The role of a Problem Manager is fundamental in ensuring smooth and efficient IT service operations. They are responsible for managing the lifecycle of all problems that arise, aiming to minimize the adverse impact of incidents and problems on the business and preventing recurrence of incidents related to these problems.
Key skills for a Problem Manager include strong analytical thinking to identify root causes, excellent communication to coordinate with IT support teams, and a proactive approach to prevent future issues. Additionally, leadership and project management skills are crucial in driving the resolution process and implementing strategic changes.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Problem Manager skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 9 essential Problem Manager skills, 11 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
9 fundamental Problem Manager skills and traits
The best skills for Problem Managers include Root Cause Analysis, Incident Management, Data Analysis, Technical Knowledge, Communication, Change Management, Risk Assessment, Documentation and Service Level Management.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 essential skills of a Problem Manager.
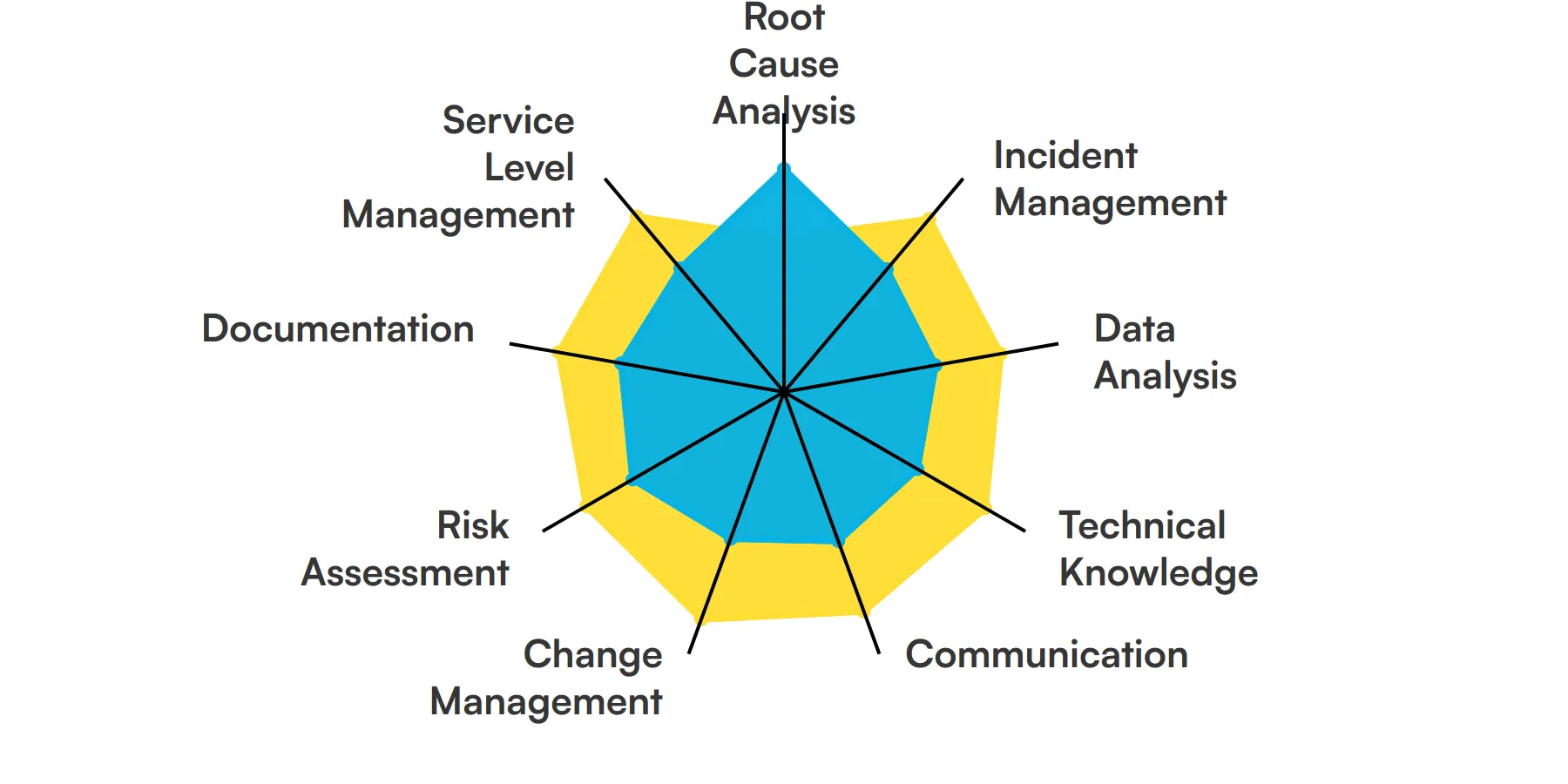
Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis is the process of identifying the underlying reasons for problems. A Problem Manager uses this skill to dig deep into issues, ensuring that the real cause is addressed rather than just the symptoms. This helps in preventing recurrence and improving overall system reliability.
