Quality Assurance Engineers are fundamental in ensuring the reliability and performance of software products. They play a critical role in identifying bugs and issues before the product reaches the end user, maintaining high standards of software quality.
The skill set required for a Quality Assurance Engineer includes proficiency in various testing methodologies, such as manual testing and automated testing tools, along with strong analytical and problem-solving abilities.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Quality Assurance Engineer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 8 essential Quality Assurance Engineer skills, 8 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
8 fundamental Quality Assurance Engineer skills and traits
The best skills for Quality Assurance Engineers include Test Automation, Bug Tracking, Programming Knowledge, Test Plan Development, Risk Analysis, Performance Testing, Security Testing and API Testing.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 8 essential skills of a Quality Assurance Engineer.
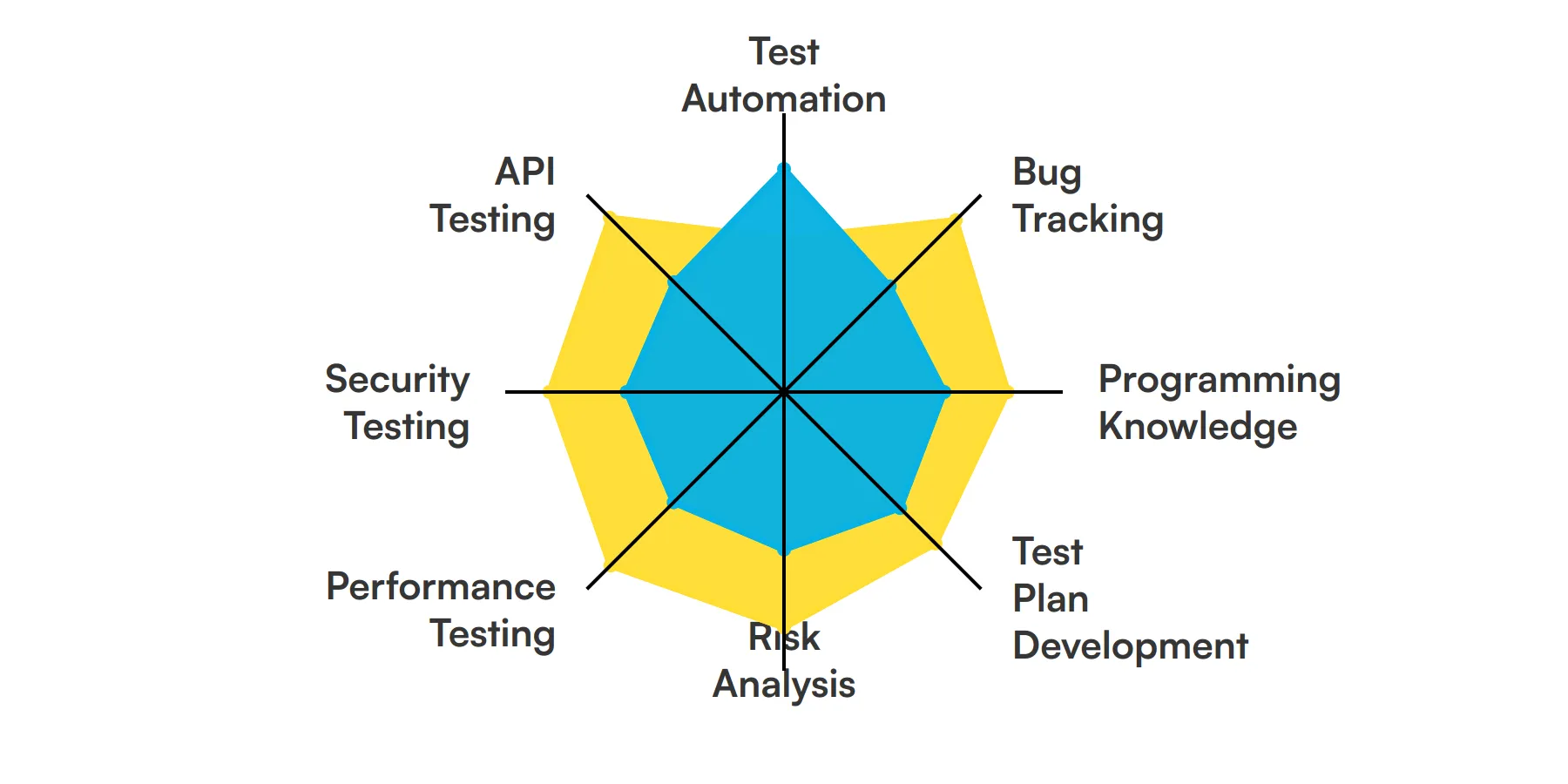
Test Automation
A Quality Assurance Engineer must be adept at using automated testing tools to streamline the testing process. This skill allows them to execute repetitive test cases without manual intervention, ensuring consistency and efficiency in testing outcomes.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Selenium Automation Tester Job Description.
