Kubernetes engineers are responsible for managing and orchestrating containerized applications. They ensure that applications run smoothly in a distributed environment, handling tasks such as deployment, scaling, and maintenance.
Skills required for a Kubernetes engineer include proficiency in containerization technologies like Docker, knowledge of Kubernetes architecture, and experience with cloud platforms. Additionally, they need strong problem-solving abilities and effective communication skills.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Kubernetes Engineer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 9 essential Kubernetes Engineer skills, 11 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
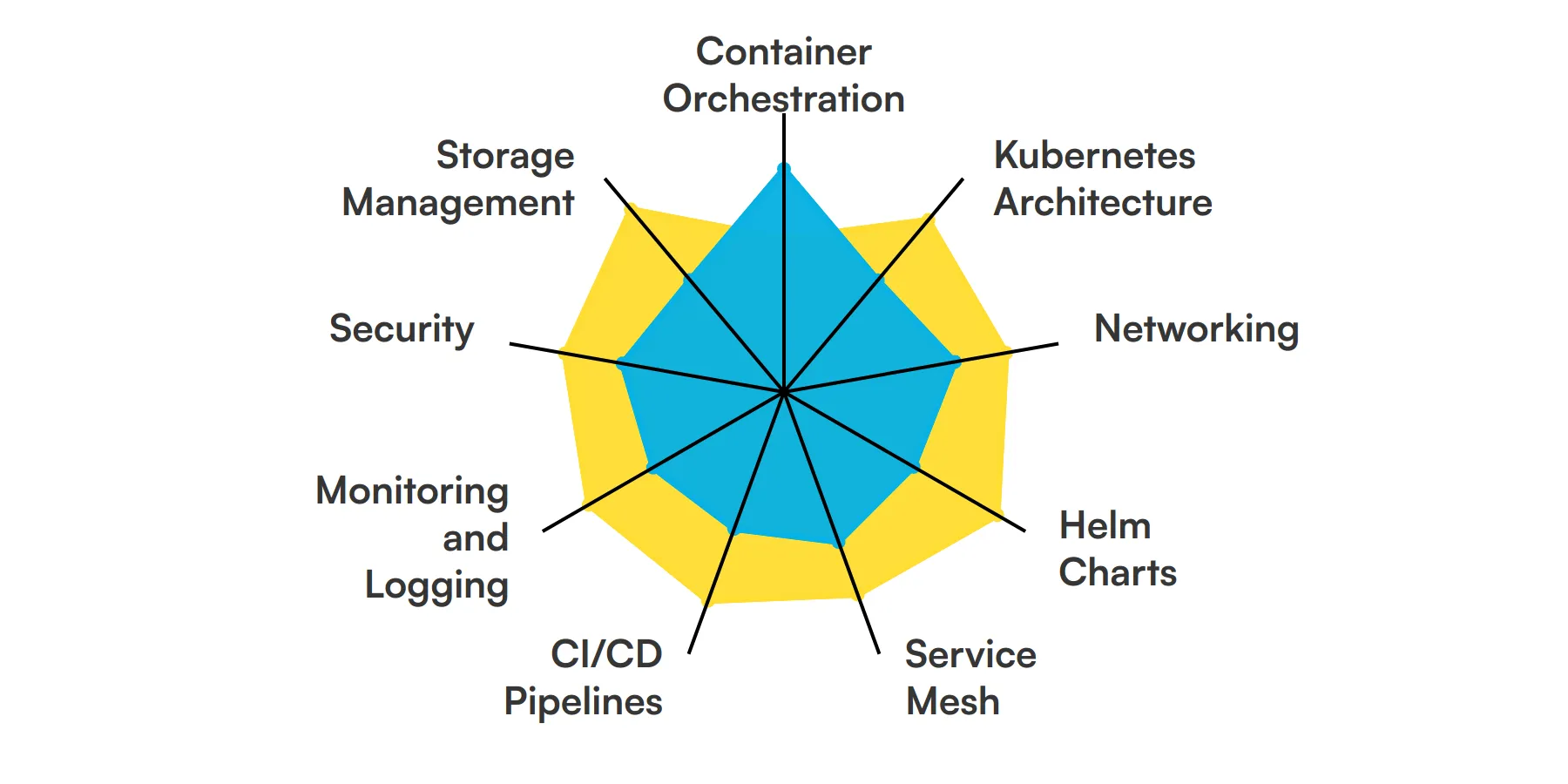
9 fundamental Kubernetes Engineer skills and traits
The best skills for Kubernetes Engineers include Container Orchestration, Kubernetes Architecture, Networking, Helm Charts, Service Mesh, CI/CD Pipelines, Monitoring and Logging, Security and Storage Management.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 essential skills of a Kubernetes Engineer.
