Network engineers are the backbone of any organization's IT infrastructure. They ensure that data flows smoothly across digital networks, keeping systems connected and operational.
The role requires a deep understanding of network technologies such as TCP/IP, routers, switches, and firewalls. Skills in troubleshooting, analytical thinking, and effective communication are also crucial for success.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Network Engineer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 7 essential Network Engineer skills, 10 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
7 fundamental Network Engineer skills and traits
The best skills for Network Engineers include Network Configuration, Troubleshooting, Security Protocols, Routing and Switching, Network Monitoring, Wireless Networking and Cloud Networking.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 7 essential skills of a Network Engineer.
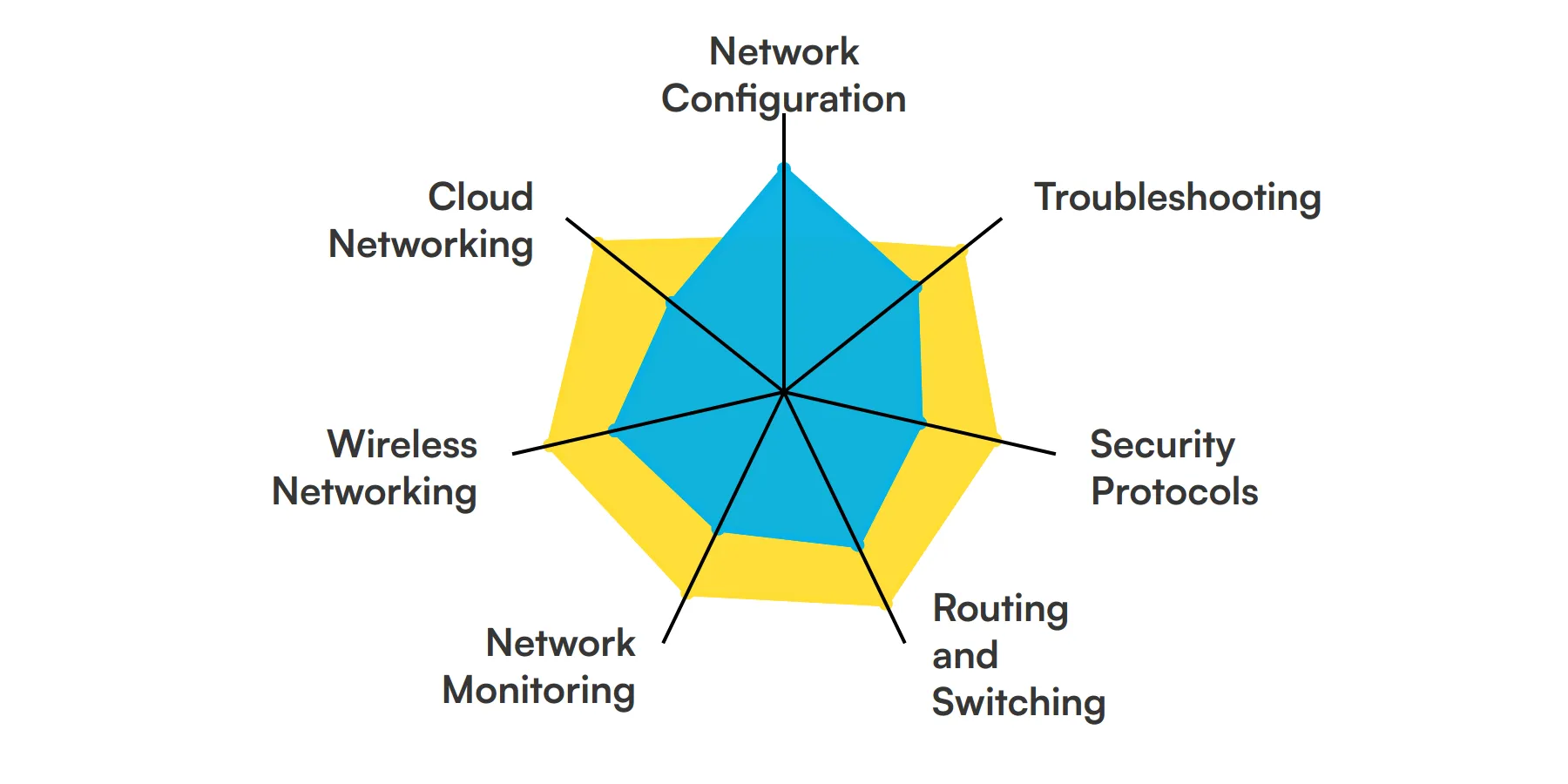
Network Configuration
Network engineers need to set up and configure network hardware and software. This involves assigning IP addresses, configuring routers and switches, and setting up firewalls to ensure secure and efficient data flow.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Network Engineer Job Description.
