Product designers are at the heart of creating intuitive and engaging products that meet the needs of users. They blend aesthetics with functionality, ensuring that every product is not only visually appealing but also user-friendly.
Essential skills for a product designer include proficiency in design software like Adobe XD and Sketch, a strong understanding of user experience (UX) principles, and the ability to conduct and interpret user research.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Product Designer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 8 essential Product Designer skills, 10 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
8 fundamental Product Designer skills and traits
The best skills for Product Designers include User Research, Prototyping, Visual Design, Interaction Design, UX Writing, Information Architecture, Responsive Design and Design Systems.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 8 essential skills of a Product Designer.
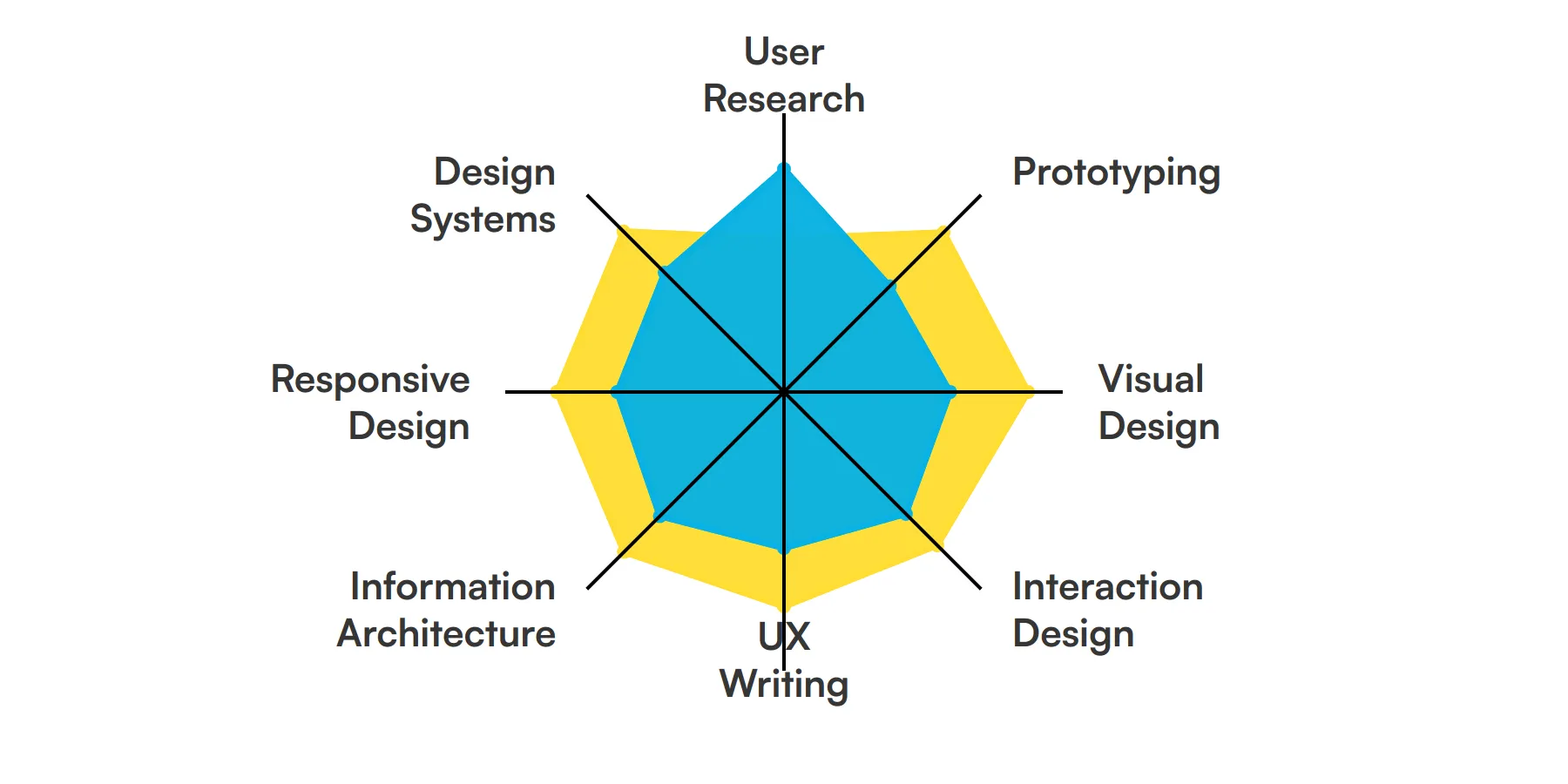
User Research
User research is fundamental for a Product Designer to understand the needs, behaviors, and motivations of users. By conducting interviews, surveys, and usability tests, a Product Designer can gather valuable insights that inform design decisions and ensure the product meets user expectations.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a UX Researcher Job Description.