Incident Management
Incident Management involves handling disruptions and restoring services as quickly as possible. A Problem Manager must be adept at coordinating responses to incidents, ensuring minimal impact on business operations. This skill is crucial for maintaining service continuity and customer satisfaction.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Incident Manager Job Description.
Data Analysis
Data Analysis is the ability to interpret and draw insights from data. Problem Managers use this skill to analyze incident trends, identify patterns, and predict potential issues. This helps in proactive problem management and informed decision-making.
Technical Knowledge
Technical Knowledge refers to understanding the systems, applications, and technologies in use. A Problem Manager needs this skill to effectively troubleshoot issues and communicate with technical teams. It ensures that they can provide accurate and relevant solutions.
Communication
Communication is about conveying information clearly and effectively. Problem Managers must communicate with various stakeholders, including technical teams, management, and customers. This skill ensures that everyone is informed and aligned on the problem resolution process.
Change Management
Change Management involves overseeing changes to systems and processes. A Problem Manager uses this skill to ensure that changes are implemented smoothly and do not introduce new issues. It helps in maintaining system stability and reliability.
Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment is the process of identifying and evaluating potential risks. Problem Managers use this skill to anticipate and mitigate issues before they escalate. This proactive approach helps in maintaining service quality and preventing major disruptions.
Documentation
Documentation involves creating detailed records of problems, solutions, and processes. A Problem Manager needs this skill to ensure that there is a clear and accessible history of issues and resolutions. This aids in knowledge sharing and future problem-solving.
Service Level Management
Service Level Management is about ensuring that services meet agreed-upon standards. Problem Managers use this skill to monitor and report on service performance, ensuring that any deviations are addressed promptly. This helps in maintaining customer satisfaction and trust.
11 secondary Problem Manager skills and traits
The best skills for Problem Managers include Project Management, Vendor Management, Negotiation, Customer Service, Time Management, Collaboration, Analytical Thinking, Process Improvement, ITIL Knowledge, Critical Thinking and Conflict Resolution.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 11 secondary skills of a Problem Manager.
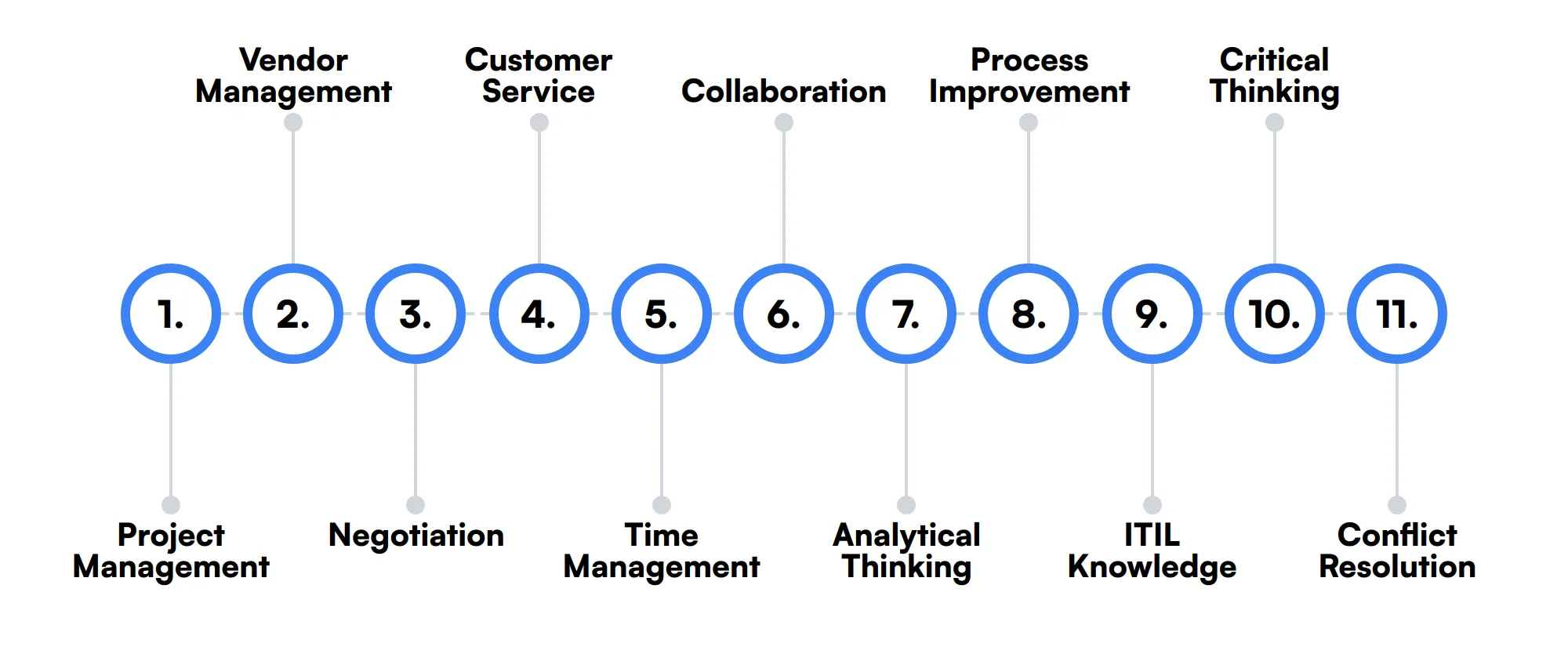
Project Management