Troubleshooting
When network issues arise, network engineers must diagnose and resolve them quickly. This skill involves identifying the root cause of problems, whether they are hardware failures, software bugs, or connectivity issues.
Security Protocols
Understanding and implementing security protocols is crucial for protecting network data. Network engineers use this skill to set up firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection systems to safeguard against cyber threats.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Routing and Switching
Network engineers must be proficient in routing and switching to manage data traffic efficiently. This includes configuring routers and switches to optimize network performance and ensure reliable connectivity.
Network Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of network performance is essential to detect and address issues proactively. Network engineers use various tools to track network health, bandwidth usage, and potential bottlenecks.
Wireless Networking
With the increasing reliance on wireless networks, network engineers need to design and manage Wi-Fi networks. This includes setting up access points, ensuring coverage, and troubleshooting connectivity issues.
Cloud Networking
As more organizations move to the cloud, network engineers must understand cloud networking. This involves configuring and managing virtual networks, ensuring secure connections, and optimizing cloud resources.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Cloud Engineer Job Description.
10 secondary Network Engineer skills and traits
The best skills for Network Engineers include Scripting, VoIP, Load Balancing, Network Design, DNS Management, Quality of Service, Network Documentation, Vendor Management, Disaster Recovery and IPv6.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 10 secondary skills of a Network Engineer.
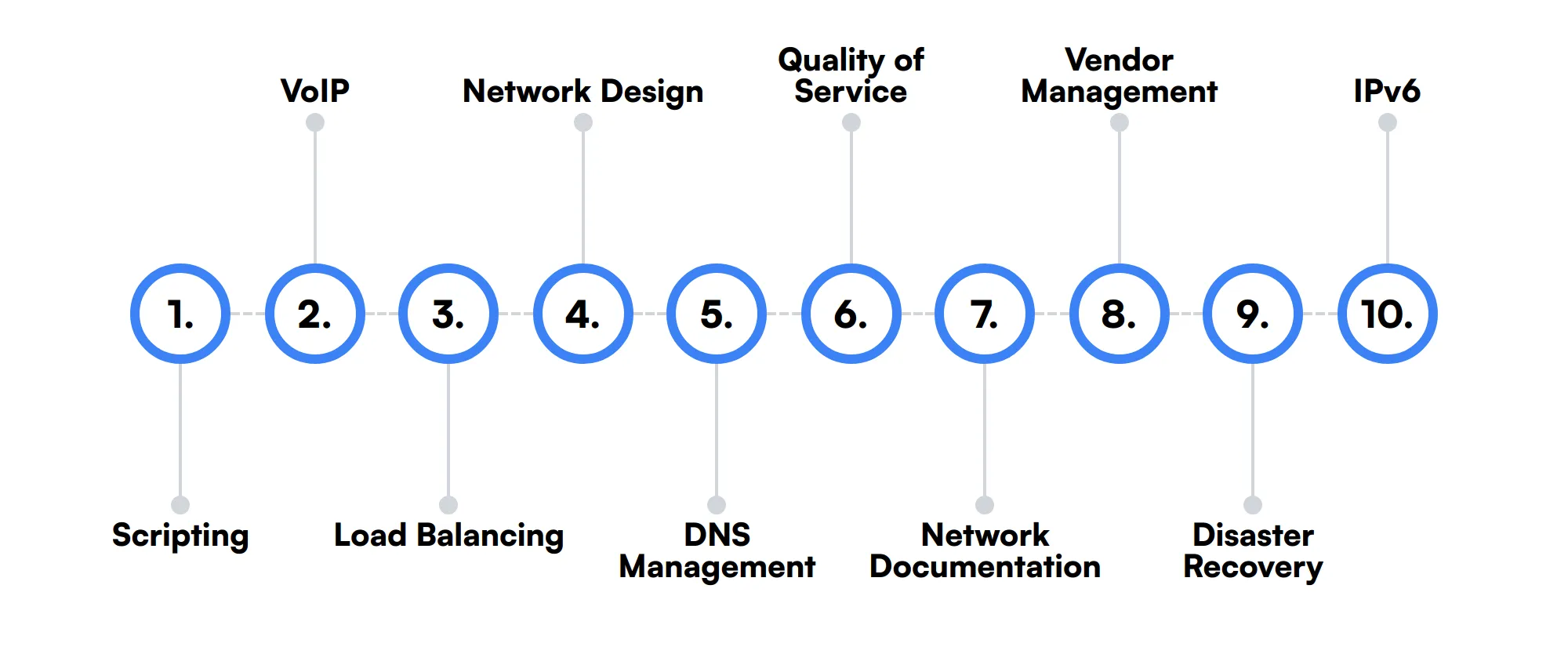
Scripting
Scripting skills help network engineers automate repetitive tasks. By writing scripts in languages like Python or Bash, they can streamline network configuration and management processes.
VoIP
Voice over IP (VoIP) technology is essential for modern communication systems. Network engineers need to set up and maintain VoIP systems to ensure clear and reliable voice communication over the network.
Load Balancing
Load balancing is crucial for distributing network traffic evenly across servers. Network engineers use this skill to enhance performance and ensure high availability of applications and services.
Network Design
