J2EE developers are the backbone of enterprise-level applications, ensuring robust, scalable, and secure solutions. They work on the server-side, managing the business logic and database interactions that power complex systems.
J2EE development skills include proficiency in Java, understanding of frameworks like Spring and Hibernate, and knowledge of web services. Additionally, skills such as problem-solving, teamwork, and effective communication are crucial for success in this role.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job J2EE Developer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 9 essential J2EE Developer skills, 11 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
9 fundamental J2EE Developer skills and traits
The best skills for J2EE Developers include Java Programming, Servlets and JSP, EJB, JDBC, JMS, XML, Web Services, Application Servers and Frameworks.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 essential skills of a J2EE Developer.
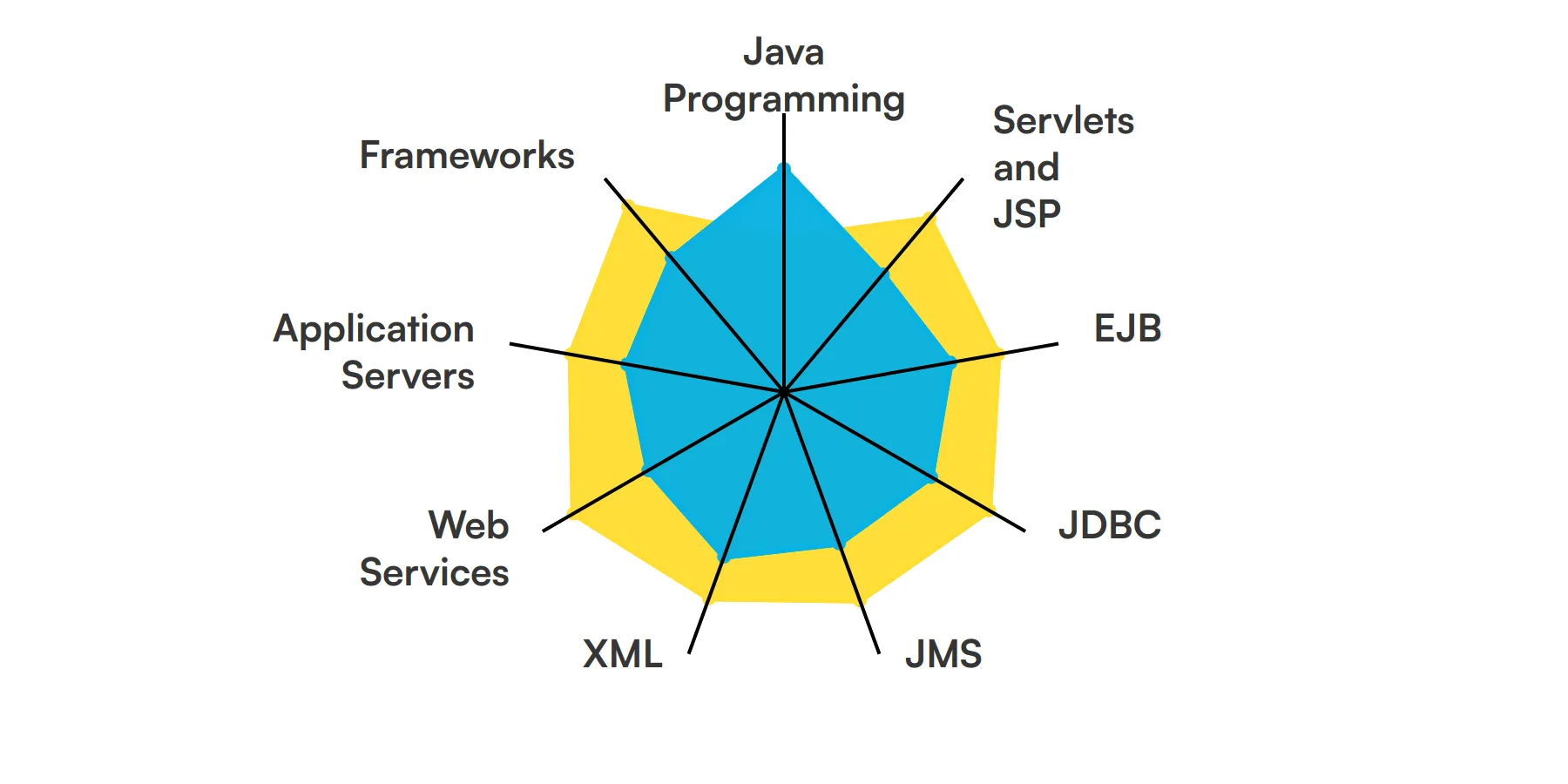
Java Programming
Java is the core language for J2EE development. A J2EE developer must be proficient in Java to build, maintain, and optimize enterprise-level applications. This includes understanding object-oriented programming principles and being able to write clean, efficient code.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Java Developer Job Description.
Servlets and JSP
Servlets and JavaServer Pages (JSP) are fundamental for creating dynamic web content in J2EE. A developer uses these technologies to handle client requests and generate responses, making them essential for building interactive web applications.
EJB
Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) are used for building scalable, transactional, and multi-user secure enterprise applications. A J2EE developer leverages EJB to manage business logic and ensure the application can handle complex transactions and operations.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
JDBC
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is crucial for database interaction. A J2EE developer uses JDBC to connect to databases, execute SQL queries, and manage data retrieval and updates, ensuring seamless data integration within the application.
JMS
Java Message Service (JMS) is used for messaging between different components of a J2EE application. A developer uses JMS to enable asynchronous communication, which is vital for building robust and scalable enterprise applications.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a J2EE Developer Job Description.
XML
XML is often used for data interchange and configuration in J2EE applications. A J2EE developer must be adept at parsing, generating, and manipulating XML to ensure smooth data exchange and configuration management.
Web Services
Web services are essential for enabling interoperability between different applications. A J2EE developer uses technologies like SOAP and REST to create and consume web services, facilitating communication between disparate systems.
Application Servers
Knowledge of application servers like Apache Tomcat, JBoss, or WebSphere is crucial. A J2EE developer deploys and manages applications on these servers, ensuring they run efficiently and securely in a production environment.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Frameworks
Familiarity with frameworks like Spring and Hibernate is important. These frameworks simplify development by providing tools for dependency injection, transaction management, and object-relational mapping, enhancing productivity and code quality.
11 secondary J2EE Developer skills and traits
The best skills for J2EE Developers include HTML/CSS, JavaScript, Version Control, Unit Testing, Build Tools, Security, Performance Tuning, Agile Methodologies, Cloud Platforms, Microservices and DevOps.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 11 secondary skills of a J2EE Developer.
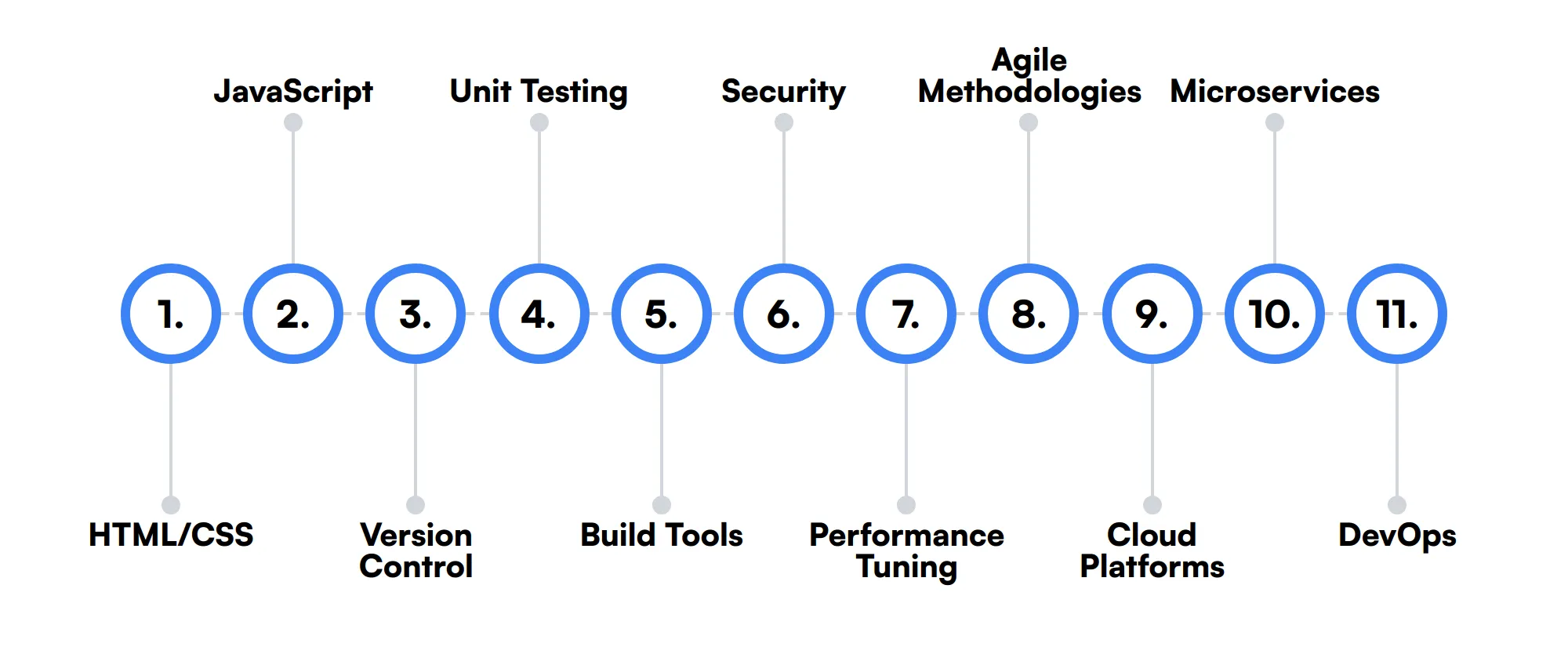
HTML/CSS
Basic knowledge of HTML and CSS is useful for front-end development. While a J2EE developer focuses on back-end logic, understanding front-end technologies helps in creating cohesive and user-friendly web applications.
JavaScript
JavaScript is essential for adding interactivity to web applications. A J2EE developer benefits from knowing JavaScript to enhance the user experience and integrate front-end and back-end functionalities seamlessly.
Version Control
Proficiency with version control systems like Git is important for managing code changes and collaborating with other developers. It ensures that a J2EE developer can track progress, revert to previous states, and work efficiently in a team.
Unit Testing
Unit testing frameworks like JUnit are crucial for ensuring code quality. A J2EE developer uses these tools to write and run tests, catching bugs early and ensuring that the application behaves as expected.
Build Tools
Knowledge of build tools like Maven or Gradle is important for automating the build process. A J2EE developer uses these tools to manage project dependencies, compile code, and package applications for deployment.
Security
Understanding security principles and practices is vital for protecting applications from threats. A J2EE developer must be aware of common vulnerabilities and implement measures like encryption, authentication, and authorization to safeguard data.
Performance Tuning
Performance tuning involves optimizing application performance. A J2EE developer uses profiling tools and techniques to identify bottlenecks, improve response times, and ensure the application can handle high loads efficiently.
Agile Methodologies
Familiarity with Agile methodologies like Scrum or Kanban is beneficial for managing development processes. A J2EE developer working in an Agile environment can adapt to changes quickly and deliver high-quality software iteratively.
Cloud Platforms
Knowledge of cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud is increasingly important. A J2EE developer may deploy and manage applications in the cloud, leveraging cloud services for scalability, storage, and computing power.
Microservices
Understanding microservices architecture is useful for building modular and scalable applications. A J2EE developer can design and implement microservices to break down complex applications into manageable, independent services.
DevOps
Familiarity with DevOps practices and tools like Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes is beneficial. A J2EE developer can automate deployment, monitor application performance, and ensure continuous integration and delivery.
How to assess J2EE Developer skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a J2EE Developer involves more than just glancing at their resume. It's about understanding how well they can apply their knowledge of Java, frameworks, and various J2EE technologies such as Servlets, JSP, EJB, and others in real-world scenarios.
While technical prowess in Java programming, handling application servers, and developing with EJB and JDBC are measurable, the subtler aspects like problem-solving with JMS, XML, and Web Services require a deeper look. This is where practical assessments come into play, offering a clear picture of a candidate's capabilities beyond theoretical knowledge.
To streamline this process and ensure you're bringing on board a developer who truly fits your project needs, consider utilizing Adaface assessments. These tests are designed to mirror actual job tasks, helping you achieve a 2x improvement in the quality of your hires while significantly cutting down on screening time.
Let’s look at how to assess J2EE Developer skills with these 6 talent assessments.
Java Online Test
Our Java Online Test evaluates candidates' knowledge of core Java concepts and advanced topics. This test is designed to assess a candidate's ability to code in Java through scenario-based and code-tracing questions.
The test covers Java syntax and semantics, web application programming, object-oriented programming, working with databases, data structures, collections framework, exception handling, multi-threading, functional programming with Lambdas & Streams API, and SOLID principles.
Successful candidates demonstrate a strong understanding of Java's core interfaces and implementations, such as List, Set, and Map, and show proficiency in concurrent programming and handling relational databases.
Java & Spring Online Test
Our Java & Spring Online Test evaluates candidates' ability to work with the Spring framework and their understanding of Java programming. This test includes scenario-based MCQs and a coding question to assess hands-on skills.
The test covers Java syntax and basics, object-oriented programming, working with databases, Spring framework basics, Spring bean lifecycle, Spring Security, dependency injection, AOP, RESTful web services, and database integration.
Candidates who perform well demonstrate a solid understanding of design patterns, testing, debugging, and software architecture, as well as proficiency in using Spring modules like Core, MVC, Security, and Boot.
EJB Online Test
Our EJB Online Test evaluates a candidate's knowledge and skills related to Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB). This test uses scenario-based multiple-choice questions to assess proficiency in EJB fundamentals and advanced topics.
The test covers EJB architecture, enterprise beans, session beans, message-driven beans, container-managed persistence, bean-managed persistence, EJB security, transactions, timer service, and interceptors.
High-scoring candidates show a deep understanding of EJB design patterns, best practices, distributed caching, clustering, and integrating EJB with other Java technologies like JPA and JMS.
Java & SQL Online Test
Our Java & SQL Online Test evaluates candidates on their ability to work with relational databases using Java. This test includes multiple-choice questions and a coding question to assess hands-on programming skills.
The test covers Java basics, object-oriented programming, exceptions, SQL basics, database design, querying and manipulating data, and Java Database Connectivity (JDBC).
Candidates who excel in this test demonstrate a strong understanding of relational databases, SQL queries, data modeling, and data manipulation using Java.
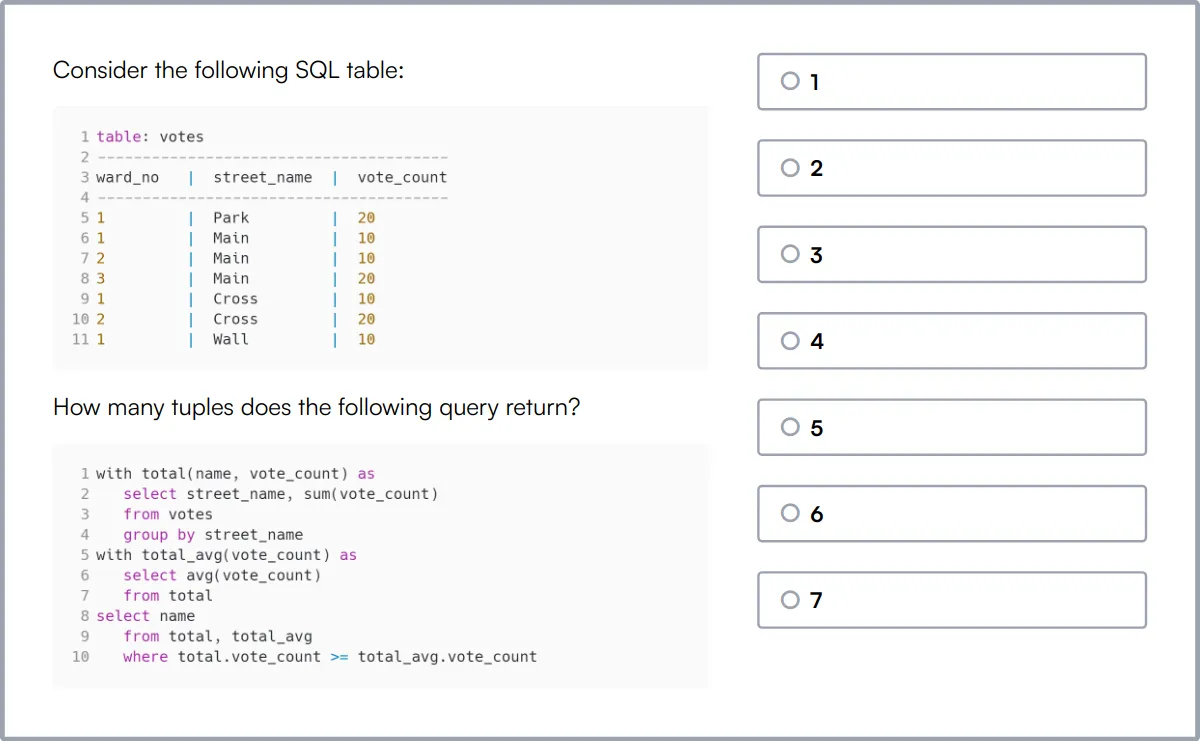
XML Web Services & XML Online Test
Our XML Web Services & XML Online Test evaluates candidates' proficiency in working with XML, a markup language widely used for data exchange in web applications. This test uses scenario-based MCQs to assess key skills.
The test covers XML compatibility, utilities, comments, images, validation, DTD, and linking.
Successful candidates demonstrate a strong understanding of XML syntax, validation, transformation using XSLT, schema design, document modeling, data binding, XPath expressions, and web service integration.