Prototyping
Prototyping allows Product Designers to create quick iterations of their designs to test functionality and user interaction. This skill is used to visualize and refine concepts before they are developed, saving time and resources in the product development process.
Visual Design
Visual design focuses on the aesthetics of a product and its related materials by strategically implementing images, colors, fonts, and other elements. A Product Designer uses this skill to enhance product usability and ensure that it is appealing to the target audience.
Interaction Design
Interaction design is about crafting the conceptual design and behavior of a product’s interface. This skill is crucial for ensuring a seamless and intuitive user experience, which a Product Designer must optimize to facilitate user satisfaction and engagement.
UX Writing
UX writing involves creating concise and clear text for user interfaces. The role of a Product Designer includes crafting copy that guides users effortlessly through a product, enhancing the overall user experience.
Information Architecture
Information architecture helps in organizing and structuring content so that users can navigate and find information easily. Product Designers use this skill to create logical and accessible layouts that improve user experience.
Responsive Design
Responsive design ensures that a product’s interface looks good and functions well on a variety of devices and screen sizes. Product Designers must master this skill to cater to the growing diversity of user devices and enhance accessibility.
Design Systems
Design systems are a comprehensive set of design standards, documentation, and principles. They help maintain consistency and scalability in the product design process, which is essential for Product Designers working on complex projects.
10 secondary Product Designer skills and traits
The best skills for Product Designers include Project Management, User Psychology, Accessibility Standards, Data Analysis, Software Proficiency, Agile Methodologies, Client Communication, Technical Writing, Color Theory and Typography.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 10 secondary skills of a Product Designer.
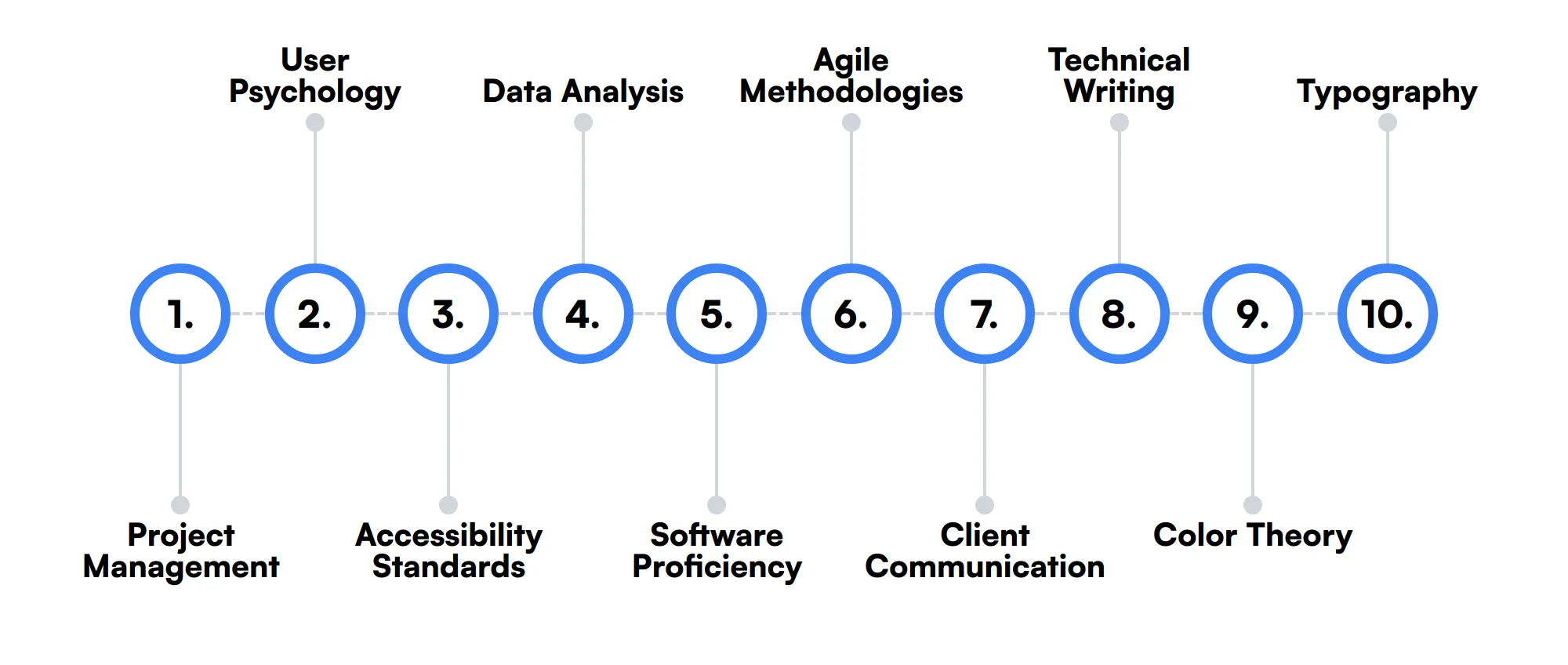
Project Management
Understanding project management principles can help Product Designers meet deadlines and collaborate effectively with cross-functional teams.
