Process Analysts play a key role in optimizing and improving business processes. They analyze workflows, identify inefficiencies, and recommend solutions to enhance productivity and performance.
Skills required for a Process Analyst include a strong understanding of process mapping, data analysis, and project management. Additionally, they need to have excellent communication and problem-solving abilities.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Process Analyst skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 9 essential Process Analyst skills, 11 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
9 fundamental Process Analyst skills and traits
The best skills for Process Analysts include Data Analysis, Process Mapping, Problem Solving, Statistical Analysis, Process Improvement, Technical Writing, Root Cause Analysis, Workflow Automation and Business Process Modeling.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 essential skills of a Process Analyst.
Data Analysis
Data analysis is the backbone of a process analyst's role. It involves examining data sets to identify trends, draw conclusions, and support decision-making. This skill helps in understanding the current state of processes and identifying areas for improvement.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Data Analyst Job Description.
Process Mapping
Process mapping involves creating visual representations of workflows. This helps in understanding the sequence of activities, identifying bottlenecks, and ensuring that processes are streamlined and efficient. A process analyst uses this skill to document and analyze the flow of information and tasks.
Problem Solving
Problem-solving is crucial for identifying issues within processes and developing effective solutions. A process analyst must be adept at diagnosing problems, brainstorming potential fixes, and implementing changes that enhance process efficiency and effectiveness.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis involves using mathematical techniques to analyze data and draw meaningful conclusions. This skill is essential for a process analyst to validate hypotheses, measure process performance, and make data-driven decisions.
Process Improvement
Process improvement focuses on enhancing existing processes to increase efficiency and effectiveness. A process analyst uses this skill to identify areas for improvement, implement changes, and monitor the impact of those changes over time.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Process Analyst Job Description.
Technical Writing
Technical writing involves creating clear and concise documentation for processes, procedures, and reports. A process analyst uses this skill to ensure that all stakeholders understand the processes and any changes made to them.
Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is a method used to identify the underlying reasons for process failures or inefficiencies. A process analyst employs this skill to dig deep into issues and develop long-term solutions that prevent recurrence.
Workflow Automation
Workflow automation involves using technology to automate repetitive tasks within a process. A process analyst leverages this skill to reduce manual effort, minimize errors, and increase overall process efficiency.
Business Process Modeling
Business process modeling is the practice of representing processes in a structured format. This helps in analyzing and improving processes. A process analyst uses this skill to create models that provide a clear understanding of how processes function and where improvements can be made.
11 secondary Process Analyst skills and traits
The best skills for Process Analysts include Project Management, Change Management, Communication, Time Management, Critical Thinking, Software Proficiency, Stakeholder Management, Lean Six Sigma, Risk Management, Benchmarking and Customer Focus.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 11 secondary skills of a Process Analyst.
Project Management
Project management skills help a process analyst to plan, execute, and oversee process improvement projects. This ensures that projects are completed on time, within scope, and on budget.
Change Management
Change management involves preparing, supporting, and helping individuals and teams in making organizational changes. A process analyst uses this skill to ensure smooth transitions when new processes are implemented.
Communication
Effective communication is key for a process analyst to convey ideas, present findings, and collaborate with stakeholders. This skill ensures that everyone involved understands the process changes and their benefits.
Time Management
Time management skills help a process analyst to prioritize tasks, meet deadlines, and manage multiple projects simultaneously. This ensures that process improvement initiatives are completed efficiently.
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking involves analyzing facts to form a judgment. A process analyst uses this skill to evaluate processes, identify inefficiencies, and develop innovative solutions.
Software Proficiency
Proficiency in software tools like Excel, Visio, and process management software is important for a process analyst. These tools aid in data analysis, process mapping, and documentation.
Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder management involves identifying and engaging with individuals who have an interest in process changes. A process analyst uses this skill to ensure that all stakeholders are informed and their concerns are addressed.
Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that combines lean manufacturing and Six Sigma principles to improve processes. A process analyst with knowledge of Lean Six Sigma can effectively reduce waste and improve quality.
Risk Management
Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with process changes. A process analyst uses this skill to ensure that potential issues are addressed before they become major problems.
Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves comparing processes against industry standards or best practices. A process analyst uses this skill to identify areas where processes can be improved to meet or exceed these standards.
Customer Focus
Customer focus involves understanding and meeting the needs of customers. A process analyst uses this skill to ensure that process improvements align with customer expectations and enhance customer satisfaction.
How to assess Process Analyst skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a Process Analyst can be a nuanced task. It's not just about what they know, but how they apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios. From data analysis and process mapping to problem-solving and workflow automation, a Process Analyst's role is multifaceted and requires a deep understanding of various methodologies and tools.
