Manufacturing engineers play a key role in designing, implementing, and improving manufacturing processes. They ensure that production lines run smoothly, efficiently, and safely, contributing to the overall quality and cost-effectiveness of the products.
Skills required for a manufacturing engineer include a strong understanding of manufacturing processes, proficiency in computer-aided design (CAD) software, and knowledge of quality control principles. Additionally, problem-solving abilities and effective communication are crucial for success in this role.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Manufacturing Engineer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 9 essential Manufacturing Engineer skills, 11 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
9 fundamental Manufacturing Engineer skills and traits
The best skills for Manufacturing Engineers include CAD Software Proficiency, Process Optimization, Material Science, Quality Control, Lean Manufacturing, Project Management, Automation Systems, Statistical Analysis and Technical Documentation.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 essential skills of a Manufacturing Engineer.
CAD Software Proficiency
A manufacturing engineer must be adept at using CAD software to design and modify parts and assemblies. This skill is crucial for creating detailed 3D models and technical drawings that guide the manufacturing process.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Manufacturing Engineer Job Description.
Process Optimization
Understanding and improving manufacturing processes is key. Engineers use this skill to identify inefficiencies, reduce waste, and enhance productivity, ensuring that production runs smoothly and cost-effectively.
Material Science
Knowledge of material properties and behaviors is essential. This helps in selecting the right materials for different applications, ensuring durability, performance, and cost-effectiveness in the final product.
Quality Control
Implementing and maintaining quality control measures ensures that products meet specified standards. This involves regular inspections, testing, and the use of statistical methods to monitor and improve quality.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean principles focus on minimizing waste without sacrificing productivity. A manufacturing engineer uses these principles to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
Project Management
Managing projects from conception to completion requires strong organizational skills. This includes planning, scheduling, resource allocation, and risk management to ensure timely and successful project delivery.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Project Manager Job Description.
Automation Systems
Familiarity with automation technologies is increasingly important. Engineers use this skill to design and implement automated systems that enhance production speed, accuracy, and consistency.
Statistical Analysis
Using statistical tools to analyze data helps in making informed decisions. This skill is used to identify trends, solve problems, and improve processes based on empirical evidence.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Technical Documentation
Creating clear and detailed technical documents is crucial. This includes writing manuals, process instructions, and reports that communicate complex information effectively to various stakeholders.
11 secondary Manufacturing Engineer skills and traits
The best skills for Manufacturing Engineers include Cost Estimation, Supply Chain Management, Root Cause Analysis, Regulatory Compliance, Environmental Sustainability, Ergonomics, Vendor Management, Data Analysis, Technical Sales Support, Prototyping and Risk Assessment.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 11 secondary skills of a Manufacturing Engineer.
Cost Estimation
Accurately estimating costs for materials, labor, and overhead is important for budgeting and financial planning. This helps in setting realistic project budgets and pricing strategies.
Supply Chain Management
Understanding the supply chain is essential for ensuring timely delivery of materials and components. This involves coordinating with suppliers, managing inventory, and optimizing logistics.
Root Cause Analysis
Identifying the root causes of defects or failures is key to preventing recurrence. This involves systematic investigation and problem-solving techniques to address underlying issues.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensuring that manufacturing processes and products comply with industry regulations and standards is critical. This involves staying updated with relevant laws and guidelines.
Environmental Sustainability
Incorporating sustainable practices into manufacturing processes helps reduce environmental impact. This includes waste reduction, energy efficiency, and the use of eco-friendly materials.
Ergonomics
Designing workspaces and processes that enhance worker comfort and safety is important. This helps in reducing the risk of injuries and improving overall productivity.
Vendor Management
Effectively managing relationships with vendors ensures a reliable supply of quality materials and components. This involves negotiation, performance evaluation, and contract management.
Data Analysis
Analyzing production data helps in identifying trends and making data-driven decisions. This skill is used to optimize processes, improve quality, and increase efficiency.
Technical Sales Support
Providing technical support to the sales team helps in addressing customer queries and requirements. This involves explaining technical details and ensuring that products meet customer needs.
Prototyping
Creating prototypes is an important step in product development. This allows for testing and validation of designs before full-scale production, ensuring that the final product meets specifications.
Risk Assessment
Identifying and mitigating risks in the manufacturing process is crucial for preventing disruptions. This involves evaluating potential hazards and implementing measures to minimize their impact.
How to assess Manufacturing Engineer skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a Manufacturing Engineer involves more than just glancing at their resume. While academic qualifications and previous job roles provide some insights, they do not fully reveal a candidate's hands-on capabilities in areas like CAD software proficiency, process optimization, or quality control.
