Financial auditors play a critical role in ensuring the accuracy and integrity of financial statements. Their work supports transparency and accountability, making them key players in the financial health of organizations.
Skills necessary for a financial auditor include a strong understanding of accounting principles, attention to detail, and analytical thinking. Additionally, auditors must possess excellent communication skills to convey their findings effectively.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Financial Auditor skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 7 essential Financial Auditor skills, 6 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
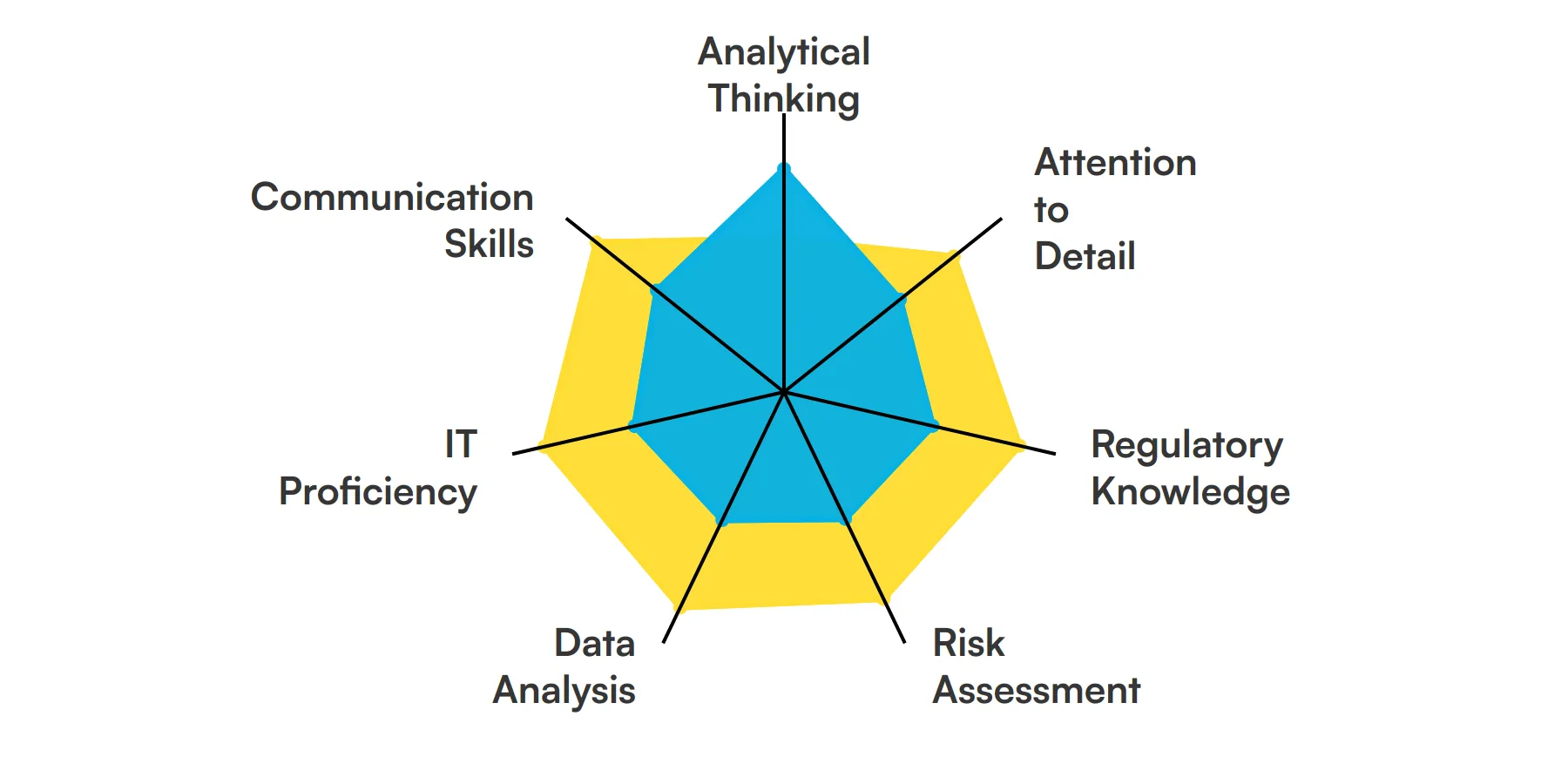
7 fundamental Financial Auditor skills and traits
The best skills for Financial Auditors include Analytical Thinking, Attention to Detail, Regulatory Knowledge, Risk Assessment, Data Analysis, IT Proficiency and Communication Skills.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 7 essential skills of a Financial Auditor.