Container Orchestration
Kubernetes engineers need to master container orchestration to manage and automate the deployment, scaling, and operations of application containers. This skill ensures that applications run smoothly across different environments.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Kubernetes Engineer Job Description.
Kubernetes Architecture
Understanding the architecture of Kubernetes is crucial for engineers to design and implement efficient cluster setups. This includes knowledge of components like the API server, etcd, and kubelet.
Networking
Networking skills are essential for configuring and managing the communication between containers and services within a Kubernetes cluster. Engineers need to handle network policies, service discovery, and load balancing.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Helm Charts
Helm charts simplify the deployment of applications on Kubernetes by packaging them into reusable templates. Engineers use Helm to manage complex applications and ensure consistent deployments.
Service Mesh
A service mesh, like Istio, helps manage microservices communication within Kubernetes. Engineers use it to handle traffic management, security, and observability, ensuring reliable service-to-service interactions.
CI/CD Pipelines
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines are vital for automating the deployment process. Kubernetes engineers set up and maintain these pipelines to ensure rapid and reliable application updates.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Devops Engineer Job Description.
Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring and logging are key to maintaining the health of a Kubernetes cluster. Engineers use tools like Prometheus and Grafana to track performance metrics and troubleshoot issues effectively.
Security
Security skills are necessary to protect Kubernetes clusters from vulnerabilities. Engineers implement role-based access control (RBAC), network policies, and secrets management to secure the environment.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Storage Management
Managing storage in Kubernetes involves configuring persistent volumes and storage classes. Engineers ensure that applications have access to the necessary storage resources for data persistence.
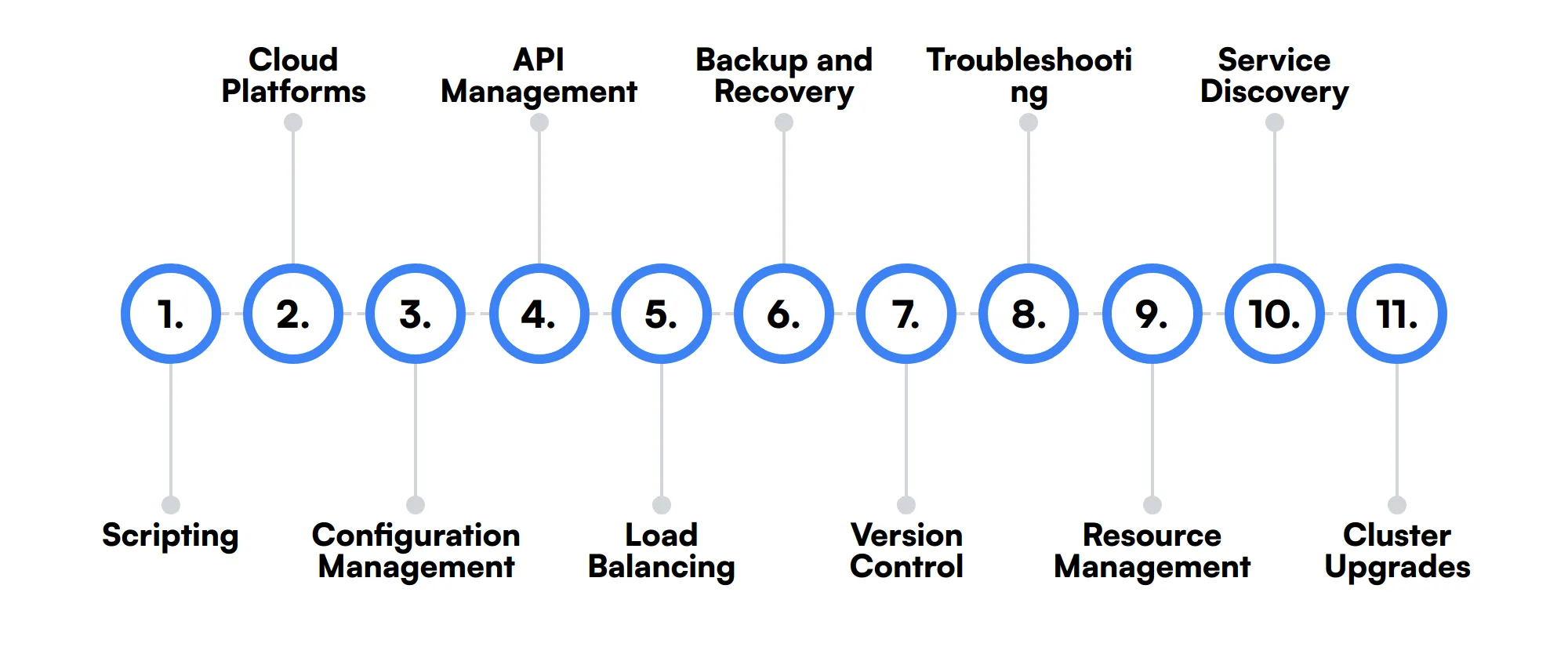
11 secondary Kubernetes Engineer skills and traits
The best skills for Kubernetes Engineers include Scripting, Cloud Platforms, Configuration Management, API Management, Load Balancing, Backup and Recovery, Version Control, Troubleshooting, Resource Management, Service Discovery and Cluster Upgrades.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 11 secondary skills of a Kubernetes Engineer.