To truly understand whether a candidate will excel in a manufacturing environment, it's necessary to evaluate their practical skills and ability to apply theoretical knowledge. This is where skills assessments come into play. By using targeted tests, you can measure a candidate's proficiency in critical areas such as material science, lean manufacturing, and automation systems.
Adaface assessments offer a tailored approach to evaluating the diverse competencies required in manufacturing engineering. From testing knowledge in statistical analysis to understanding technical documentation, these assessments help streamline the hiring process, ensuring you find the right fit for your team. With Adaface, you can achieve a 85% reduction in screening time.
Let’s look at how to assess Manufacturing Engineer skills with these 6 talent assessments.
SOLID, Technical Aptitude & Coding Online Test
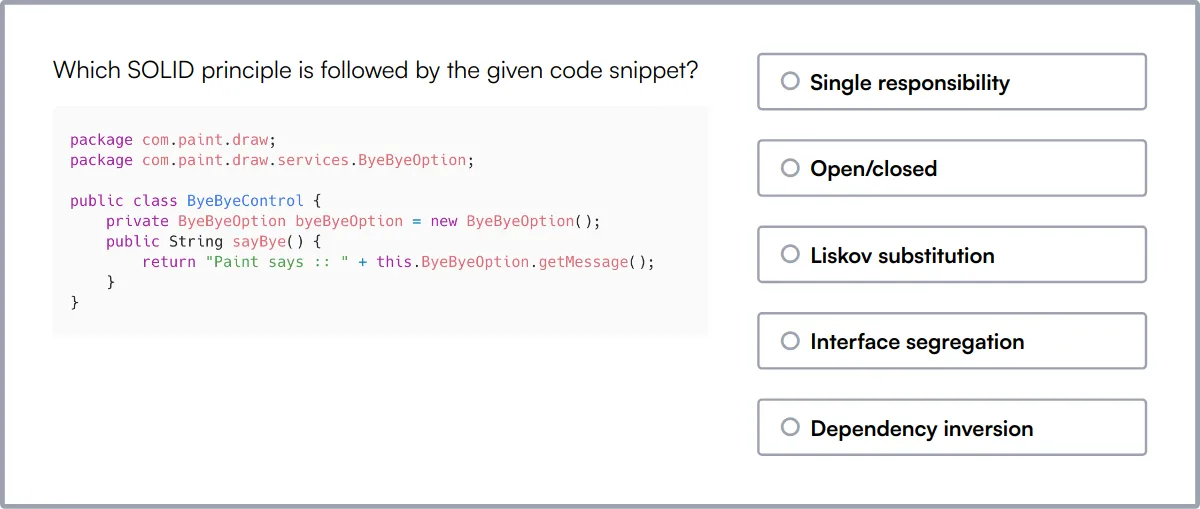
The SOLID, Technical Aptitude & Coding Online Test evaluates candidates on their understanding of software design principles based on SOLID principles. This test is important for assessing a candidate's ability to design and implement software systems using best practices.
The test covers SOLID Principles, Object Oriented Design, Technical Aptitude, and Data Structures. It includes scenario-based MCQs that assess knowledge of Single Responsibility, Open/Closed, Liskov Substitution, Interface Segregation, and Dependency Inversion principles. Additionally, it evaluates familiarity with design patterns, refactoring techniques, code smells, and anti-patterns.
Successful candidates demonstrate a strong grasp of software design principles and the ability to apply them in real-world scenarios. They also show proficiency in identifying and addressing code smells and anti-patterns.
Loadrunner Online Test
The Loadrunner Online Test evaluates a candidate's knowledge and skills in using Loadrunner, a performance testing tool for web applications. This test is crucial for assessing a candidate's ability to ensure the performance and scalability of web applications.
The test covers Loadrunner basics, Scripting and scenarios, Load testing concepts, Performance monitoring and analysis, Script enhancement and customization, Parameterization and correlation, Think time and pacing, Response time and throughput, Error handling and debugging, and Test execution and result analysis.
Candidates who perform well on this test demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of performance testing and the ability to effectively use Loadrunner to identify and resolve performance issues in web applications.
QA Engineer Test
The QA Engineer Test uses scenario-based MCQs to evaluate candidates on their understanding of various testing methodologies and test automation frameworks. This test is essential for assessing a candidate's ability to ensure the quality and reliability of software products.
The test covers Quality Assurance (QA), Testing Fundamentals, Test Design Techniques, Software Life Cycle, QA Programming, Program Testing, Selenium fundamentals, and Linux fundamentals. It includes questions on regression testing, test reporting, documentation, and risk assessment.
High-scoring candidates demonstrate proficiency in test planning and execution, bug tracking, and the use of test automation tools like Selenium. They also show a solid understanding of the software life cycle and the ability to perform risk assessments.
Project Management Test
The Project Management Test assesses a candidate's ability to plan and execute projects from conception to implementation. This test is important for evaluating a candidate's project management skills and their ability to deliver projects on time and within budget.