Analytical Thinking
Financial auditors must dissect complex financial statements and identify discrepancies or patterns that could indicate financial mismanagement or fraud. This skill is fundamental in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Data Analyst Job Description.
Attention to Detail
In auditing, the smallest oversight can lead to significant errors. Auditors need a keen eye for detail to spot any irregularities in the financial documents they review, ensuring that every figure is accurate and accounted for.
Regulatory Knowledge
Understanding the latest financial regulations and compliance requirements is crucial for auditors. This knowledge helps them ensure that the organizations they audit are adhering to governmental guidelines and avoiding legal issues.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Risk Assessment
Auditors evaluate the potential risks associated with financial activities. This involves analyzing current practices and predicting future challenges, which is essential for advising organizations on risk management strategies.
Data Analysis
The ability to interpret and analyze data using statistical tools is key for auditors. This skill helps in making informed conclusions about the financial health of an organization.
IT Proficiency
In today’s digital age, financial auditors must be proficient with auditing software and other technological tools that assist in analyzing financial data and automating repetitive tasks.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a IT Specialist Job Description.
Communication Skills
Effective communication is necessary for auditors to convey their findings clearly and persuasively to stakeholders. This includes writing detailed reports and presenting complex information in an understandable manner.
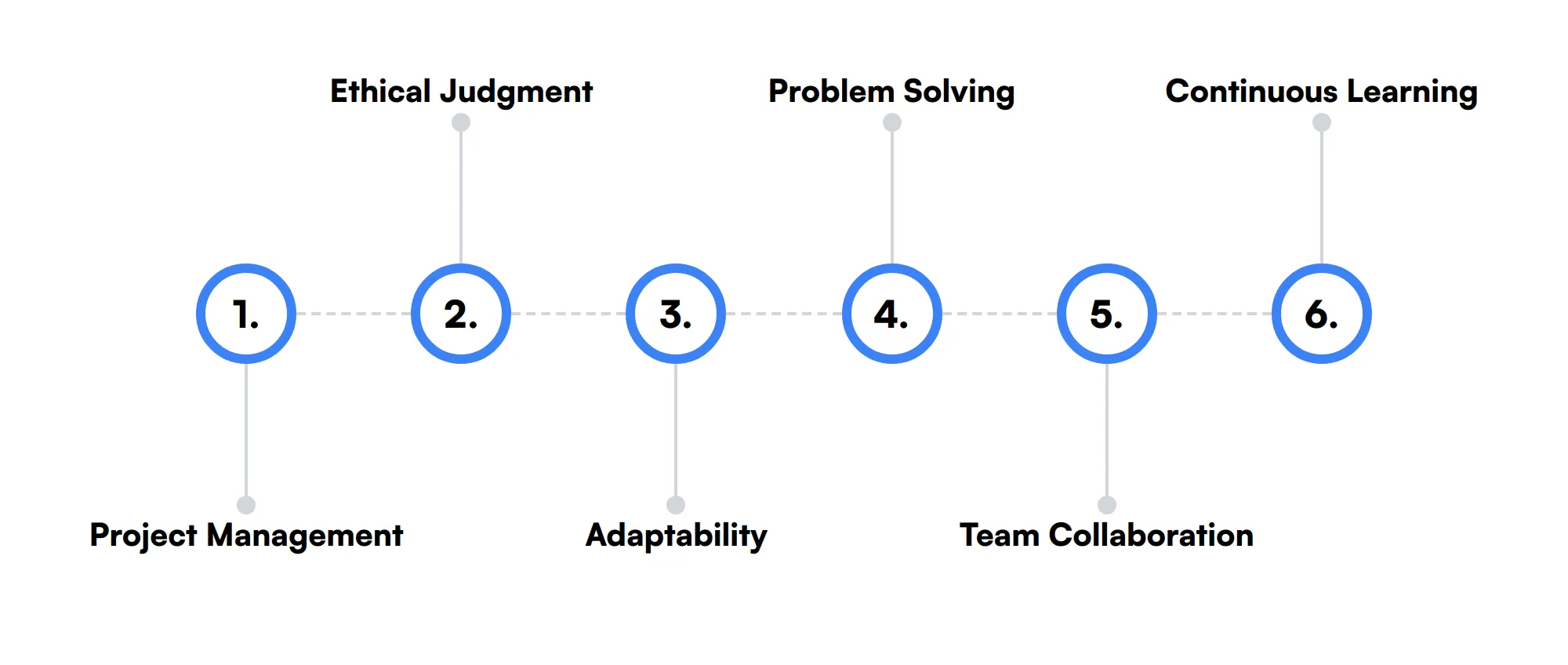
6 secondary Financial Auditor skills and traits
The best skills for Financial Auditors include Project Management, Ethical Judgment, Adaptability, Problem Solving, Team Collaboration and Continuous Learning.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 6 secondary skills of a Financial Auditor.