Scripting
Scripting skills, particularly in languages like Bash or Python, help engineers automate repetitive tasks and streamline cluster management.
Cloud Platforms
Familiarity with cloud platforms like AWS, GCP, or Azure is beneficial for deploying and managing Kubernetes clusters in a cloud environment.
Configuration Management
Tools like Ansible or Terraform are used for configuration management and infrastructure as code, aiding in the consistent setup of Kubernetes environments.
API Management
Understanding API management helps engineers integrate and manage APIs within the Kubernetes ecosystem, ensuring smooth communication between services.
Load Balancing
Load balancing skills are important for distributing traffic across multiple services and ensuring high availability and reliability of applications.
Backup and Recovery
Knowledge of backup and recovery processes ensures that data and applications can be restored quickly in case of failures or disasters.
Version Control
Proficiency with version control systems like Git is essential for managing code changes and collaborating with other team members.
Troubleshooting
Strong troubleshooting skills enable engineers to diagnose and resolve issues within the Kubernetes cluster, ensuring minimal downtime.
Resource Management
Effective resource management involves optimizing the use of CPU, memory, and storage to ensure the efficient operation of the Kubernetes cluster.
Service Discovery
Service discovery skills help in configuring and managing how services find and communicate with each other within the Kubernetes environment.
Cluster Upgrades
Knowledge of cluster upgrade processes ensures that Kubernetes clusters are kept up-to-date with the latest features and security patches.
How to assess Kubernetes Engineer skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a Kubernetes Engineer involves more than just glancing at their resume. It requires a deep dive into their practical abilities in managing complex Kubernetes environments. Understanding their proficiency in container orchestration, Kubernetes architecture, and other key areas is essential to determine if they're the right fit for your team.
Traditional interviews might not fully reveal a candidate's capabilities in areas like networking, Helm charts, service mesh, CI/CD pipelines, monitoring and logging, security, and storage management. This is where skills-based assessments come into play. By using targeted tests, you can measure a candidate's practical skills and problem-solving abilities directly related to your needs.
For an effective and streamlined screening process, consider utilizing Adaface assessments. These tests are designed to reflect real-world problems, helping you identify candidates who are truly proficient in Kubernetes. By integrating these assessments into your hiring process, you can achieve a significant reduction in screening time and improve the quality of your hires.
Let’s look at how to assess Kubernetes Engineer skills with these 5 talent assessments.
Kubernetes Online Test
Our Kubernetes Online Test evaluates candidates on their comprehensive understanding of Kubernetes, from architecture and containerization to security and scaling.
The test assesses knowledge in areas such as Kubernetes deployments, services, networking, and troubleshooting, focusing on practical applications and real-world scenarios.
Successful candidates demonstrate proficiency in managing Kubernetes environments, including effective scaling, load balancing, and ensuring robust security measures.
Network Engineer Online Test
The Network Engineer Online Test measures candidates' expertise in network design, security, and troubleshooting, essential for maintaining robust networking infrastructures.
This test covers critical aspects like routing, switching, network protocols, and performance optimization, emphasizing problem-solving skills in network management.