User Psychology
Knowledge of user psychology enables Product Designers to predict how users will react to certain design elements, which can influence design strategies.
Accessibility Standards
Familiarity with accessibility standards ensures that designs are usable by people with a wide range of physical and cognitive abilities.
Data Analysis
Analyzing user data can provide insights into how users interact with a product, which can inform iterative design improvements.
Software Proficiency
Proficiency in design and prototyping software like Sketch, Adobe XD, and Figma is necessary for creating high-fidelity design prototypes.
Agile Methodologies
Understanding Agile methodologies can help Product Designers work more effectively in fast-paced development environments.
Client Communication
Effective communication skills are important for Product Designers to understand client needs and convey design concepts clearly.
Technical Writing
Ability to produce clear documentation, such as design specifications and user guides, supports development and ensures design intent is maintained.
Color Theory
A strong grasp of color theory can enhance the visual appeal of designs and improve user engagement.
Typography
Understanding typography can significantly impact the readability and aesthetic quality of a product’s interface.
How to assess Product Designer skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a Product Designer involves more than just glancing at their portfolio or resume. It requires a deep dive into their practical abilities across various domains such as User Research, Prototyping, and Visual Design, among others. Understanding how to evaluate these skills effectively is key to finding the right candidate for your team.
Traditional interviews might not fully capture a candidate's proficiency in Interaction Design or UX Writing. This is where practical assessments come into play. By using skill-based assessments, you can see a candidate's thought process, creativity, and problem-solving skills in action.
For instance, Adaface offers tailored assessments that can help you evaluate a Product Designer's competencies across necessary skills like Information Architecture and Responsive Design. These assessments are designed to mirror real-world tasks that a designer would face, ensuring that you can assess their practical skills effectively. By integrating Adaface assessments into your hiring process, you can achieve a 85% reduction in screening time while also improving the quality of your hires.
Let’s look at how to assess Product Designer skills with these 2 talent assessments.
UI/UX Design Test
Our UI/UX Design Test evaluates a candidate's skills in creating user-friendly and visually appealing designs. It covers a wide range of topics, including wire-framing, prototyping, and A/B testing.
The test assesses their understanding of design thinking, UX design principles, and interaction design principles. Candidates are also tested on their ability to create effective landing pages and understand customer journeys.
Successful candidates demonstrate proficiency in UI fundamentals, visual design principles, and mobile app design considerations. They also show knowledge of accessibility guidelines and UX writing and content strategy.
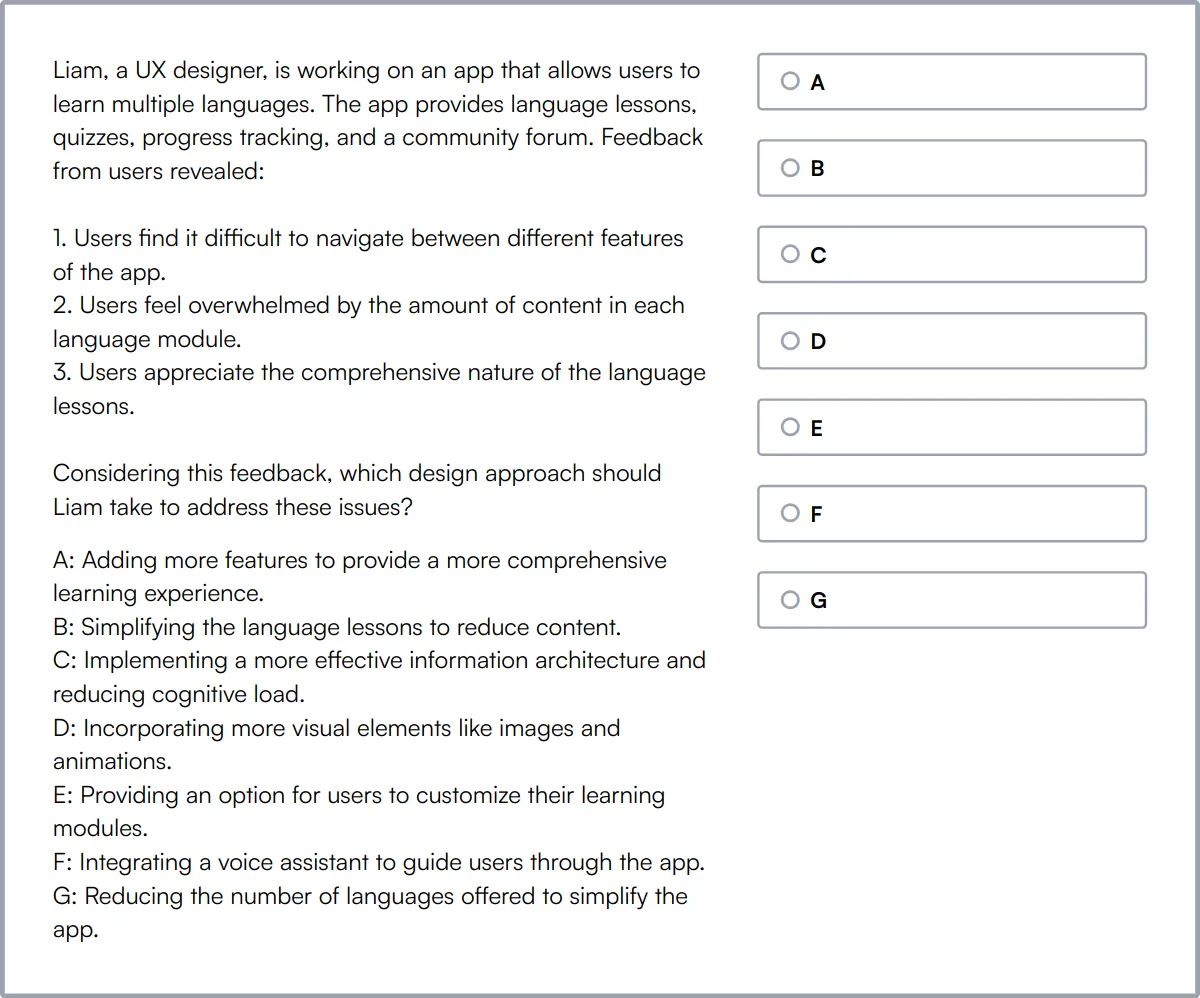
Content Strategy Test
Our Content Strategy Test evaluates candidates' abilities to develop effective content strategies for digital platforms. It covers areas such as audience analysis, content planning, and user experience optimization.