Bug Tracking
Effective bug tracking is critical for a Quality Assurance Engineer to manage and document issues found during testing. This skill involves using tools like JIRA or Bugzilla to track, prioritize, and report defects, facilitating smooth communication and quick resolution.
Programming Knowledge
Understanding programming languages such as Java, Python, or C# is essential for creating and understanding test scripts. This knowledge helps a Quality Assurance Engineer to interact more effectively with the development team and tailor testing tools to project needs.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Test Plan Development
Developing comprehensive test plans is a key skill for a Quality Assurance Engineer. It involves outlining the testing strategy, objectives, resources, schedule, and deliverables, ensuring a structured approach to quality assurance.
Risk Analysis
Risk analysis enables a Quality Assurance Engineer to prioritize testing efforts based on potential impact. This skill involves assessing the likelihood and consequences of defects, helping to allocate resources more effectively to ensure product reliability.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Risk Analyst Job Description.
Performance Testing
Performance testing is crucial to assess how a system operates under stress. A Quality Assurance Engineer uses this skill to simulate different load scenarios and identify potential bottlenecks, ensuring the product can handle real-world conditions.
Security Testing
Security testing is increasingly important in today’s digital age. A Quality Assurance Engineer must be skilled in identifying vulnerabilities within software to prevent potential threats, safeguarding user data and maintaining trust.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
API Testing
API testing is essential to ensure that the software components interact correctly. A Quality Assurance Engineer uses this skill to verify the logic of the backend processes and ensure that the system meets the defined requirements.
8 secondary Quality Assurance Engineer skills and traits
The best skills for Quality Assurance Engineers include SQL Knowledge, Agile Methodologies, Version Control, Cross-browser Testing, Mobile Testing, Communication Skills, Documentation and Continuous Integration.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 8 secondary skills of a Quality Assurance Engineer.
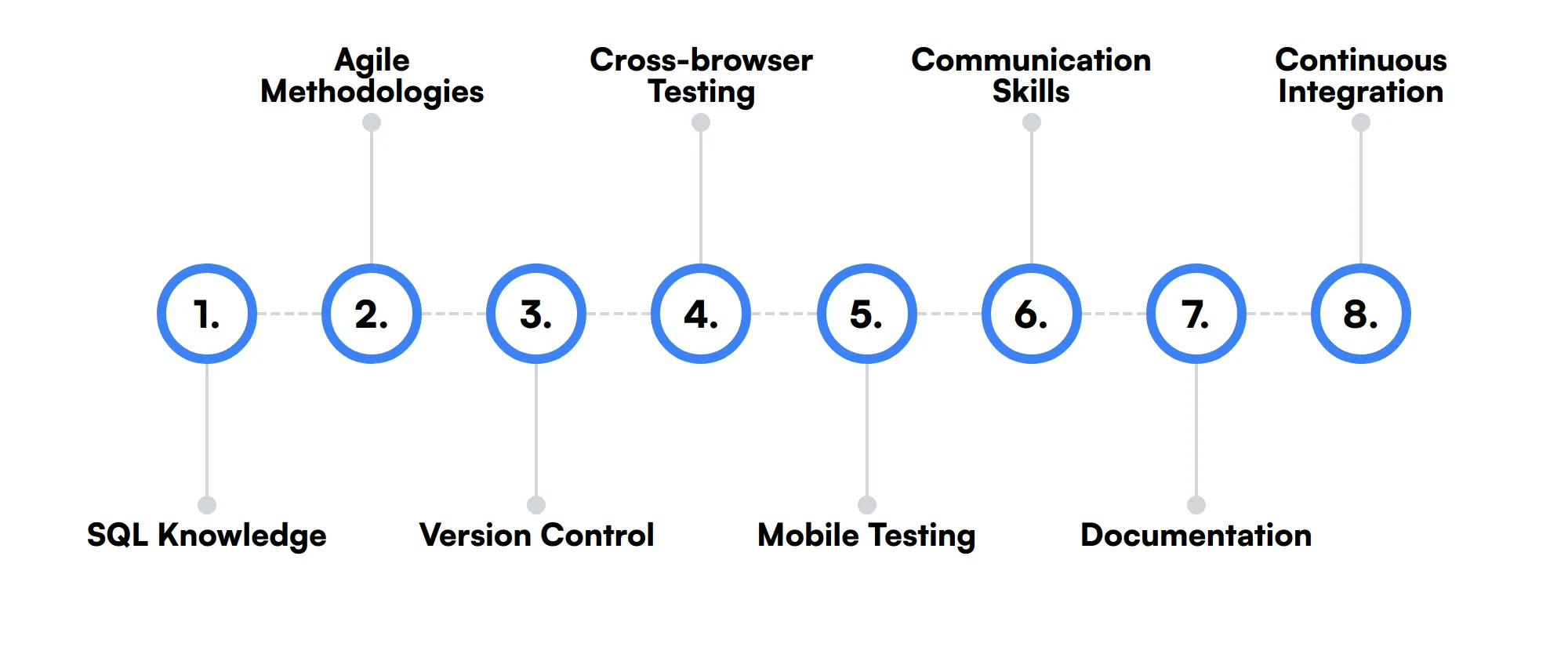
SQL Knowledge
Understanding SQL helps a Quality Assurance Engineer verify data integrity and perform back-end testing. This skill is useful for checking that data is stored and retrieved correctly from databases.
Agile Methodologies
Familiarity with Agile methodologies is beneficial for a Quality Assurance Engineer as it helps them adapt to rapid development environments and collaborate effectively with cross-functional teams.
Version Control