The test covers Cost and budget estimation, Situational judgement, Understanding of key project roles and stages, Designing a project plan, Resolving issues and handling changes, Managing and controlling resources, Stakeholder management, Prioritizing tasks in real-time, Basics of agile project management and Scrum, Basics of traditional (waterfall) project management, Risk analysis, and Creating and analyzing project reports.
Candidates who excel in this test demonstrate strong project management skills, including the ability to manage resources, handle changes, and communicate effectively with stakeholders. They also show proficiency in both agile and traditional project management methodologies.

Cucumber Test
The Cucumber Testing Online Test uses scenario-based MCQs to evaluate candidates on their knowledge of the Cucumber framework and its use in BDD (Behavior-Driven Development) testing. This test is important for assessing a candidate's ability to create and execute automated tests using Cucumber.
The test covers Cucumber - Development, Cucumber - Reports, Cucumber - Running tests, Cucumber - Debugging, Cucumber - Command line, and Advance features of Cucumber. It evaluates proficiency in creating and executing feature files, writing step definitions, and understanding Gherkin syntax.
Successful candidates demonstrate a strong understanding of BDD principles and the ability to use Cucumber to automate tests effectively. They also show proficiency in debugging and generating reports using the Cucumber framework.
Statistics Test
The Statistics Online Test evaluates a candidate's understanding and proficiency in statistical concepts and analysis. This test is crucial for assessing a candidate's ability to analyze and interpret data effectively.
The test covers Statistics Fundamentals, Inference: p-values and confidence intervals, Data Sampling, Regression, Sampling Distributions, Exploratory Data Analysis, Non-parametric statistics, Probability, and Data Analysis.
Candidates who perform well on this test demonstrate a strong grasp of statistical methods and the ability to apply them in real-world scenarios. They also show proficiency in data analysis and the ability to draw meaningful insights from data.
Summary: The 9 key Manufacturing Engineer skills and how to test for them
| Manufacturing Engineer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. CAD Software Proficiency | Evaluate ability to design and modify detailed engineering drawings. |
| 2. Process Optimization | Assess skills in improving manufacturing processes for better efficiency. |
| 3. Material Science | Check understanding of material properties and their applications in manufacturing. |
| 4. Quality Control | Gauge capability to maintain and improve product quality standards. |
| 5. Lean Manufacturing | Determine proficiency in minimizing waste and maximizing productivity. |
| 6. Project Management | Evaluate skills in planning, executing, and closing engineering projects. |
| 7. Automation Systems | Assess knowledge in implementing and managing automated manufacturing systems. |
| 8. Statistical Analysis | Check ability to analyze data for process improvements and decision-making. |
| 9. Technical Documentation | Gauge proficiency in creating clear and comprehensive technical documents. |
Backend Engineer Online Test
Manufacturing Engineer skills FAQs
What are the key CAD software skills required for a Manufacturing Engineer?
Manufacturing Engineers should be proficient in using CAD software like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, or CATIA. They need to create detailed designs, understand geometric dimensions and tolerances, and modify designs based on feedback.
How can you assess a candidate's expertise in process optimization?
To evaluate a candidate's process optimization skills, present them with a scenario that involves streamlining a manufacturing process. Ask them to identify inefficiencies and propose improvements, focusing on their approach to reducing waste and increasing productivity.
What is the importance of material science knowledge in manufacturing engineering?
Understanding material science is crucial for Manufacturing Engineers as it helps them select the right materials based on durability, cost, and performance requirements. This knowledge is key to ensuring product quality and sustainability.
How does lean manufacturing contribute to a Manufacturing Engineer's role?
Lean manufacturing principles help Manufacturing Engineers reduce waste and improve efficiency in production processes. Familiarity with lean tools and techniques like Kaizen, 5S, and value stream mapping is beneficial.
What should a Manufacturing Engineer know about quality control?
A Manufacturing Engineer must understand quality control processes, including statistical process control, inspection techniques, and ISO standards. They should be able to design and implement QC systems that minimize defects and ensure product quality.
How can project management skills be assessed during the hiring process?
Assess project management skills by asking candidates about their experience with planning, executing, and leading projects. Discuss specific tools they've used, such as Gantt charts or Agile methodologies, and how they handle project challenges.
What role does risk assessment play in manufacturing engineering?
Risk assessment is key to preempting potential issues in manufacturing processes. Engineers must evaluate and mitigate risks related to safety, production delays, and cost overruns to ensure smooth operations and project success.
Why is vendor management important for Manufacturing Engineers?
Effective vendor management ensures that materials and components meet quality standards and are delivered on time. Manufacturing Engineers need to negotiate with suppliers, manage contracts, and maintain strong professional relationships.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