Traditional resumes and interviews often fall short in revealing a candidate's true capabilities. This is where skills-based assessments come into play. By leveraging tools like Adaface on-the-job skill tests, you can gain a clearer picture of a candidate's proficiency in key areas such as statistical analysis, root cause analysis, and business process modeling. These assessments can help you achieve 2x improved quality of hires and an 85% reduction in screening time.
Let’s look at how to assess Process Analyst skills with these 6 talent assessments.
Data Analysis Test
Data Analysis Test assesses a candidate's ability to handle, modify, analyze, and interpret data. The test uses scenario-based MCQ questions to screen for experience with analyzing data to find possible outcomes, detect anomalies, extract meaningful insights, project estimates, and visualize data using charts and graphs.
The test evaluates skills in data modelling, business analysis fundamentals, data interpretation, and SQL. Candidates are tested on their ability to work with data queries, perform data operations, and investigate data correlations and rankings.
Successful candidates demonstrate proficiency in using popular data tools like Excel and have a strong grasp of data analysis concepts, including aggregations, statistics, and data investigations.
Data Interpretation Assessment Test
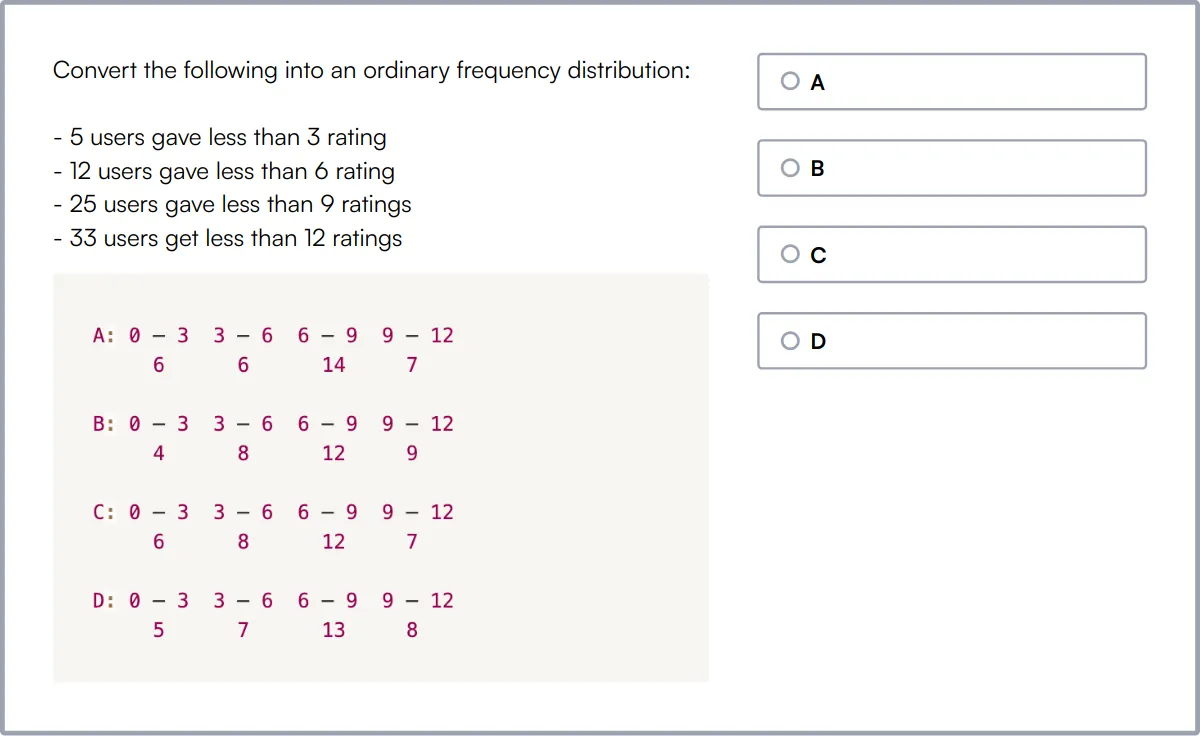
Data Interpretation Assessment Test evaluates a candidate's ability to analyze complex data, extract meaningful insights, and structure observations from multiple data sources like tables, charts, and graphs.
The test covers reading data, drawing inferences, interpreting graphs, and analyzing charts and tables. Candidates are assessed on their ability to visualize data and make informed decisions based on their interpretations.
High-scoring candidates show strong analytical skills and the ability to synthesize information from various data sources to provide clear and actionable insights.
Problem Solving Test
Problem Solving Test evaluates a candidate's ability to understand instructions, analyze data, and respond to complex problems or situations. The questions are designed to get insights into their problem-solving, learning agility, and coachability.
