Rust developers are responsible for building safe, concurrent, and fast software applications. They leverage Rust's unique features to create systems that are both reliable and efficient, making it a popular choice for performance-critical applications.
Skills required for a Rust developer include a strong understanding of Rust's syntax and semantics, proficiency in systems programming, and the ability to write safe and concurrent code. Additionally, problem-solving skills and effective communication are key to succeeding in this role.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Rust Developer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 9 essential Rust Developer skills, 11 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
9 fundamental Rust Developer skills and traits
The best skills for Rust Developers include Rust Programming, Memory Management, Concurrency, Error Handling, Tooling, Systems Programming, Testing, Debugging and Performance Optimization.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 essential skills of a Rust Developer.
Rust Programming
A Rust developer must have a deep understanding of the Rust programming language. This includes knowledge of its syntax, semantics, and unique features like ownership and borrowing. Mastery of Rust allows developers to write safe and efficient code, which is crucial for system-level programming.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Rust Developer Job Description.
Memory Management
Rust's ownership model is designed to manage memory safely and efficiently without a garbage collector. A Rust developer needs to understand how to manage memory manually, ensuring that resources are allocated and deallocated properly to avoid leaks and other issues.
Concurrency
Concurrency is a core feature of Rust, allowing developers to write programs that can perform multiple tasks simultaneously. Understanding Rust's concurrency model, including threads and async programming, is essential for building high-performance applications.
Error Handling
Rust provides robust error handling mechanisms through the Result and Option types. A Rust developer must be adept at using these types to handle errors gracefully, ensuring that the program can recover from unexpected conditions without crashing.
Tooling
Familiarity with Rust's ecosystem of tools, such as Cargo (the package manager and build system), rustfmt (code formatter), and Clippy (linter), is essential. These tools help maintain code quality and streamline the development process.
Systems Programming
Rust is often used for systems programming, which involves writing software that interacts closely with hardware. A Rust developer should understand low-level programming concepts, such as memory allocation, pointers, and system calls.
Testing
Writing tests is a critical part of software development. Rust developers should be proficient in using Rust's built-in testing framework to write unit tests, integration tests, and benchmarks to ensure their code is reliable and performs well.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Debugging
Debugging is an essential skill for any developer. Rust developers should be familiar with debugging tools like GDB and LLDB, as well as Rust-specific tools like rust-gdb and rust-lldb, to diagnose and fix issues in their code.
Performance Optimization
Rust is known for its performance. A Rust developer should have the skills to profile and optimize their code, ensuring it runs as efficiently as possible. This includes understanding how to use tools like perf and flamegraph.
11 secondary Rust Developer skills and traits
The best skills for Rust Developers include Version Control, Linux/Unix, Networking, WebAssembly, Database Management, API Design, Cryptography, Cross-Platform Development, Embedded Systems, DevOps and Cloud Services.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 11 secondary skills of a Rust Developer.
Version Control
Proficiency with version control systems like Git is important for managing code changes and collaborating with other developers. This skill helps maintain a clean and organized codebase.
Linux/Unix
Many Rust applications are deployed on Linux/Unix systems. Familiarity with these operating systems, including command-line tools and shell scripting, can be beneficial for a Rust developer.
Networking
Understanding networking concepts and protocols can be useful, especially if the Rust developer is working on networked applications or services. This includes knowledge of TCP/IP, HTTP, and other relevant protocols.
WebAssembly
Rust can compile to WebAssembly, allowing developers to run Rust code in the browser. Knowledge of WebAssembly can be a valuable skill for Rust developers working on web applications.
Database Management
Interacting with databases is a common task for many applications. Rust developers should be familiar with database management systems and how to use Rust libraries to connect and interact with databases.
API Design
Designing and implementing APIs is a common task for many developers. Rust developers should understand how to create RESTful and GraphQL APIs, ensuring they are well-documented and easy to use.
Cryptography
For applications that require security, knowledge of cryptographic principles and libraries is important. Rust developers should understand how to implement encryption, hashing, and other security measures.
Cross-Platform Development
Rust can be used to develop cross-platform applications. Understanding how to write code that runs on multiple operating systems can be a valuable skill for Rust developers.