Project Management
Organizing and managing an audit from start to finish requires good project management skills to ensure that all aspects of the audit are completed on time and within budget.
Ethical Judgment
Auditors frequently face ethical dilemmas; hence, the ability to maintain integrity and make ethical decisions is important to uphold the profession’s standards.
Adaptability
The financial landscape is constantly changing, and auditors need to adapt quickly to new regulations, technologies, and financial practices.
Problem Solving
When issues arise, auditors must be capable of identifying effective solutions swiftly to prevent or mitigate financial discrepancies.
Team Collaboration
Auditors often work in teams, and being able to collaborate effectively ensures that audits are conducted smoothly and efficiently.
Continuous Learning
The field of auditing is ever-evolving, and professionals must continually update their knowledge and skills to stay relevant and effective in their roles.
How to assess Financial Auditor skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a financial auditor goes beyond scanning a resume. While academic qualifications and past job experiences are informative, they don't fully reveal a candidate's proficiency in essential areas such as analytical thinking, attention to detail, and IT proficiency.
In today's fast-paced financial environments, auditors must adeptly navigate through complex data, understand and apply relevant regulations, and communicate findings clearly. Therefore, a more dynamic approach to evaluating these skills is necessary. This is where practical assessments come into play.
Using tailored assessments like those offered by Adaface can transform the hiring process. By simulating real-world scenarios that auditors face, these tests provide a clear picture of how candidates handle tasks that mirror actual job demands. Adaface assessments are designed to measure competencies across various dimensions such as risk assessment and regulatory knowledge, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of each candidate.
Let’s look at how to assess Financial Auditor skills with these 6 talent assessments.
Analytical Skills Test
The Analytical Skills Test evaluates a candidate's ability to comprehend scenarios, identify key information, apply logic, find patterns, and draw conclusions.
The test assesses their understanding of Logical Reasoning, Data Visualization, Data Sufficiency, Verbal Reasoning, Numerical Reasoning, Critical Thinking, and Problem Solving.
Successful candidates demonstrate strong logical reasoning, data interpretation, and problem-solving skills.
Attention To Detail Test
The Attention to Detail Test evaluates a candidate's ability to focus on tasks and their willingness to be thorough for detail-oriented work.
The test assesses their skills in Following instructions, Verifying data, Checking consistency, Proof-reading, Identifying mistakes, and Detecting typos.
Candidates who excel in this test are meticulous and ensure high-quality work by paying close attention to details.
GDPR Online Test
The GDPR Online Test uses scenario-based MCQs to evaluate candidates on their understanding of GDPR regulations and best practices for data protection and privacy.
The test assesses their knowledge of Data Privacy, Data Protection, Data Security, Data Breach, Data Processing, Consent Management, Data Retention, Data Subject Rights, Data Transfer, Data Controllers, and Data Processors.
High-scoring candidates demonstrate a strong understanding of GDPR compliance and the ability to manage data protection risks effectively.
Aptitude Test for Auditors
The Aptitude Test for Auditors uses scenario-based MCQs to evaluate candidates on their aptitude for auditing, risk assessment, and compliance.