The test assesses skills in abstract reasoning, critical thinking, deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, pattern matching, and spatial reasoning. Candidates navigate through various logical, data interpretation, and spatial reasoning scenarios.
Successful candidates demonstrate strong critical thinking and problem-solving abilities, showcasing their capacity to handle complex and abstract challenges effectively.
Statistics Test
Statistics Test evaluates a candidate's understanding and proficiency in statistical concepts and analysis. It covers topics such as statistical methods, data analysis, numerical reasoning, and quantitative aptitude.
The test assesses knowledge in statistics fundamentals, inference, data sampling, regression, sampling distributions, exploratory data analysis, non-parametric statistics, and probability. Candidates are tested on their ability to apply statistical methods to real-world data.
Candidates who perform well demonstrate a strong grasp of statistical concepts and the ability to analyze and interpret data accurately, making informed decisions based on statistical evidence.
Loadrunner Online Test
Loadrunner Online Test evaluates a candidate's knowledge and skills in using Loadrunner, a performance testing tool used to test the performance and scalability of web applications.
The test covers Loadrunner basics, scripting and scenarios, load testing concepts, performance monitoring and analysis, script enhancement and customization, parameterization and correlation, think time and pacing, response time and throughput, error handling and debugging, and test execution and result analysis.
Candidates who excel in this test demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of Loadrunner and its application in performance testing, showcasing their ability to effectively monitor, analyze, and optimize web application performance.
Technical Aptitude Test
Technical Aptitude Test uses scenario-based multiple-choice questions to evaluate a candidate's general technical aptitude and problem-solving skills.
The test covers programming fundamentals, data structures, algorithm basics, and technical aptitude. Candidates are assessed on their ability to apply critical thinking, logical reasoning, and analytical skills to solve complex technical problems.
High-scoring candidates demonstrate strong technical knowledge and problem-solving abilities, showcasing their capacity to handle various technical challenges effectively.
Summary: The 9 key Process Analyst skills and how to test for them
| Process Analyst skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Data Analysis | Evaluate candidate's ability to interpret and derive insights from data. |
| 2. Process Mapping | Assess understanding and application of visualizing business processes effectively. |
| 3. Problem Solving | Test how candidates approach and resolve various challenges. |
| 4. Statistical Analysis | Check proficiency in using statistical methods to analyze data sets. |
| 5. Process Improvement | Review ability to optimize processes for better efficiency and outcomes. |
| 6. Technical Writing | Judge clarity, coherence, and technical accuracy in written communication. |
| 7. Root Cause Analysis | Determine skill in identifying underlying causes of issues. |
| 8. Workflow Automation | Evaluate expertise in automating repetitive tasks and processes. |
| 9. Business Process Modeling | Assess ability to model processes that align with business goals. |
Business Analyst Aptitude Online Test
Process Analyst skills FAQs
What skills should a Process Analyst have for effective data analysis?
A Process Analyst should be proficient in SQL, Excel, and data visualization tools like Tableau. Understanding statistical methods and having the ability to interpret data trends are also important.
How can a recruiter assess problem-solving skills in Process Analyst candidates?
Recruiters can assess problem-solving skills by presenting candidates with real-world scenarios related to process inefficiencies and asking them to propose feasible solutions. Behavioral interview questions can also reveal how candidates have handled past challenges.
What is the importance of process mapping in a Process Analyst's role?
Process mapping is key for identifying and documenting the steps in a business process. It helps in visualizing the current process and is the first step in process improvement by highlighting areas of delay, redundancy, or error.
Why is stakeholder management important for a Process Analyst?
Effective stakeholder management ensures that all parties involved are aligned, which is critical for successful process changes. It involves communication and negotiation skills to manage expectations and foster collaboration.
What tools should a Process Analyst be proficient in for workflow automation?
Process Analysts should be skilled in using BPM (Business Process Management) tools like Kissflow, Zoho Creator, or Microsoft Power Automate to design, execute, and automate business processes.
How does Lean Six Sigma contribute to a Process Analyst’s effectiveness?
Lean Six Sigma provides methodologies to reduce waste and improve quality. Mastery of these principles allows a Process Analyst to enhance process efficiency and effectiveness, leading to better business outcomes.
What role does communication play in the success of a Process Analyst?
Communication is key in translating complex process details into understandable terms for stakeholders, facilitating training sessions, and writing clear process documentation. It bridges the gap between technical and non-technical audiences.
How can project management skills benefit a Process Analyst?
Project management skills help Process Analysts plan, execute, and monitor process improvement projects. They ensure projects stay on track, within budget, and meet the desired outcomes.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