Embedded Systems
Rust is increasingly being used for embedded systems development. Knowledge of embedded systems programming can be beneficial for Rust developers working in this domain.
DevOps
Understanding DevOps practices, including continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), can help Rust developers streamline their development process and ensure their applications are deployed smoothly.
Cloud Services
Familiarity with cloud services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud can be useful for Rust developers, especially if they are working on applications that are deployed in the cloud.
How to assess Rust Developer skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a Rust developer involves more than just glancing at a resume. It's about understanding how well they can handle the complexities of Rust programming, from memory management to concurrency and beyond.
While the list of technical skills such as error handling, systems programming, and performance optimization is critical, evaluating how a developer applies these skills in real-world scenarios is key. This is where practical assessments come into play.
Using Adaface assessments, you can measure a candidate's proficiency across various aspects of Rust development. These tests are designed to mirror actual challenges developers face, ensuring that you can identify candidates who are truly adept at Rust programming. With Adaface, companies have seen a 2x improvement in the quality of their hires.
Moreover, the ability to test skills like testing, debugging, and tool usage in an integrated environment means you can confidently assess a candidate's readiness for your projects, significantly reducing the time spent in screening.
Let’s look at how to assess Rust Developer skills with these 2 talent assessments.
Rust Online Test
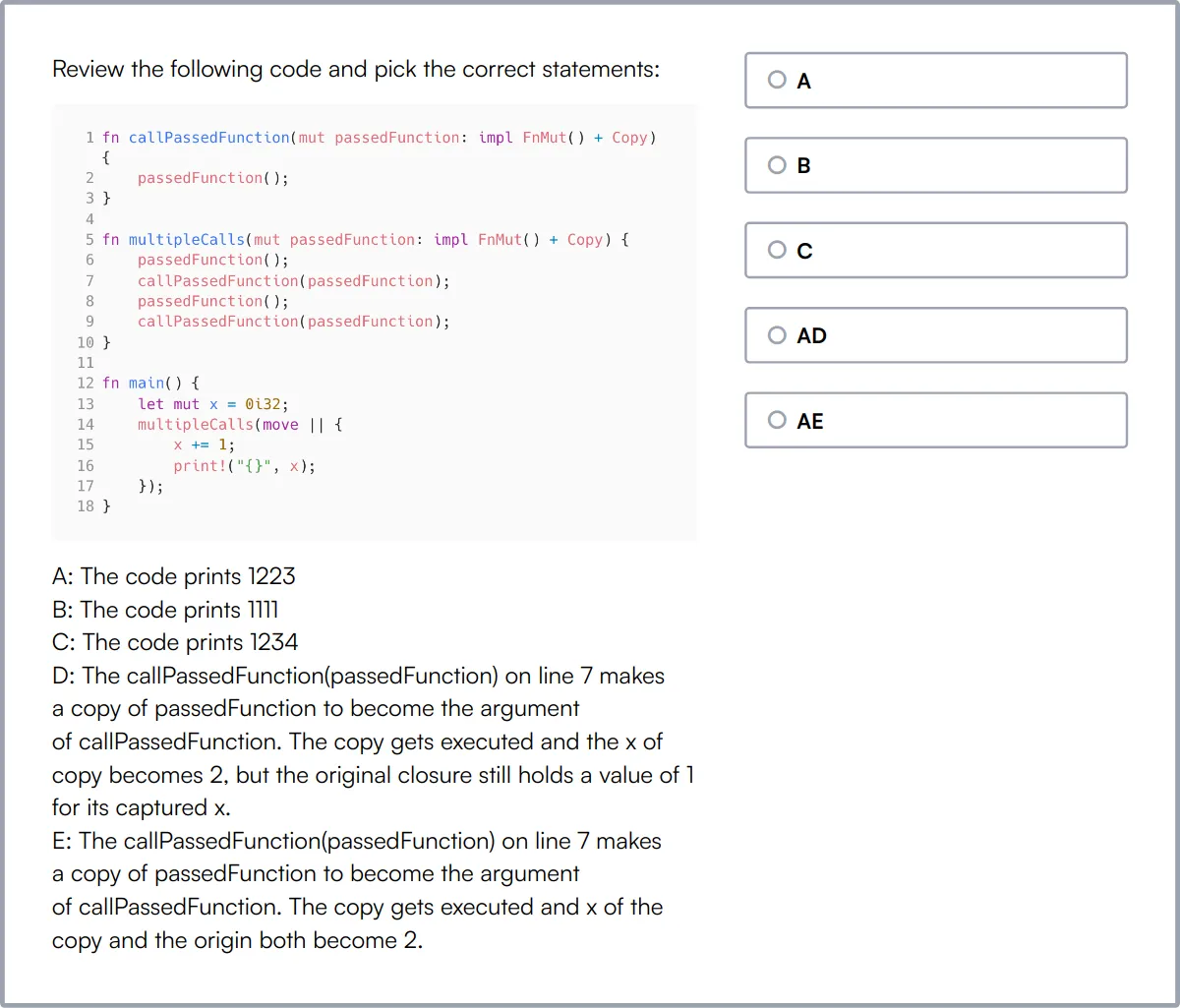
Our Rust Online Test evaluates a candidate's proficiency in the Rust programming language, including syntax, data types, memory management, and concurrency. The test includes scenario-based MCQs and a coding question to assess hands-on Rust programming skills.