Project Management involves planning, executing, and closing projects. While not the primary focus, a Problem Manager may use this skill to manage problem resolution initiatives and ensure timely completion.
Vendor Management
Vendor Management is about overseeing relationships with third-party service providers. A Problem Manager might need this skill to coordinate with vendors during problem resolution and ensure they meet their service commitments.
Negotiation
Negotiation involves reaching agreements through discussion. Problem Managers may use this skill to negotiate timelines, resources, and solutions with various stakeholders, ensuring that the best possible outcomes are achieved.
Customer Service
Customer Service is about addressing customer needs and concerns. A Problem Manager may need this skill to handle escalations and ensure that customers are kept informed and satisfied throughout the problem resolution process.
Time Management
Time Management is the ability to prioritize tasks and manage time effectively. Problem Managers use this skill to ensure that problems are resolved within acceptable timeframes, minimizing impact on business operations.
Collaboration
Collaboration involves working effectively with others. A Problem Manager needs this skill to coordinate with different teams and departments, ensuring a unified approach to problem resolution.
Analytical Thinking
Analytical Thinking is the ability to break down complex problems into manageable parts. Problem Managers use this skill to systematically approach problem-solving, ensuring thorough and effective resolutions.
Process Improvement
Process Improvement involves identifying and implementing ways to enhance processes. A Problem Manager may use this skill to streamline problem management procedures, making them more efficient and effective.
ITIL Knowledge
ITIL Knowledge refers to understanding the IT Infrastructure Library framework. A Problem Manager benefits from this skill by applying best practices in IT service management, ensuring a structured and effective approach to problem resolution.
Critical Thinking
Critical Thinking is the ability to evaluate information and make reasoned decisions. Problem Managers use this skill to assess situations, consider various solutions, and choose the most effective course of action.
Conflict Resolution
Conflict Resolution involves addressing and resolving disagreements. A Problem Manager may need this skill to handle conflicts that arise during problem resolution, ensuring a smooth and cooperative process.
How to assess Problem Manager skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a Problem Manager can be a challenging task. It's not just about verifying their technical knowledge, but also understanding their ability to handle complex situations and communicate effectively. A Problem Manager needs to excel in areas like Root Cause Analysis, Incident Management, and Data Analysis, among others.