Using version control systems like Git is important for maintaining current and historical versions of files such as test scripts and documentation, allowing for better management of resources.
Cross-browser Testing
Cross-browser testing ensures that applications perform consistently across different web browsers. This skill is important for a Quality Assurance Engineer to guarantee a uniform user experience.
Mobile Testing
As mobile applications become more prevalent, having the ability to test on different mobile platforms and devices is crucial for ensuring that applications perform well on all potential user devices.
Communication Skills
Strong communication skills are necessary for a Quality Assurance Engineer to effectively convey testing outcomes, collaborate with team members, and advocate for quality practices throughout the development process.
Documentation
Proper documentation skills are essential for creating clear, concise test cases, reports, and results that are understandable and actionable for the development team and stakeholders.
Continuous Integration
Understanding and implementing continuous integration practices helps a Quality Assurance Engineer integrate their work frequently into the main branch, ensuring early detection of integration bugs.
How to assess Quality Assurance Engineer skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a Quality Assurance Engineer involves more than just glancing at their resume. It's about understanding how well they can handle real-world testing scenarios, from Test Automation to Security Testing. Each skill, whether it's crafting detailed Test Plans or conducting thorough Risk Analysis, plays a critical role in ensuring software meets its quality benchmarks before reaching users.
Traditional hiring methods often fall short in accurately gauging these complex technical abilities. This is where practical assessments come into play. By integrating skills assessments into your hiring process, you can directly measure each candidate's proficiency in essential areas such as Bug Tracking, Performance Testing, and API Testing.
Adaface assessments offer a streamlined approach to evaluate these competencies. With tests designed to mirror actual job tasks, you can ensure candidates are tested on relevant skills, leading to a 2x improvement in the quality of hires. Discover more about how Adaface can transform your hiring process at Adaface Quality Assurance Engineer Tests.
Let’s look at how to assess Quality Assurance Engineer skills with these 6 talent assessments.
Selenium Online Test
Our Selenium Online Test evaluates a candidate's proficiency in using Selenium Webdriver for automation testing. This includes their ability to interact with live websites, perform cross-browser testing, and develop custom testing frameworks.
The test assesses their understanding of Selenium architecture, API testing, and performance testing capabilities. Candidates are also tested on their experience with programming languages and database interactions within Selenium environments.