Candidates excelling in this test are adept at designing and implementing complex network solutions that ensure optimal performance and security.
Azure DevOps Test
Our Azure DevOps Test is designed to assess a candidate's skills in Azure environments and their application of DevOps practices.
The test evaluates proficiency in cloud computing, Azure infrastructure services, and continuous integration and delivery pipelines.
High-scoring candidates will have demonstrated strong capabilities in implementing and managing DevOps solutions using Azure, enhancing operational efficiency and deployment cycles.
Elasticsearch Test
The Elasticsearch Test gauges a candidate's ability to configure, manage, and scale Elasticsearch environments effectively.
It focuses on data indexing, search queries, cluster management, and performance optimization, crucial for handling large datasets and complex search operations.
Candidates proficient in this test can effectively manage and troubleshoot Elasticsearch clusters, ensuring high availability and performance.
Cyber Security Assessment Test
Our Cyber Security Assessment Test evaluates a candidate's understanding of network security, cryptography, and various cyber threats.
The test addresses key security concepts and practices such as network defenses, risk assessments, and the mitigation of cybersecurity attacks.
Successful candidates will have demonstrated the ability to implement comprehensive security measures and respond effectively to cyber threats.
Summary: The 9 key Kubernetes Engineer skills and how to test for them
| Kubernetes Engineer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Container Orchestration | Evaluate ability to manage and deploy containerized applications at scale. |
| 2. Kubernetes Architecture | Assess understanding of Kubernetes components and their interactions. |
| 3. Networking | Check knowledge of Kubernetes networking and service discovery. |
| 4. Helm Charts | Gauge proficiency in using Helm for Kubernetes application deployment. |
| 5. Service Mesh | Determine experience with service mesh for microservices communication. |
| 6. CI/CD Pipelines | Evaluate skills in integrating Kubernetes with CI/CD tools. |
| 7. Monitoring and Logging | Assess capability to implement monitoring and logging in Kubernetes. |
| 8. Security | Check understanding of Kubernetes security best practices and policies. |
| 9. Storage Management | Evaluate knowledge of managing persistent storage in Kubernetes. |
Kubernetes Online Test
Kubernetes Engineer skills FAQs
What are the key skills required for a Kubernetes Engineer?
A Kubernetes Engineer should have skills in container orchestration, Kubernetes architecture, networking, Helm charts, service mesh, CI/CD pipelines, monitoring and logging, security, storage management, scripting, cloud platforms, configuration management, API management, load balancing, backup and recovery, version control, troubleshooting, resource management, service discovery, and cluster upgrades.
How can recruiters assess a candidate's knowledge in Kubernetes architecture?
Recruiters can assess a candidate's knowledge in Kubernetes architecture by asking them to explain the components of a Kubernetes cluster, such as the master node, worker nodes, etcd, kube-apiserver, kube-scheduler, and kube-controller-manager.
What questions can be asked to evaluate a candidate's experience with Helm charts?
Ask candidates to describe how they have used Helm charts to manage Kubernetes applications, including creating, versioning, and deploying charts. You can also ask them to explain the structure of a Helm chart.
How do you test a candidate's proficiency in Kubernetes networking?
To test proficiency in Kubernetes networking, ask candidates to explain how Kubernetes handles networking, including concepts like Services, Ingress, Network Policies, and CNI plugins. Practical tasks like setting up a network policy can also be useful.
What are some ways to assess a candidate's skills in CI/CD pipelines for Kubernetes?
Assess skills in CI/CD pipelines by asking candidates to describe their experience with tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or Argo CD. Request examples of how they have implemented CI/CD pipelines for Kubernetes deployments.
How can you evaluate a candidate's ability to manage Kubernetes security?
Evaluate Kubernetes security skills by asking about their experience with Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), network policies, secrets management, and security scanning tools. Practical scenarios like securing a Kubernetes cluster can also be useful.
What should you ask to gauge a candidate's troubleshooting skills in Kubernetes?
Gauge troubleshooting skills by presenting common issues such as pod failures, network connectivity problems, or resource constraints. Ask candidates to describe their approach to diagnosing and resolving these issues.
How do you assess a candidate's experience with Kubernetes monitoring and logging?
Assess experience with monitoring and logging by asking candidates to describe the tools they have used, such as Prometheus, Grafana, and ELK stack. Request examples of how they have set up monitoring and logging for Kubernetes clusters.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