The test covers a range of topics such as standard Rust operators and syntax, enums and pattern matching, generic structs, smart pointers, and reference counting. It also evaluates knowledge of thread pools and workers, ownership concepts, loops and strings, and OOP concepts.
Successful candidates demonstrate a strong understanding of generic iterators, concurrency, and threads. They can write safe and efficient Rust code that meets specific requirements.
Manual Testing Online Test
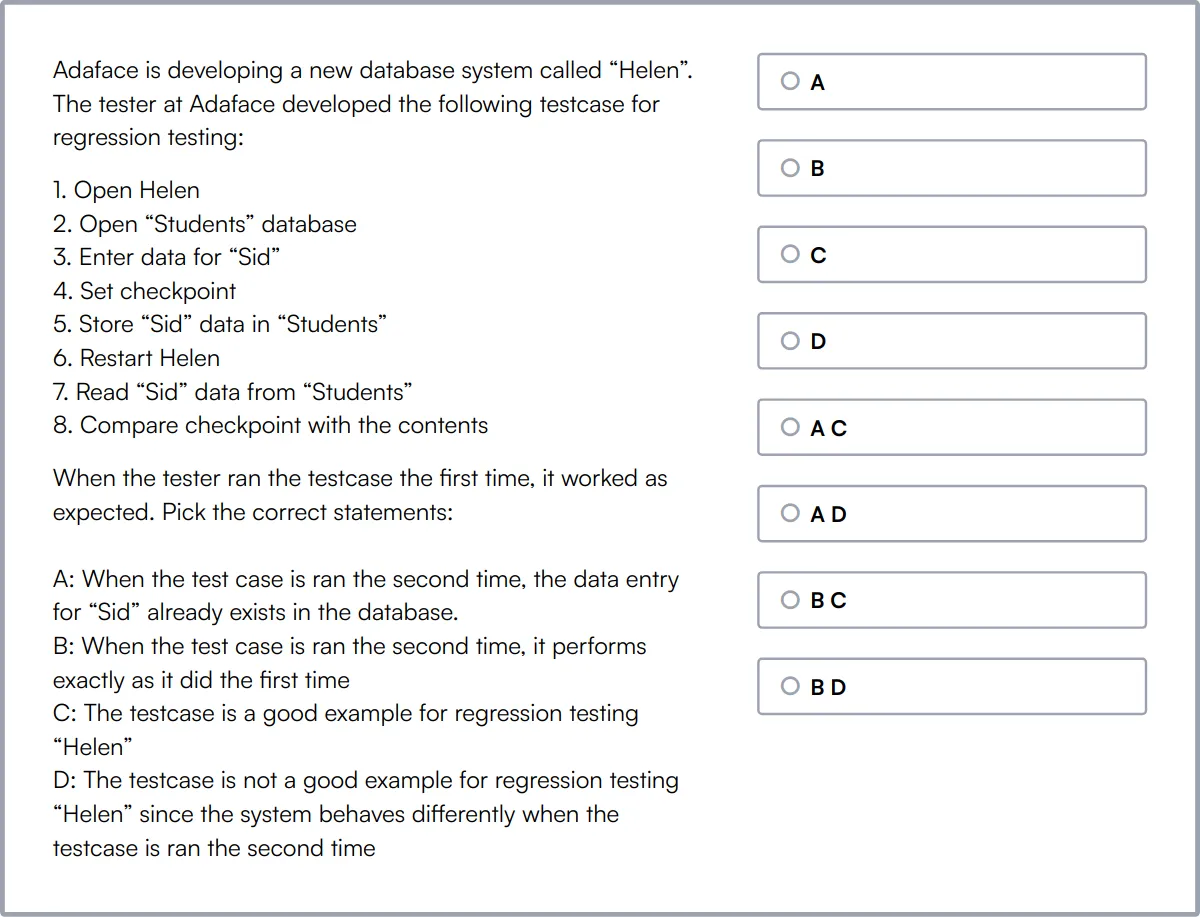
Our Manual Testing Online Test assesses a candidate's knowledge of manual software testing, including designing and executing test cases, creating and managing bug reports, and testing various types of software.
The test evaluates skills in manual software testing, testing fundamentals, test case writing, test plan development, and test strategy. It also covers test management, documentation skills, and different testing types such as mobile app testing and penetration testing.
Candidates who perform well show proficiency in test strategy development, test management, and documentation skills. They are adept at identifying defects in software products through manual testing methods.
Summary: The 9 key Rust Developer skills and how to test for them
| Rust Developer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Rust Programming | Evaluate a developer's proficiency in Rust syntax and idiomatic practices. |
| 2. Memory Management | Assess understanding and application of Rust's ownership and borrowing concepts. |
| 3. Concurrency | Check ability to implement safe and efficient concurrent programs in Rust. |
| 4. Error Handling | Review how a developer uses Rust's error handling patterns and types. |
| 5. Tooling | Examine familiarity with Rust's compilation, build tools, and package management. |
| 6. Systems Programming | Assess skills in low-level system details handling using Rust. |
| 7. Testing | Determine capability to write and manage comprehensive test suites. |
| 8. Debugging | Evaluate problem-solving skills through debugging Rust applications. |
| 9. Performance Optimization | Assess ability to enhance and optimize Rust code performance. |