Successful candidates demonstrate a strong ability to build and customize data-driven and hybrid testing frameworks, and generate detailed reports on their findings.
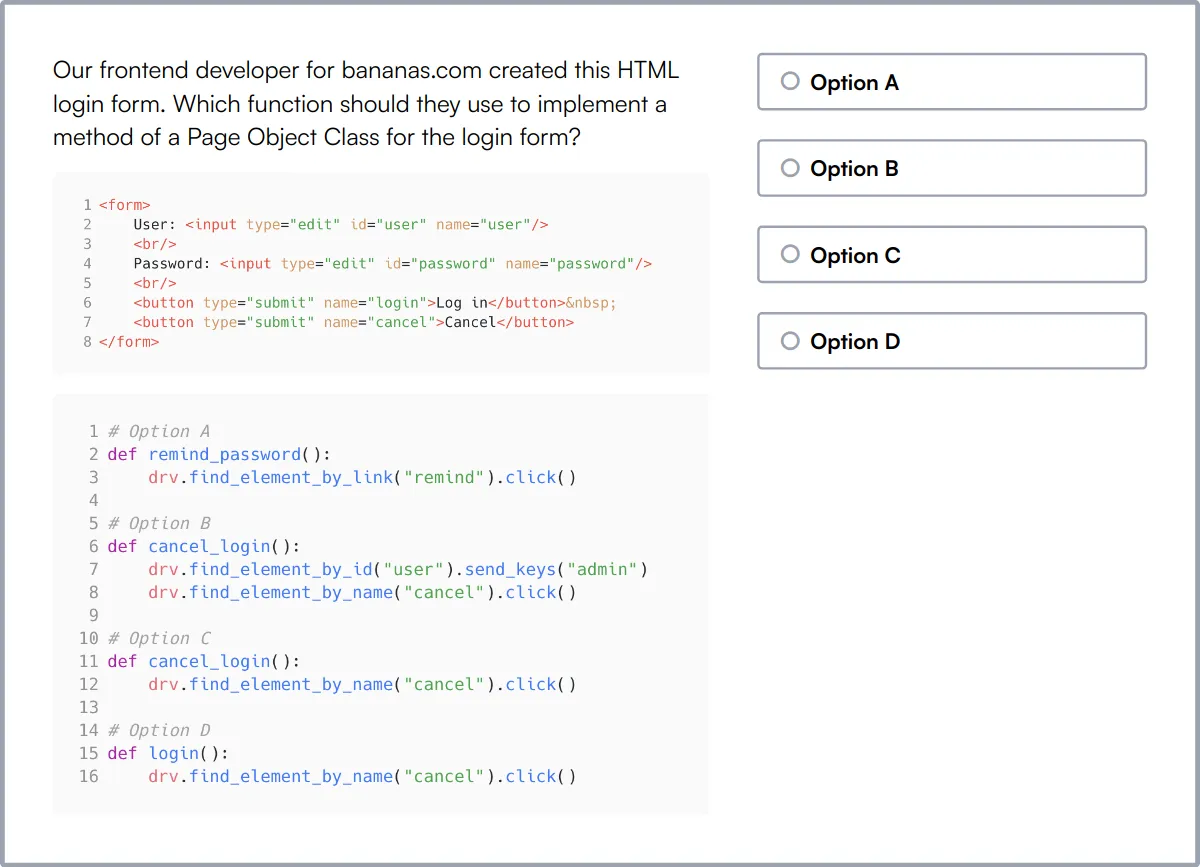
Jira Online Test
Our Jira Online Test measures a candidate's understanding of Jira Software Cloud, focusing on Agile project management methodologies such as Scrum and Kanban.
This test evaluates their knowledge in managing backlogs, sprints, Agile boards, and administering Jira configurations to optimize project workflows.
Candidates proficient in these areas are well-equipped to handle project management tasks efficiently, ensuring smooth operations and timely delivery of software projects.
Python Online Test
Our Python Online Test assesses a candidate's ability to effectively use Python for programming, covering core aspects like data structures, OOP, and error handling.
The test challenges candidates with scenarios involving file management, web scraping, and database manipulation, requiring a deep understanding of Python's in-built functions and modules.