The test assesses their understanding of Auditing principles, Financial statements analysis, Internal controls and risk management, Fraud detection and prevention, International auditing standards, and Accounting regulations and laws.
Candidates who perform well demonstrate a solid grasp of auditing standards, risk management, and regulatory compliance.
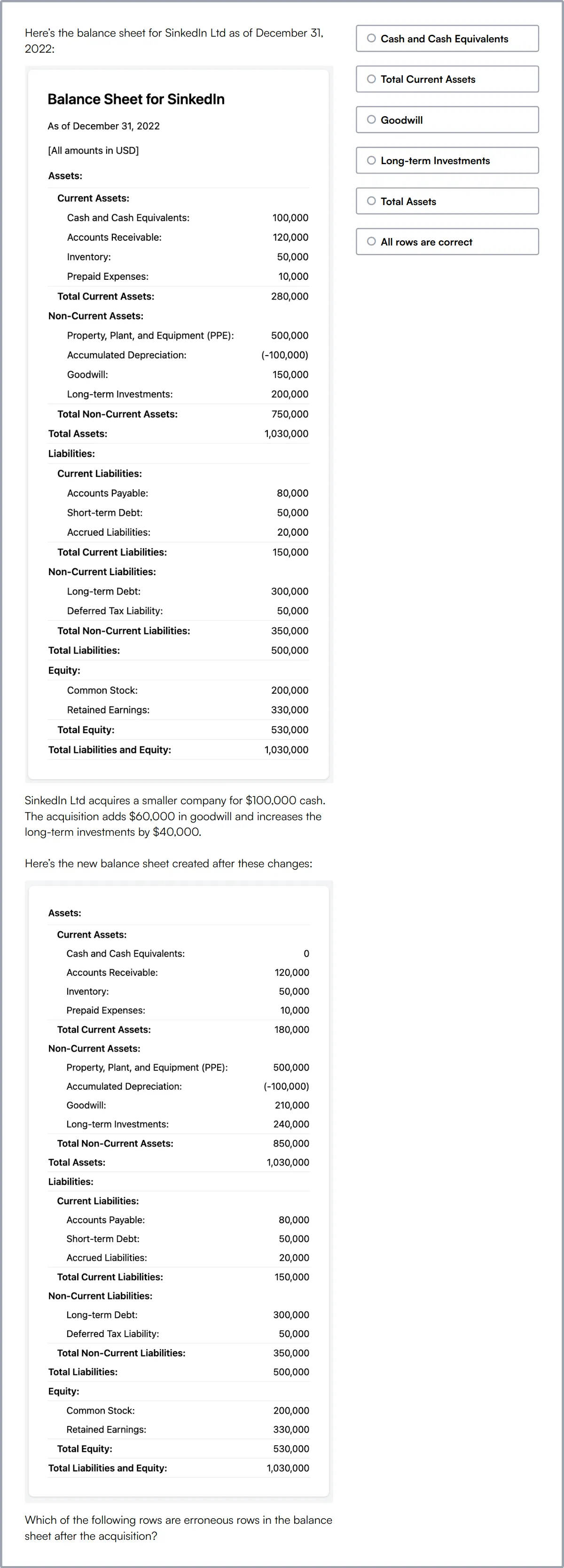
Data Analysis Test
The Data Analysis Test assesses a candidate's ability to handle, modify, analyze, and interpret data.
The test evaluates their skills in Data modelling, Data analysis, Business analysis, Data interpretation, Data queries and databases (SQL), Data operations, Data investigations, and Popular data tools (Excel).
Successful candidates show proficiency in analyzing data, detecting anomalies, extracting insights, and visualizing data using charts and graphs.