Designing a network involves planning its layout, selecting appropriate hardware, and ensuring scalability. Network engineers use this skill to create efficient and future-proof network architectures.
DNS Management
Domain Name System (DNS) management is vital for translating domain names into IP addresses. Network engineers configure and maintain DNS servers to ensure reliable domain resolution.
Quality of Service
Quality of Service (QoS) settings help prioritize network traffic to ensure critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth. Network engineers configure QoS to optimize performance for essential services.
Network Documentation
Keeping detailed network documentation is important for troubleshooting and future upgrades. Network engineers create and maintain records of network configurations, topologies, and changes.
Vendor Management
Working with hardware and software vendors is part of a network engineer's role. This skill involves evaluating products, negotiating contracts, and managing relationships to ensure the best solutions for the network.
Disaster Recovery
Planning for disaster recovery ensures network resilience in case of failures. Network engineers develop and implement strategies to restore network functionality quickly after disruptions.
IPv6
With the depletion of IPv4 addresses, understanding IPv6 is becoming increasingly important. Network engineers need to configure and manage IPv6 networks to ensure future compatibility.
How to assess Network Engineer skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a Network Engineer can be a challenging task, given the wide range of technical proficiencies required. From network configuration and troubleshooting to understanding security protocols and cloud networking, a Network Engineer must be adept in various domains to ensure seamless network operations.
Resumes and certifications can provide a snapshot of a candidate's background, but they often fall short in demonstrating real-world proficiency and problem-solving abilities. Skills-based assessments are a reliable way to gauge a candidate's true capabilities and fit for your specific needs.
For a comprehensive evaluation, consider using Adaface assessments, which can help you achieve 2x improved quality of hires and an 85% reduction in screening time. These assessments are designed to test a candidate's practical knowledge in key areas such as routing and switching, network monitoring, wireless networking, and more.
Let’s look at how to assess Network Engineer skills with these 5 talent assessments.
CISCO Routing Switching Test
Our CISCO Routing Switching Test evaluates candidates on their expertise in network routing and switching concepts, specifically using CISCO network equipment.