High-scoring individuals demonstrate not only proficiency in writing clean, efficient Python code but also in debugging and optimizing scripts for performance.
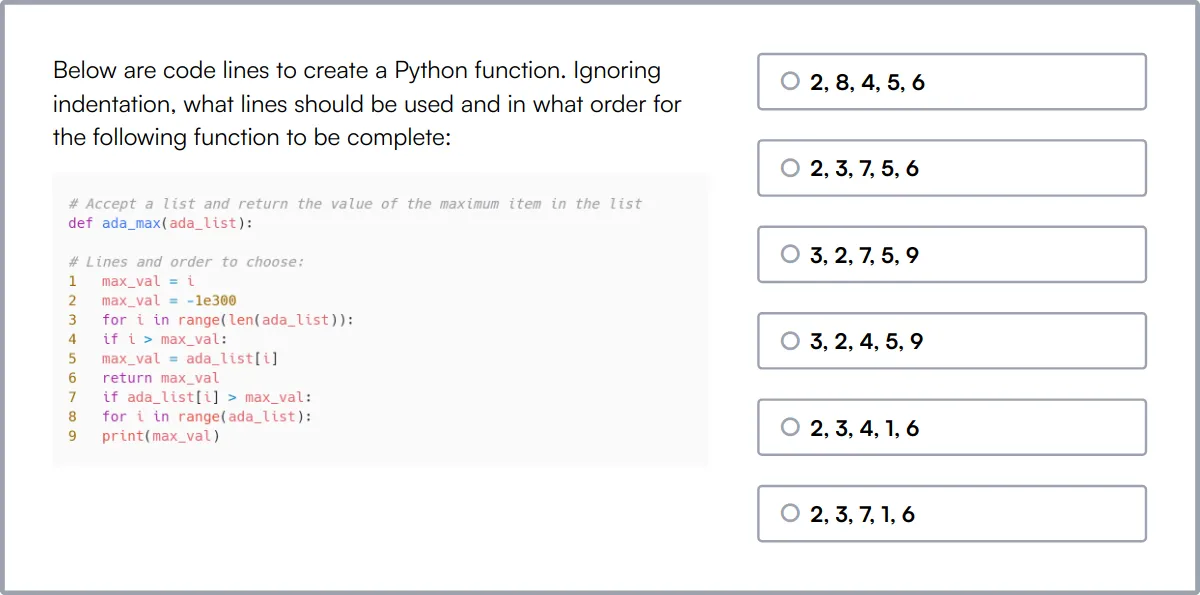
Quality Assurance Aptitude Test
Our Quality Assurance Aptitude Test evaluates candidates on their aptitude for various quality assurance tasks, including test planning, design, and defect tracking.
The test covers a comprehensive range of QA topics such as software testing methodologies, regression testing, performance testing, and security testing.
Candidates who excel in this test are adept at designing effective test strategies and are capable of identifying and addressing potential issues in software applications.
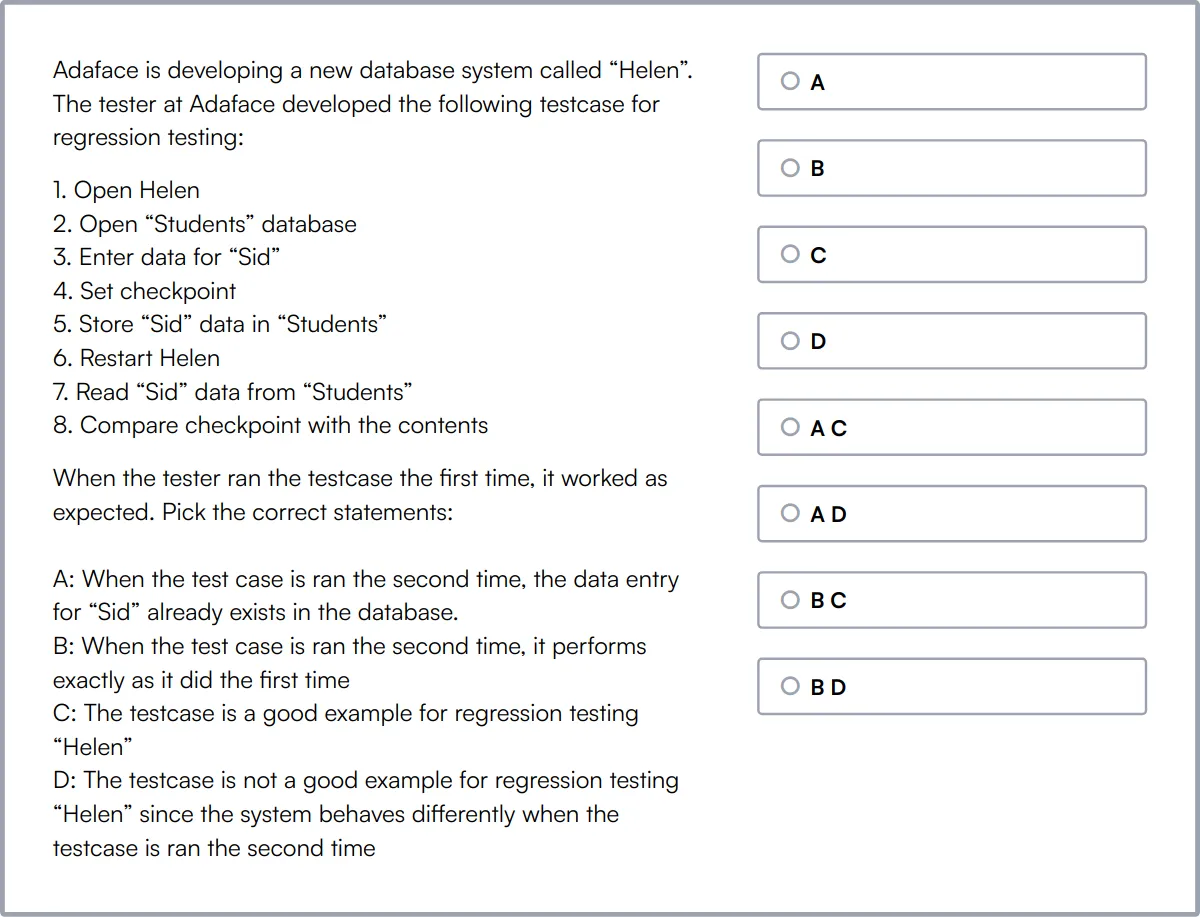
Critical Thinking Test
Our Critical Thinking Test assesses a candidate's ability to analyze information, recognize assumptions, and make logical decisions.
It challenges candidates to evaluate arguments, identify inconsistencies, and predict outcomes, which are essential skills in problem-solving and decision-making processes.
Those who perform well on this test are typically strong in forming coherent arguments and making reasoned decisions that are crucial in high-stakes environments.
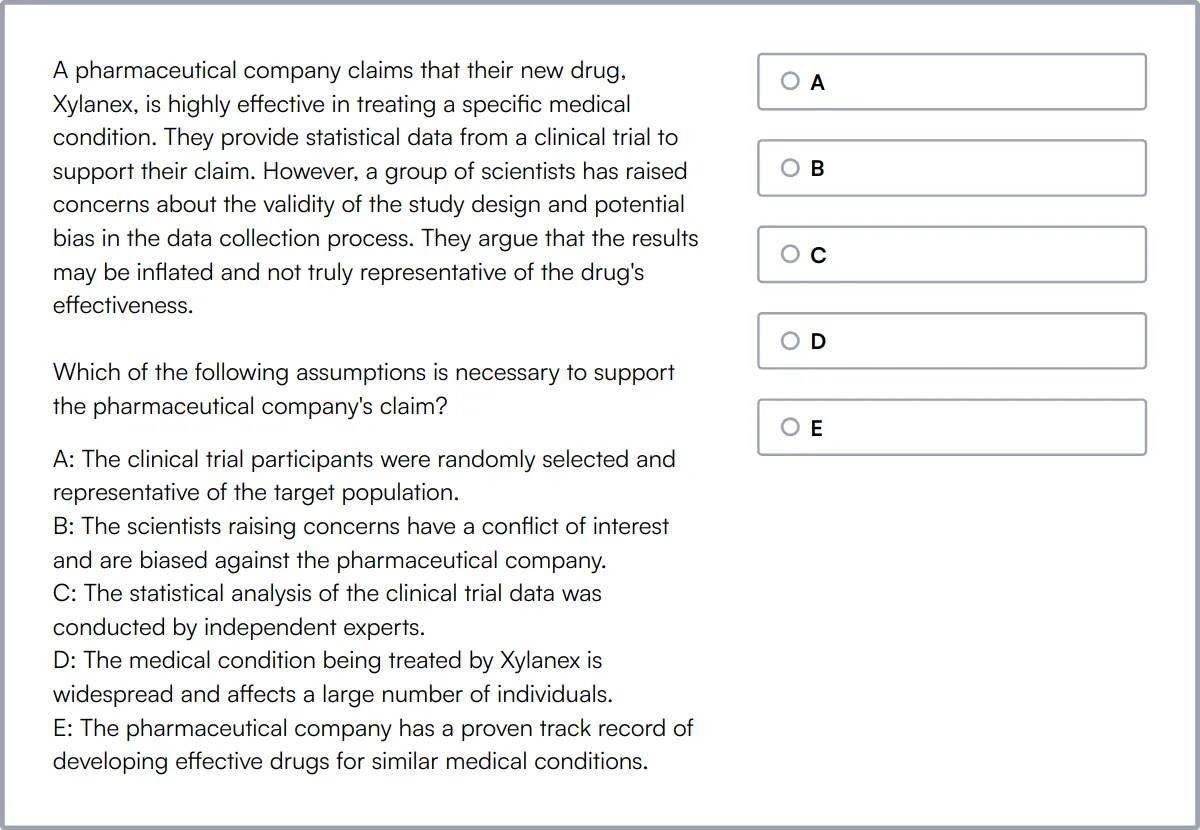
QA Engineer Test
Our QA Engineer Test is designed to evaluate a candidate's expertise in quality assurance, focusing on testing fundamentals, test design techniques, and software life cycle.
