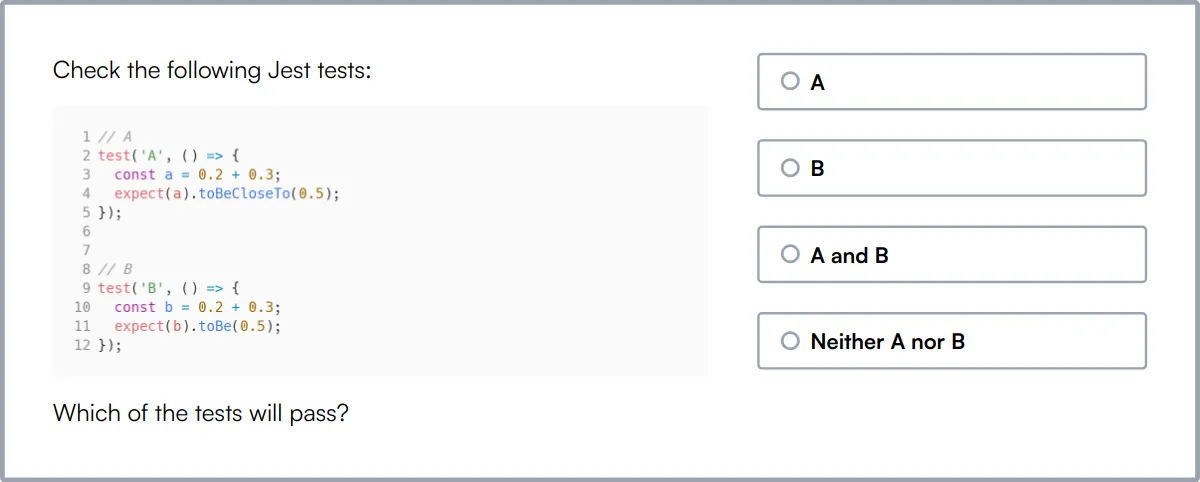
Jest Test
Our Jest Test evaluates a candidate's knowledge of Jest, a popular JavaScript testing framework used for testing React and Node.js applications.
The test covers testing fundamentals, test-driven development, Jest configuration and setup, test matchers and assertions, mocking and spying, async testing, and snapshot testing.
Candidates are assessed on their ability to write effective and maintainable test cases, debug and troubleshoot testing issues, and integrate Jest with other tools and frameworks.
Summary: The 9 key Spring Boot Developer skills and how to test for them
| Spring Boot Developer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Java Programming | Evaluate developer's proficiency in Java syntax and object-oriented programming. |
| 2. Spring Framework | Assess knowledge in Spring core concepts and best practices. |
| 3. RESTful APIs | Check ability to design and integrate well-defined web services. |
| 4. Spring Security | Review understanding of authentication and authorization mechanisms. |
| 5. JPA/Hibernate | Test skills in ORM frameworks and database interaction. |
| 6. Maven/Gradle | Examine expertise in managing project dependencies and builds. |
| 7. Unit Testing | Determine proficiency in writing and maintaining test cases. |
| 8. Microservices | Evaluate design and management of independently deployable services. |
| 9. Docker/Kubernetes | Assess deployment and scaling of applications using containers. |
Spring Online Test
Spring Boot Developer skills FAQs
What are the key Java programming skills needed for a Spring Boot developer?
A Spring Boot developer should be proficient in core Java concepts like OOP, exception handling, collections, and concurrency. Knowledge of Java 8 features such as streams and lambdas is also beneficial.
How important is understanding RESTful APIs for a Spring Boot developer?
Understanding RESTful APIs is critical for Spring Boot developers as it enables them to design and develop scalable web services that can communicate with clients and other services in a standardized format.
What role does Spring Security play in a Spring Boot application?
Spring Security is used to add authentication and authorization to Spring Boot applications. It helps in securing REST APIs, managing roles, and protecting resources from unauthorized access.
Why is knowledge of Maven or Gradle important for Spring Boot developers?
Maven and Gradle are build tools that manage project dependencies and automate builds. Understanding these tools is important for efficient project setup, dependency management, and build processes in Spring Boot development.
Can you explain the importance of unit testing in Spring Boot development?
Unit testing is crucial in Spring Boot development to ensure individual components function correctly. It helps in identifying bugs early in the development cycle, leading to more reliable and maintainable code.
What is the significance of Docker and Kubernetes in Spring Boot microservices?
Docker and Kubernetes facilitate containerization and orchestration of Spring Boot microservices, allowing for easier deployment, scaling, and management of applications across different environments.
How does Spring Cloud enhance Spring Boot microservices?
Spring Cloud provides tools for developers to quickly build some of the common patterns in distributed systems (e.g., configuration management, service discovery). This simplifies the development of resilient and scalable microservices.
What is the role of Kafka or RabbitMQ in Spring Boot applications?
Kafka and RabbitMQ are used for handling asynchronous messaging in Spring Boot applications. They enable efficient communication between different parts of an application or between different applications, supporting better scalability and integration.
Assess and hire the best Spring Boot Developers with Adaface
Assessing and finding the best Spring Boot Developer is quick and easy when you use talent assessments. You can check out our product tour, sign up for our free plan to see talent assessments in action or view the demo here:

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