The test assesses knowledge of routing protocols like OSPF and BGP, switching technologies including VLANs and STP, and the ability to configure and troubleshoot CISCO devices using CLI and SNMP.
Successful candidates demonstrate a thorough understanding of network management, IP addressing, subnetting, and the configuration of virtual LANs and Quality of Service (QoS).

Technical Support Test
Our Technical Support Test measures a candidate's understanding of IT infrastructure support, including operating systems, networking, and hardware/software troubleshooting.
This test covers a range of topics from networking concepts to IT service protocols, database management, and scripting languages like Python and Bash. It also evaluates incident reporting, data backup procedures, and customer service skills.
Candidates who excel in this test are adept at problem-solving and critical thinking, essential for handling real-world technical support scenarios.
Cyber Security Assessment Test
Our Cyber Security Assessment Test focuses on evaluating candidates' knowledge in cybersecurity, including understanding of network security, cyber attacks, and cryptography.
The test examines abilities to detect and mitigate security risks such as SQL injections and malware, and to implement cybersecurity defenses like DDoS protection, firewalls, and VPNs.
High-scoring candidates will show proficiency in setting up and managing cybersecurity measures, risk assessments, and penetration testing.
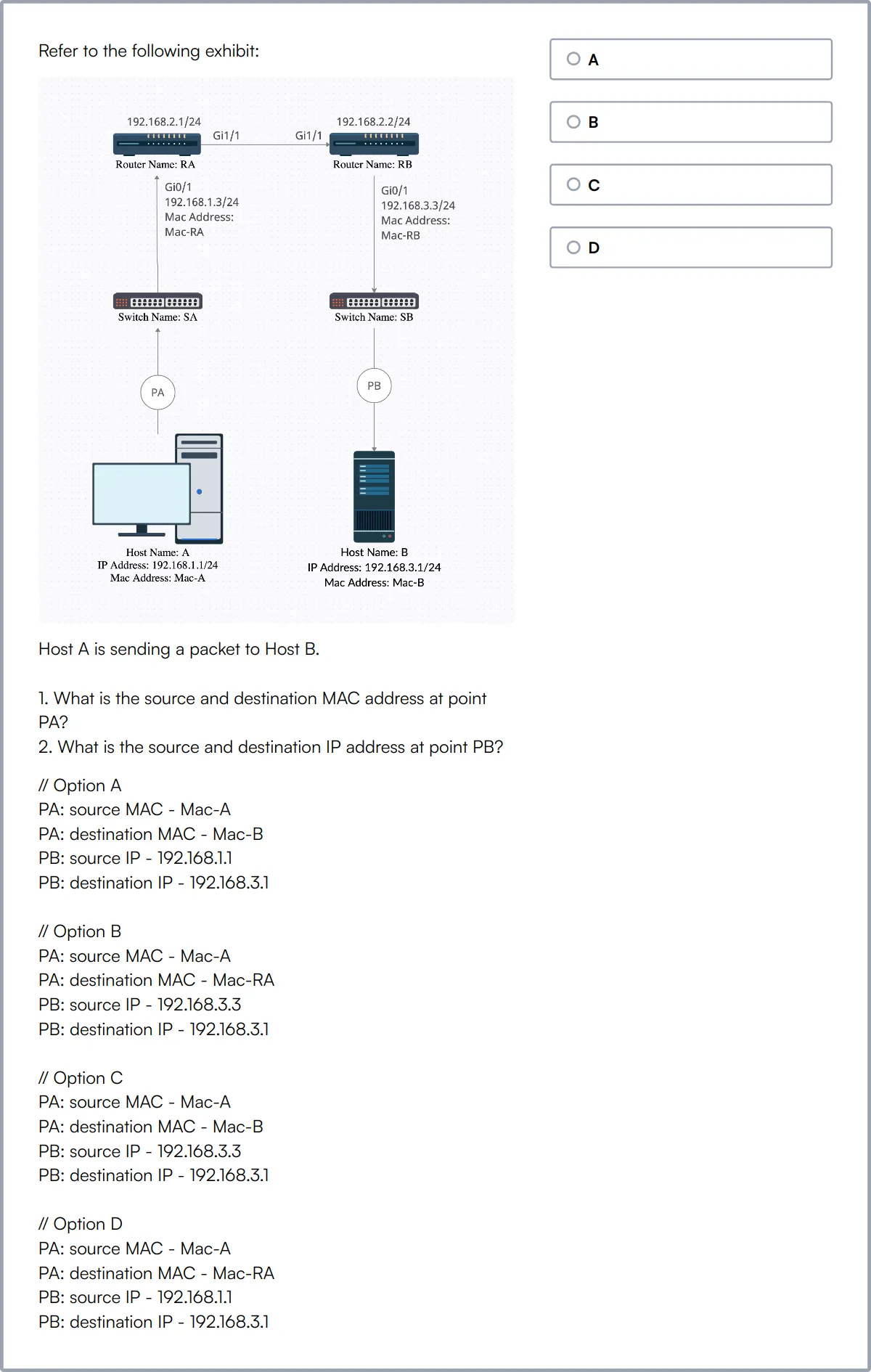
Network Engineer Online Test
Our Network Engineer Online Test assesses candidates on their technical knowledge and practical skills in network design, management, and troubleshooting.
The test evaluates proficiency in network protocols, security, IP addressing, subnetting, as well as routing and switching techniques. It also covers network performance optimization and wireless networking.