This test assesses knowledge in areas such as Selenium fundamentals, Linux fundamentals, and QA programming, along with practical skills in program testing.
Candidates who score well are proficient in creating and executing test plans, reporting on test outcomes, and ensuring software quality throughout the development process.

Summary: The 8 key Quality Assurance Engineer skills and how to test for them
| Quality Assurance Engineer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Test Automation | Evaluate ability to create and maintain automated test scripts. |
| 2. Bug Tracking | Check proficiency in identifying, documenting, and managing bugs. |
| 3. Programming Knowledge | Assess understanding of coding principles and languages. |
| 4. Test Plan Development | Review skills in designing comprehensive test plans. |
| 5. Risk Analysis | Gauge capability to identify and mitigate potential risks. |
| 6. Performance Testing | Measure skills in evaluating system performance under load. |
| 7. Security Testing | Assess ability to identify and address security vulnerabilities. |
| 8. API Testing | Evaluate proficiency in testing and validating APIs. |
Quality Assurance Aptitude Test
Quality Assurance Engineer skills FAQs
What is the importance of test automation in QA?
Test automation helps in executing repetitive test cases, ensuring faster feedback and higher test coverage. It allows QA engineers to focus on more complex testing scenarios.
How can bug tracking skills be assessed?
Assess bug tracking skills by evaluating the candidate's experience with tools like JIRA or Bugzilla. Ask them to describe their process for logging, tracking, and resolving bugs.
Why is programming knowledge necessary for QA engineers?
Programming knowledge is necessary for writing automated tests, understanding code logic, and collaborating with developers. It enhances the ability to identify and fix issues.
What should be included in a test plan?
A test plan should include objectives, scope, resources, schedule, test environment, test criteria, and risk analysis. It serves as a roadmap for the testing process.
How do you assess a candidate's experience with performance testing?
Ask about their experience with tools like JMeter or LoadRunner. Request examples of past performance testing projects and the metrics they used to measure performance.
What is the role of SQL knowledge in QA?
SQL knowledge is essential for validating data integrity, performing backend testing, and writing queries to verify database operations. It ensures accurate data handling.
How can communication skills be evaluated in a QA engineer?
Evaluate communication skills through behavioral interview questions. Assess their ability to explain complex technical issues, collaborate with team members, and document findings clearly.
Why is continuous integration important in QA?
Continuous integration ensures that code changes are automatically tested and integrated into the main branch. It helps in identifying issues early and maintaining code quality.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