Traditional resumes and interviews might not give you a complete picture of a candidate's capabilities. Skills-based hiring practices, such as talent assessments, are a reliable way to evaluate a candidate's competencies. For instance, Adaface on-the-job skill tests can help you achieve 2x improved quality of hires by focusing on real-world scenarios and practical skills.
When assessing a Problem Manager, it's important to consider their proficiency in key areas like Technical Knowledge, Communication, Change Management, Risk Assessment, Documentation, and Service Level Management. These skills are critical for ensuring that problems are managed effectively and that the organization can maintain high service levels.
Let’s look at how to assess Problem Manager skills with these 6 talent assessments.
Problem Solving Test
Our Problem Solving Test evaluates a candidate's ability to understand instructions, analyze data, and respond to complex problems or situations. This test is designed to provide insights into their problem-solving skills, learning agility, and coachability.
The test covers abstract reasoning, critical thinking, deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, pattern matching, and spatial reasoning. Candidates are presented with logical reasoning, data interpretation, spatial reasoning, abstract reasoning, and critical thinking questions.
Successful candidates demonstrate strong analytical skills and the ability to approach problems from multiple angles. They show proficiency in identifying patterns, making logical deductions, and interpreting complex data.
ITIL Test
Our ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) Test uses scenario-based multiple-choice questions to evaluate candidates on their knowledge and understanding of ITIL principles and practices. This test is crucial for assessing their ability to apply ITIL concepts to real-world scenarios.