The test assesses their skills in understanding and defining target audience, content auditing, and content gap analysis. Candidates are also evaluated on their ability to perform keyword research and SEO and develop a content calendar.
High-scoring candidates show proficiency in content performance measurement, multichannel content strategy, and crisis communication. They also demonstrate an understanding of the content lifecycle and content governance.
Summary: The 8 key Product Designer skills and how to test for them
| Product Designer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. User Research | Evaluate how effectively a candidate gathers and analyzes user feedback. |
| 2. Prototyping | Assess ability to create functional models for early stage testing. |
| 3. Visual Design | Review portfolio for aesthetic appeal and professional presentation. |
| 4. Interaction Design | Observe how interactions are crafted to facilitate user engagement. |
| 5. UX Writing | Check clarity, tone, and conciseness of user-directed text. |
| 6. Information Architecture | Examine organization of information for intuitiveness and accessibility. |
| 7. Responsive Design | Test designs on various devices for seamless user experience. |
| 8. Design Systems | Investigate understanding and implementation of design standards and libraries. |
Visual Reasoning Test
Product Designer skills FAQs
What are the key skills to look for when hiring a Product Designer?
Focus on User Research, Prototyping, Visual Design, Interaction Design, and UX Writing. Also, assess their knowledge in Information Architecture, Responsive Design, and Design Systems.
How can recruiters assess a candidate's proficiency in user research?
Ask candidates to describe past projects where they conducted user research. Request specifics on their methodologies, tools used, and how their findings influenced the final product design.
What tools should a Product Designer be proficient in?
Look for proficiency in tools like Sketch, Adobe XD, Figma, and InVision. Familiarity with front-end coding languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can also be beneficial.
Why is understanding user psychology important for a Product Designer?
Understanding user psychology helps designers create more intuitive and engaging products. It allows them to predict user behavior and design for optimal user experiences.
How important is typography knowledge in product design?
Typography is critical as it impacts usability and readability. A designer's ability to choose and use type effectively can greatly affect the product's visual appeal and user experience.
What is the role of project management skills in a Product Designer's role?
Project management skills help designers meet deadlines, manage resources, and coordinate with other team members effectively, ensuring smooth progress and timely delivery of design projects.
How can a Product Designer's understanding of accessibility standards impact a product?
A strong grasp of accessibility standards ensures that products are usable by people with a wide range of disabilities, thus expanding the user base and meeting legal compliance.
What is the significance of Agile methodologies in product design?
Agile methodologies allow Product Designers to work in iterative cycles, adapt to changes quickly, and collaborate more effectively with cross-functional teams.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