Candidates proficient in this test are capable of designing, implementing, and maintaining complex network infrastructures and resolving network issues effectively.
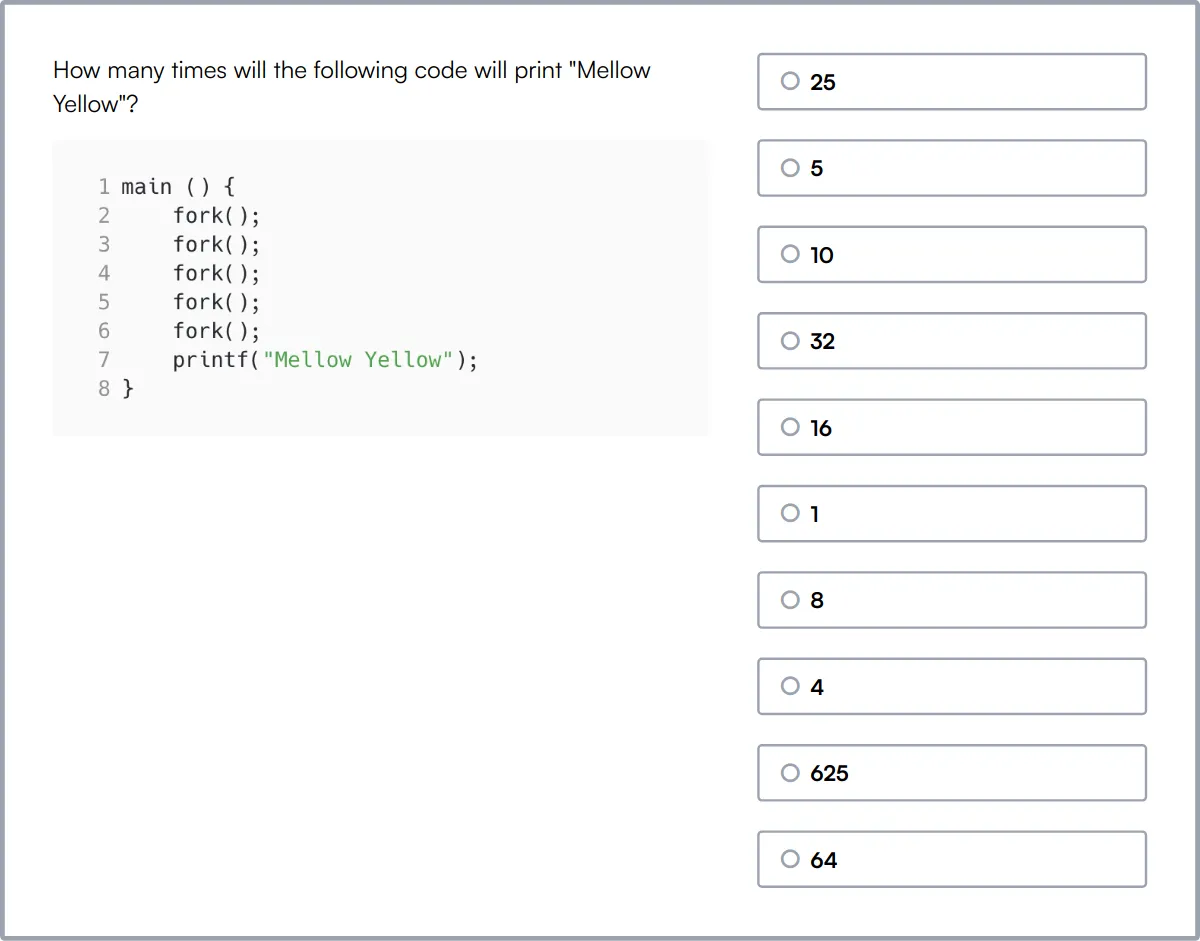
Cloud Computing Online Test
Our Cloud Computing Online Test assesses a candidate's understanding of cloud computing concepts, including cloud service and deployment models, virtualization, and cloud security.
This test evaluates knowledge in managing cloud storage, database management, cloud networking, and the use of cloud orchestration and automation tools.
Successful candidates demonstrate a strong grasp of scalability and elasticity in cloud environments, crucial for managing modern cloud infrastructures.
Summary: The 7 key Network Engineer skills and how to test for them
| Network Engineer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Network Configuration | Evaluate the ability to set up and manage network devices. |
| 2. Troubleshooting | Assess problem-solving skills in identifying and resolving network issues. |
| 3. Security Protocols | Check knowledge of implementing and maintaining network security measures. |
| 4. Routing and Switching | Gauge proficiency in configuring and managing routers and switches. |
| 5. Network Monitoring | Determine capability in using tools to monitor network performance. |
| 6. Wireless Networking | Evaluate skills in setting up and managing wireless networks. |
| 7. Cloud Networking | Assess experience with cloud-based network services and infrastructure. |
Network Engineer Online Test
Network Engineer skills FAQs
What are the key skills required for a Network Engineer?
Network Engineers should be proficient in network configuration, troubleshooting, and monitoring. They also need to understand security protocols, routing and switching, wireless and cloud networking, and disaster recovery.
How can recruiters assess the troubleshooting skills of a Network Engineer?