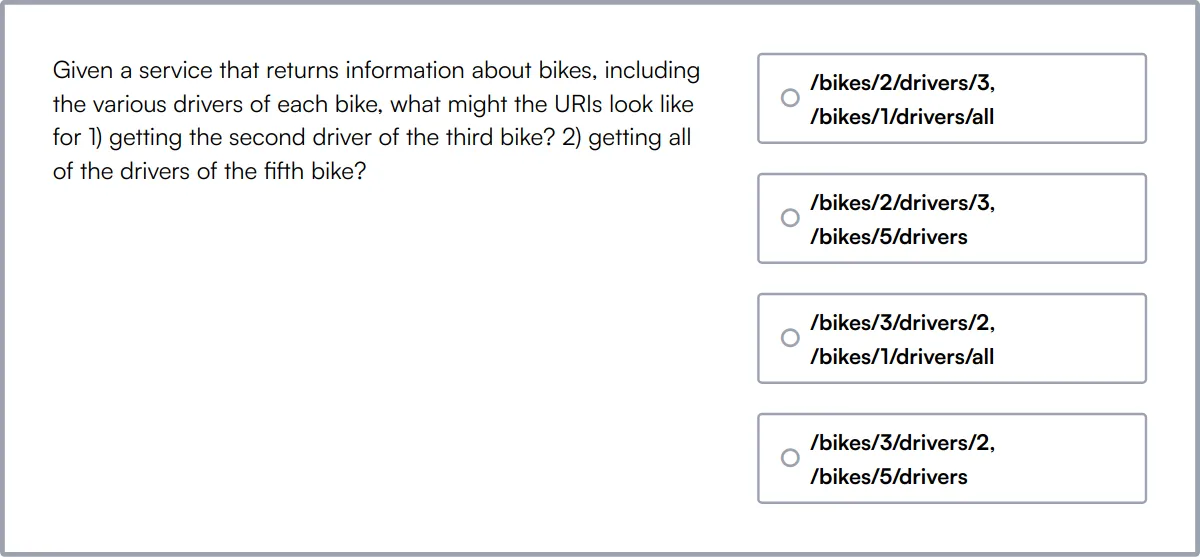
REST API Test
Our REST API Test evaluates a candidate's understanding of RESTful APIs and their ability to create, interact, and test them. This test includes multiple-choice questions and a coding question to assess hands-on skills.
The test covers REST API basics, API design, best practices, designing backend services, HTTP methods, status codes, authentication, and serialization formats.
Candidates who perform well demonstrate a strong understanding of REST principles, API integrations, and best practices for designing and testing RESTful APIs.
Summary: The 9 key J2EE Developer skills and how to test for them
| J2EE Developer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Java Programming | Evaluate developer's proficiency in Java language and object-oriented concepts. |
| 2. Servlets and JSP | Assess ability to handle web requests and generate dynamic content. |
| 3. EJB | Check understanding of enterprise JavaBeans for business logic implementation. |
| 4. JDBC | Test knowledge of Java database connectivity and SQL handling. |
| 5. JMS | Review proficiency in handling Java messaging services and integration. |
| 6. XML | Examine skills in XML parsing, manipulation, and data interchange. |
| 7. Web Services | Evaluate understanding of SOAP and RESTful service development. |
| 8. Application Servers | Assess deployment and management skills on servers like Tomcat or WebSphere. |
| 9. Frameworks | Check familiarity with Java frameworks like Spring or Hibernate. |
Blockchain Developer Test
J2EE Developer skills FAQs
What are the key skills to look for in a J2EE Developer?
Key skills include Java Programming, Servlets and JSP, EJB, JDBC, JMS, XML, Web Services, and Application Servers.
How can I assess a candidate's Java Programming skills?
Use coding tests and technical interviews to evaluate their understanding of Java syntax, OOP principles, and problem-solving abilities.
Why is knowledge of Servlets and JSP important for J2EE Developers?
Servlets and JSP are fundamental for building web applications in J2EE, enabling dynamic content generation and server-side processing.
What is the role of EJB in J2EE development?
EJB (Enterprise JavaBeans) is used for building scalable, transactional, and secure enterprise-level applications.
How do you evaluate a developer's experience with Application Servers?
Ask about their experience with servers like Apache Tomcat, JBoss, or WebSphere, and their ability to deploy and manage applications on these platforms.
What frameworks should a J2EE Developer be familiar with?
Common frameworks include Spring, Hibernate, and Struts. Assess their experience through project discussions and practical tests.
How important is knowledge of Agile Methodologies for a J2EE Developer?
Agile methodologies are important for collaborative and iterative development. Look for experience with Scrum or Kanban.
What tools are used for version control in J2EE development?
Git is the most commonly used version control tool. Assess their experience with branching, merging, and pull requests.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