The test covers IT service continuity planning, service desk operations, release management, service capacity management, configuration management, and problem management. Candidates are evaluated on their familiarity with ITIL terminology, concepts, and processes.
High-scoring candidates show a deep understanding of ITIL frameworks and can effectively manage IT services, ensuring continuity and efficiency. They are adept at handling service transitions, operations, and continual service improvements.
Data Analysis Test
Our Data Analysis Test assesses a candidate's ability to handle, modify, analyze, and interpret data. This test is designed to screen for experience with analyzing data to find possible outcomes, detect anomalies, and extract meaningful insights.
The test covers data modeling, business analysis fundamentals, data interpretation, SQL queries, and data operations. Candidates are presented with scenario-based questions on data analysis, business analysis, data interpretation, and SQL.
Successful candidates demonstrate proficiency in using data tools like Excel, interpreting charts and graphs, and performing data investigations. They can effectively analyze data to make informed business decisions and project estimates.
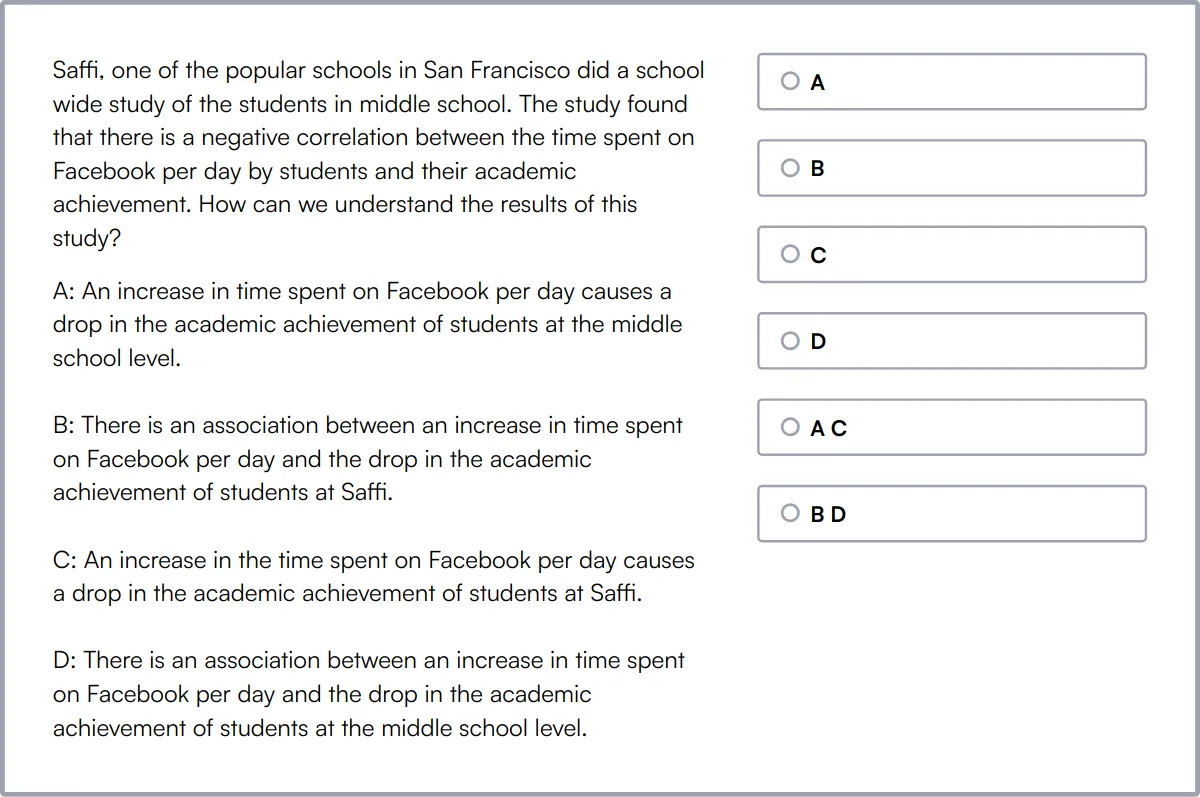
Technical Aptitude Test
Our Technical Aptitude Test uses scenario-based multiple-choice questions to evaluate a candidate's general technical aptitude and problem-solving skills. This test covers a broad range of technical topics.
The test includes programming fundamentals, data structures, algorithm basics, and technical aptitude. Candidates are assessed on their ability to apply critical thinking, logical reasoning, and analytical skills to solve complex technical problems.
High-scoring candidates show a strong understanding of basic computer concepts, programming, and data structures. They can effectively tackle technical challenges and demonstrate solid problem-solving abilities.
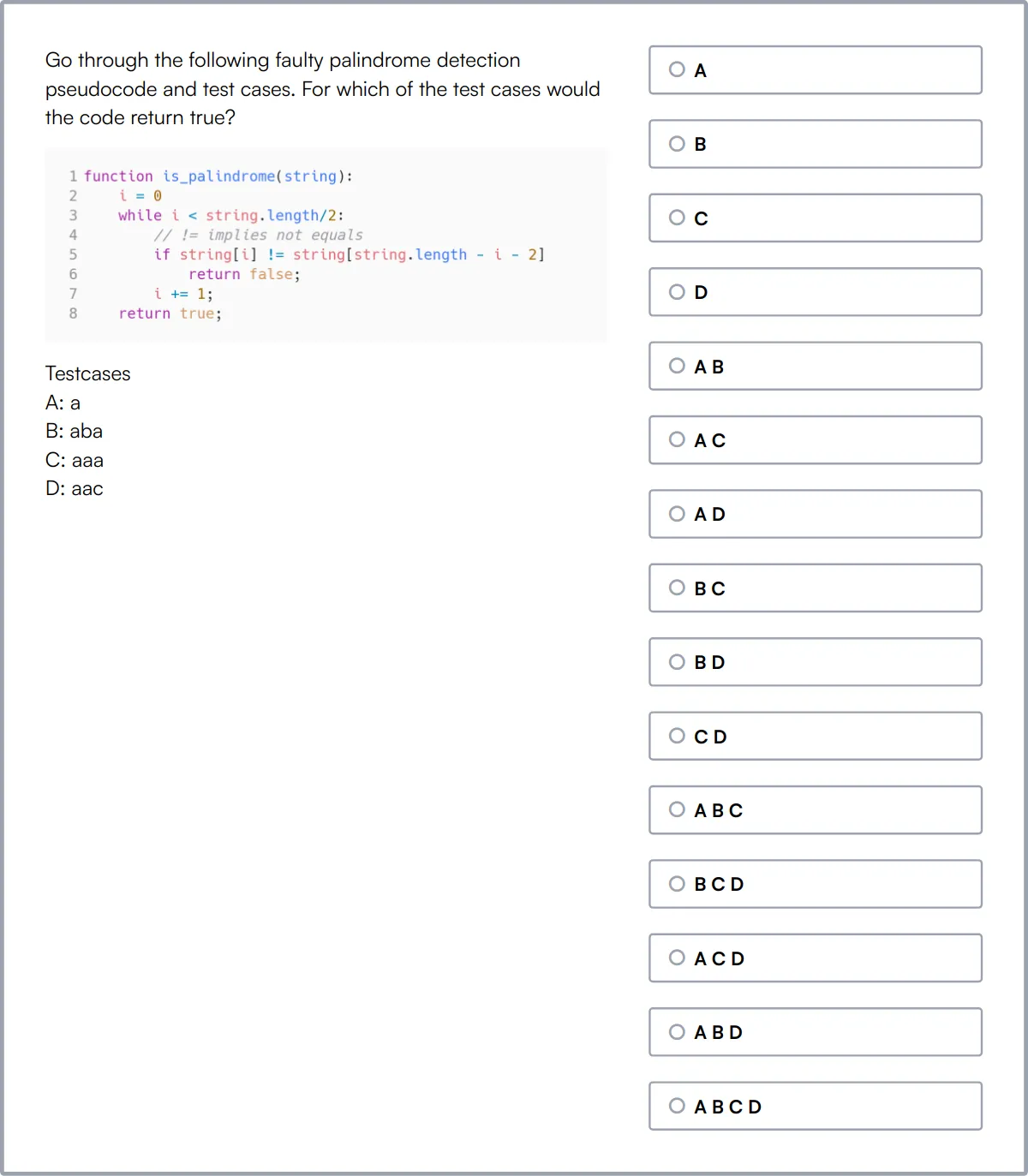
Communication Skills Test
Our Communication Skills Test evaluates candidates' communication skills, including verbal and written communication, active listening, and interpersonal skills. This test is designed to assess their ability to effectively communicate in various professional scenarios.
The test covers communication skills, situational judgement, attention to detail, critical thinking, and verbal reasoning. Candidates are presented with situational judgement, communication skills, critical thinking, and verbal reasoning questions.
Successful candidates demonstrate strong verbal and written communication skills, the ability to think critically, and attention to detail. They can effectively interact with customers, colleagues, and stakeholders.
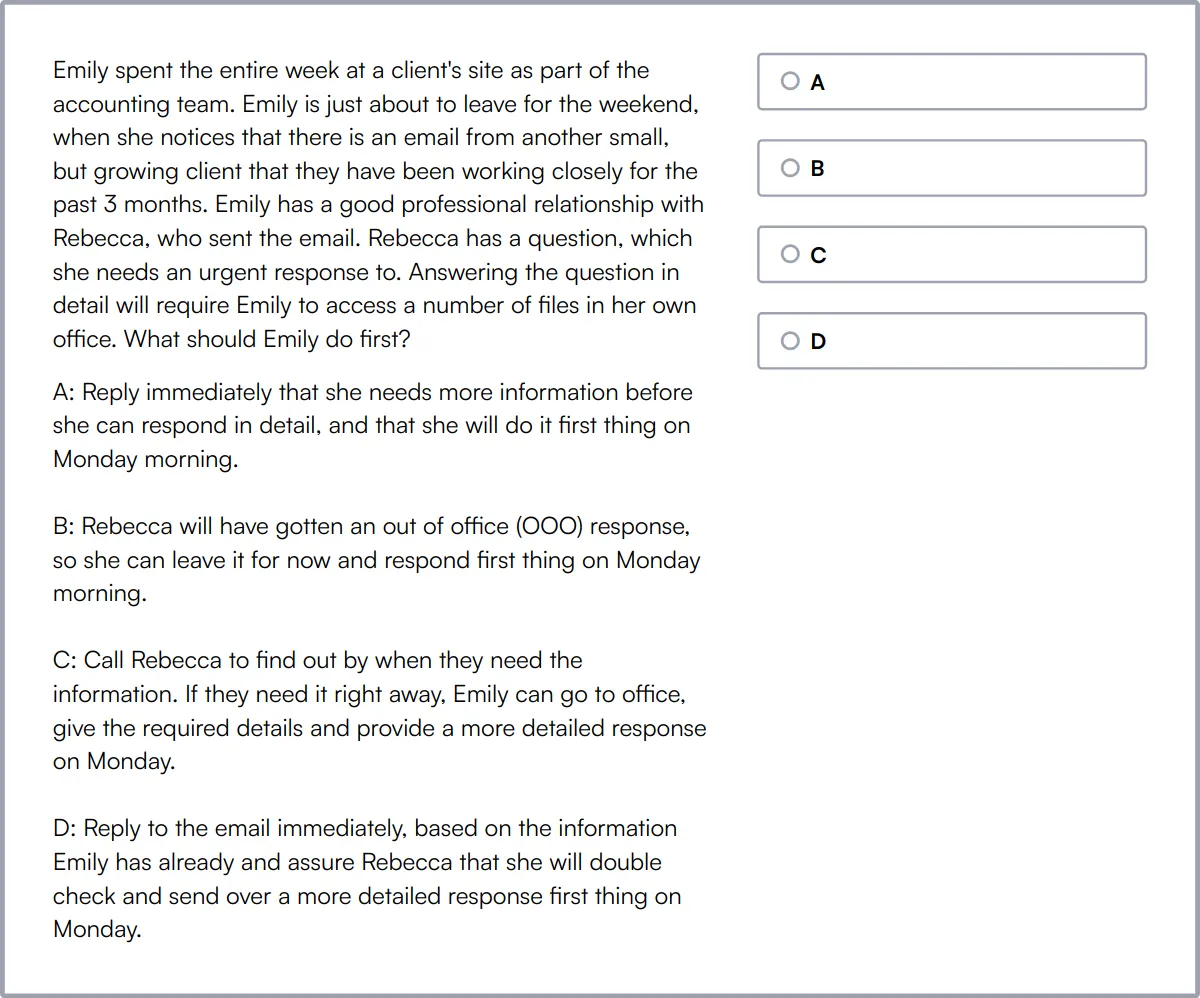
Project Management Test
Our Project Management Test assesses a candidate's ability to plan projects from conception to implementation. This test evaluates their skills in mapping timelines, assessing risks, allocating budgets, and managing stakeholders.
The test covers cost and budget estimation, situational judgement, project planning, issue resolution, resource management, and stakeholder management. Candidates are presented with project management, critical thinking, and Agile/Scrum questions.
High-scoring candidates show proficiency in both Agile and traditional project management methodologies. They can effectively prioritize tasks, manage resources, and deliver projects on time while handling changes and risks.

Summary: The 9 key Problem Manager skills and how to test for them
| Problem Manager skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Root Cause Analysis | Evaluate ability to identify and address underlying issues. |
| 2. Incident Management | Assess skills in handling and resolving incidents promptly. |
| 3. Data Analysis | Check proficiency in interpreting and utilizing data for decision-making. |
| 4. Technical Knowledge | Gauge understanding of relevant technical systems and tools. |
| 5. Communication | Measure effectiveness in conveying information clearly and concisely. |
| 6. Change Management | Evaluate capability to manage and implement changes smoothly. |
| 7. Risk Assessment | Assess ability to identify and mitigate potential risks. |
| 8. Documentation | Check skills in creating clear, comprehensive documentation. |
| 9. Service Level Management | Evaluate ability to maintain and improve service quality. |
Accounting Assessment Test
Problem Manager skills FAQs
What is Root Cause Analysis in a Problem Manager role?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) involves identifying the underlying causes of incidents to prevent recurrence. It requires analytical thinking and technical knowledge.
How can recruiters assess a candidate's Incident Management skills?
Ask candidates to describe past incidents they managed, focusing on their approach to resolution and communication with stakeholders.
Why is Data Analysis important for a Problem Manager?
Data Analysis helps in identifying trends and patterns in incidents, which is crucial for proactive problem management and process improvement.
What technical knowledge should a Problem Manager possess?
A Problem Manager should have a solid understanding of the IT infrastructure, systems, and applications relevant to their organization.
How can communication skills be evaluated in a Problem Manager candidate?
Assess communication skills through behavioral interview questions and by evaluating their ability to explain complex issues clearly.
What role does Change Management play in Problem Management?
Change Management ensures that changes are implemented smoothly and effectively, minimizing the risk of new incidents.
How can recruiters gauge a candidate's Risk Assessment capabilities?
Ask candidates to provide examples of how they have identified and mitigated risks in previous roles.
What is the importance of ITIL Knowledge for a Problem Manager?
ITIL Knowledge provides a framework for best practices in IT service management, which is essential for effective problem management.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