Recruiters can assess troubleshooting skills by presenting candidates with common network issues and asking them to outline their approach to solving them. Scenario-based questions or practical tests during interviews can be very effective.
What is the importance of scripting knowledge for Network Engineers?
Scripting automates repetitive tasks and helps in managing network configurations more efficiently. Knowledge of scripting languages like Python or PowerShell is beneficial for streamlining network operations.
Why is knowledge of cloud networking important for modern Network Engineers?
With many businesses moving to cloud-based solutions, understanding cloud networking is necessary for designing, implementing, and maintaining network infrastructure in cloud environments, ensuring scalability and security.
How do Network Engineers use Quality of Service (QoS) in their work?
QoS is used by Network Engineers to prioritize network traffic, ensuring that critical applications, such as VoIP and video conferencing, receive the necessary bandwidth and performance levels to function effectively.
What role does disaster recovery play in the responsibilities of a Network Engineer?
Network Engineers design and implement disaster recovery plans to ensure network availability and data integrity in case of hardware failures or other disruptions. This involves regular backups and failover mechanisms.
How can recruiters verify a candidate's expertise in network security protocols?
Recruiters can verify a candidate's network security expertise by asking about their experience with implementing security measures, familiarity with security protocols, and their approach to network security challenges.
What should Network Engineers know about IPv6?
Network Engineers should understand IPv6 to address the limitations of IPv4, including the larger address space, improved routing and autoconfiguration capabilities, and enhanced security features.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