Rust Online Test
Rust Developer skills FAQs
What are the key skills to look for in a Rust developer?
Key skills include Rust programming, memory management, concurrency, error handling, and systems programming. Familiarity with tooling, testing, and debugging is also important.
How can I assess a candidate's proficiency in Rust programming?
You can assess proficiency through coding tests, technical interviews, and reviewing their contributions to open-source Rust projects. Look for clean, idiomatic Rust code.
Why is memory management important for Rust developers?
Memory management is crucial in Rust due to its ownership model, which ensures memory safety without a garbage collector. Assess understanding through questions on ownership, borrowing, and lifetimes.
What tools should a Rust developer be familiar with?
Rust developers should know tools like Cargo (package manager), rustc (compiler), Clippy (linter), and Rustfmt (formatter). Familiarity with debugging tools like GDB or LLDB is also beneficial.
How do you evaluate a candidate's experience with concurrency in Rust?
Ask about their experience with Rust's concurrency primitives like threads, async/await, and channels. Review their code for proper handling of concurrent tasks and data races.
What is the significance of WebAssembly for Rust developers?
WebAssembly allows Rust code to run in web browsers, enabling high-performance web applications. Assess knowledge by asking about their experience with compiling Rust to WebAssembly and related tools like wasm-bindgen.
How can you test a Rust developer's debugging skills?
Evaluate their debugging skills by presenting them with a Rust codebase containing bugs and asking them to identify and fix the issues. Look for systematic problem-solving approaches.
What should you look for in a Rust developer's experience with cloud services?
Check for experience with deploying Rust applications on cloud platforms like AWS, GCP, or Azure. Ask about their familiarity with cloud-native tools and services relevant to Rust development.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts



