Information Architects play a crucial role in structuring the vast amount of information within an organization. They ensure that data is organized in a way that meets both user needs and business goals, making it easily accessible and usable.
Skills required for an Information Architect include a deep understanding of information science, user experience design, and data management. Additionally, strong analytical skills and the ability to communicate complex information clearly are essential.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Information Architect skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 9 essential Information Architect skills, 11 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
9 fundamental Information Architect skills and traits
The best skills for Information Architects include User Research, Wireframing, Information Organization, Content Auditing, Taxonomy Design, Prototyping, Usability Testing, Navigation Design and Content Strategy.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 essential skills of a Information Architect.
User Research
Understanding user needs and behaviors is key for an Information Architect. This skill involves conducting interviews, surveys, and usability tests to gather insights. These insights help in creating user-centered designs that improve the overall user experience.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a UX Researcher Job Description.
Wireframing
Wireframing is the process of creating a visual guide that represents the skeletal framework of a website or application. Information Architects use wireframes to plan the layout and structure, ensuring that the information is organized logically and is easy to navigate.
Information Organization
This skill involves categorizing and structuring information in a way that makes it easily accessible and understandable. Information Architects use this skill to create intuitive navigation systems and content hierarchies that enhance user experience.
Content Auditing
Content auditing involves evaluating existing content to determine its effectiveness and relevance. Information Architects use this skill to identify gaps, redundancies, and opportunities for improvement, ensuring that the content meets user needs and business goals.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Taxonomy Design
Designing a taxonomy involves creating a classification system that organizes content into categories and subcategories. Information Architects use this skill to ensure that users can find information quickly and easily, improving the overall usability of the system.
Prototyping
Prototyping involves creating interactive models of a website or application to test and refine design concepts. Information Architects use this skill to validate their designs with users and stakeholders, making necessary adjustments before final implementation.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Product Designer Job Description.
Usability Testing
Usability testing is the process of evaluating a product by testing it with real users. Information Architects use this skill to identify usability issues and gather feedback, which helps in refining the design to better meet user needs.
Navigation Design
Navigation design focuses on creating a system that allows users to move through a website or application easily. Information Architects use this skill to design menus, links, and other navigational elements that guide users to the information they need.
Content Strategy
Content strategy involves planning, creating, and managing content to achieve business objectives. Information Architects use this skill to ensure that the content is relevant, consistent, and aligned with user needs and organizational goals.
11 secondary Information Architect skills and traits
The best skills for Information Architects include SEO Knowledge, HTML/CSS, Analytics, Project Management, Collaboration, Accessibility, Content Management Systems, Visual Design, Technical Writing, Data Modeling and User Interface Design.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 11 secondary skills of a Information Architect.
SEO Knowledge
Understanding search engine optimization helps Information Architects ensure that content is discoverable by search engines. This skill involves using keywords, meta tags, and other techniques to improve search engine rankings.
HTML/CSS
Basic knowledge of HTML and CSS is useful for Information Architects to understand how their designs will be implemented. This skill helps in creating more realistic wireframes and prototypes.
Analytics
Analytics involves using data to measure the effectiveness of a website or application. Information Architects use this skill to track user behavior, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to improve the user experience.
Project Management
Project management skills help Information Architects coordinate with different teams and manage timelines. This skill ensures that projects are completed on time and meet the desired quality standards.
Collaboration
Collaboration involves working effectively with designers, developers, and other stakeholders. Information Architects use this skill to ensure that everyone is aligned and working towards the same goals.
Accessibility
Understanding accessibility ensures that websites and applications are usable by people with disabilities. Information Architects use this skill to design inclusive experiences that meet accessibility standards.
Content Management Systems
Familiarity with content management systems (CMS) helps Information Architects manage and organize digital content. This skill is useful for implementing and maintaining the information architecture.
Visual Design
While not the primary focus, having a sense of visual design helps Information Architects create more appealing and user-friendly interfaces. This skill complements their work in organizing and structuring information.
Technical Writing
Technical writing involves creating clear and concise documentation. Information Architects use this skill to write guidelines, user manuals, and other documentation that supports the information architecture.
Data Modeling
Data modeling involves creating a visual representation of data structures. Information Architects use this skill to design databases and other systems that store and organize information efficiently.
User Interface Design
Understanding user interface design helps Information Architects create more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces. This skill involves designing elements like buttons, forms, and icons that users interact with.
How to assess Information Architect skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of an Information Architect can be a challenging task. It's not just about knowing the tools and techniques, but also understanding how well they can apply these skills in real-world scenarios. From user research to navigation design, each skill plays a crucial role in creating a seamless user experience.
Traditional resumes and interviews might not give you the full picture of a candidate's abilities. This is where skills-based assessments come into play. By using targeted assessments, you can evaluate a candidate's proficiency in key areas like wireframing, content auditing, and usability testing.
For a more streamlined and effective hiring process, consider using Adaface assessments. These tests can help you achieve a 2x improved quality of hires and an 85% reduction in screening time. With Adaface, you can confidently assess the competencies of your potential Information Architects.
Let’s look at how to assess Information Architect skills with these 3 talent assessments.
UI/UX Design Test
Our UI/UX Design Test evaluates a candidate's ability to design and optimize user interfaces and user experiences. The test covers a broad range of topics from wire-framing and prototyping to user research and visual design principles.
The test assesses candidates on their understanding of UI fundamentals, interaction design, and visual design principles. It also evaluates their skills in creating user-centric designs through scenario-based questions on A/B testing, landing pages, and mobile app design considerations.
Successful candidates demonstrate a strong grasp of design thinking, accessibility guidelines, and UX writing. The test includes questions that gauge their proficiency in applying UX design principles to create engaging and effective user interfaces.
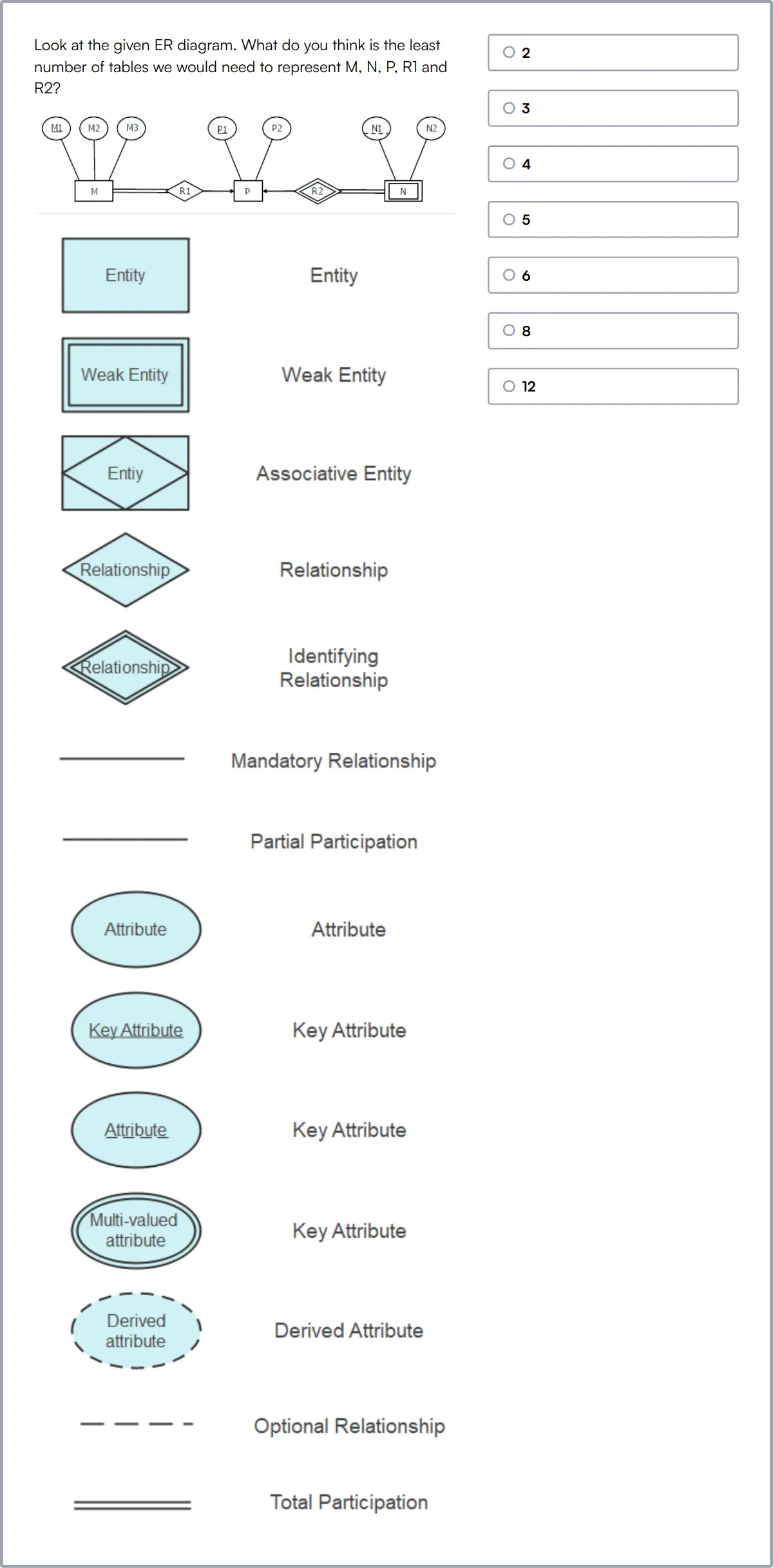
Data Modeling Skills Test
Our Data Modeling Skills Test assesses a candidate's expertise in database design and data integrity. It includes a comprehensive evaluation of skills in SQL, ER diagrams, and normalization.
This test challenges candidates to demonstrate their knowledge in data modeling, relational schema, and data mapping. It also tests their ability to handle data validation and transformation effectively through multiple-choice questions.
High-scoring candidates will show a deep understanding of data integrity and the ability to design efficient relational schemas. The test also measures their skills in SQL, crucial for effective data manipulation and querying.
Content Strategy Test
Our Content Strategy Test evaluates candidates on their ability to develop and implement effective content strategies. The test covers audience analysis, content planning, and multichannel content strategy.
Candidates are tested on their understanding of content auditing, gap analysis, and the development of a content calendar. The test also assesses their skills in keyword research, SEO, and content performance measurement.
Successful candidates will demonstrate a strong capability in managing the content lifecycle and optimizing user experience through strategic content placement. The test includes critical thinking and attention to detail questions to assess their strategic planning skills.
Summary: The 9 key Information Architect skills and how to test for them
| Information Architect skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. User Research | Evaluate ability to gather and interpret user needs and behaviors. |
| 2. Wireframing | Assess skill in creating clear, functional layout blueprints. |
| 3. Information Organization | Check how well information is structured for usability. |
| 4. Content Auditing | Review capability to analyze and evaluate existing content. |
| 5. Taxonomy Design | Determine proficiency in categorizing and labeling information. |
| 6. Prototyping | Gauge skill in creating interactive, testable design models. |
| 7. Usability Testing | Assess ability to conduct and analyze user experience tests. |
| 8. Navigation Design | Evaluate how effectively navigation structures are designed. |
| 9. Content Strategy | Check skill in planning and managing content lifecycle. |
Cyber Security Assessment Test
Information Architect skills FAQs
What skills are most important for an Information Architect?
Key skills include User Research, Wireframing, Information Organization, and Prototyping. Understanding of SEO, HTML/CSS, and Content Management Systems is also beneficial.
How can recruiters assess a candidate's proficiency in wireframing?
Review the candidate's portfolio for examples of wireframes. Additionally, ask them to describe their process and tools used during the interview.
What is the role of usability testing in an Information Architect's job?
Usability testing helps ensure that the end product is user-friendly and meets the needs of the target audience. It involves gathering feedback from users and making necessary adjustments.
Why is knowledge of SEO important for Information Architects?
SEO knowledge helps in structuring information in a way that improves visibility on search engines, enhancing the reach and effectiveness of the content.
How does an Information Architect use analytics in their work?
Analytics are used to track user behavior and engagement, providing insights that guide improvements in site structure and content strategy.
What should recruiters look for when assessing a candidate's skills in content strategy?
Candidates should demonstrate an ability to plan, develop, and manage content that aligns with business goals. Look for experience in content auditing and strategy development.
How important is visual design for an Information Architect?
While not the primary focus, visual design complements an Information Architect's work by enhancing the usability and appeal of interfaces. A good grasp of visual design principles can be a plus.
Can you explain the significance of taxonomy design in information architecture?
Taxonomy design is crucial for organizing content logically and intuitively, making it easier for users to navigate and find information quickly.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