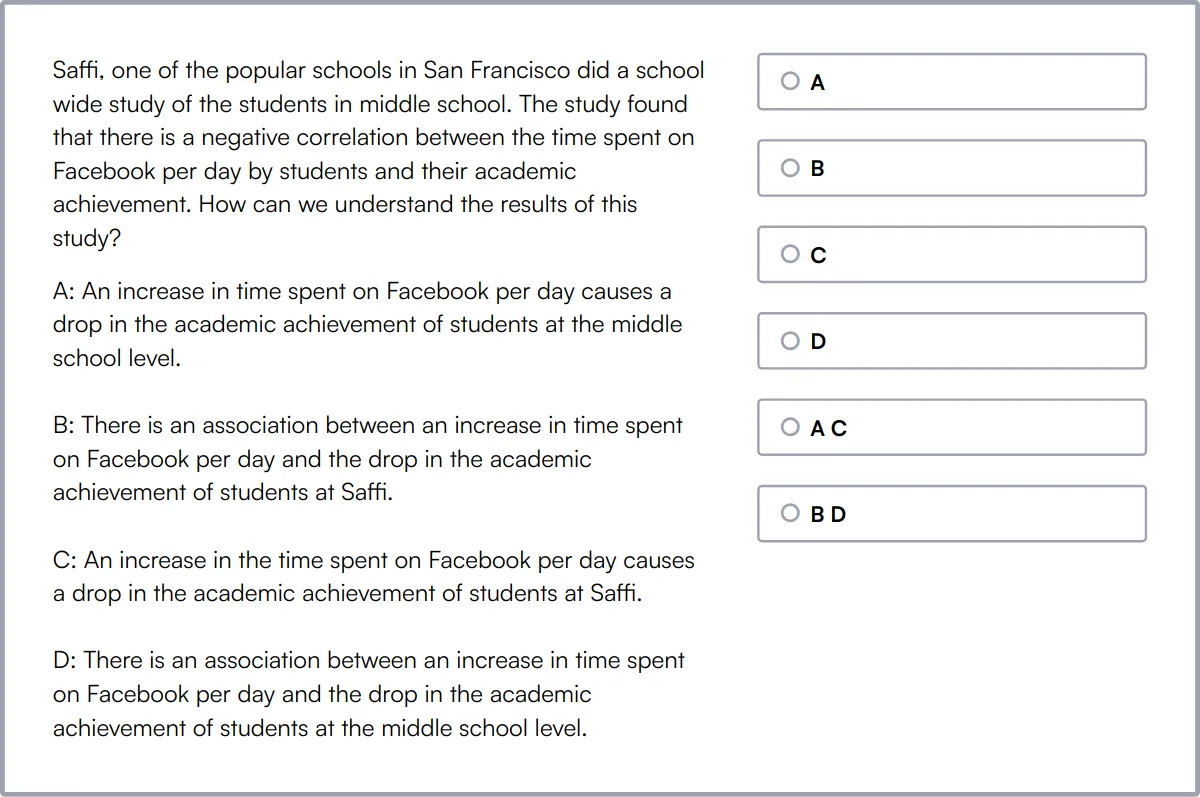
Basic Computer Skills Test
The Basic Computer Skills Test evaluates a candidate's knowledge of fundamental computer skills.
The test covers Basic Computer Skills, Data Entry, Excel, Typing, and System Administration.
Candidates who excel in this test demonstrate a solid understanding of essential computer operations and data management.
Summary: The 7 key Financial Auditor skills and how to test for them
| Financial Auditor skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Analytical Thinking | Evaluate ability to break down complex financial data and identify patterns. |
| 2. Attention to Detail | Check for accuracy and thoroughness in financial reports and documentation. |
| 3. Regulatory Knowledge | Assess understanding of financial regulations and compliance requirements. |
| 4. Risk Assessment | Gauge ability to identify and evaluate financial risks. |
| 5. Data Analysis | Measure proficiency in interpreting and analyzing financial data sets. |
| 6. IT Proficiency | Test skills in using financial software and tools. |
| 7. Communication Skills | Evaluate clarity and effectiveness in conveying financial information. |
Financial Accounting Online Test
Financial Auditor skills FAQs
What is the importance of analytical thinking in a Financial Auditor role?
Analytical thinking helps auditors evaluate financial data, identify trends, and detect discrepancies. It ensures accurate financial reporting and compliance.
How can recruiters assess attention to detail in candidates?
Recruiters can use detailed-oriented tasks or case studies during interviews. Reviewing past work for accuracy and thoroughness also helps.
Why is regulatory knowledge important for Financial Auditors?
Regulatory knowledge ensures auditors are aware of current laws and standards, helping organizations stay compliant and avoid legal issues.
What methods can be used to evaluate a candidate's risk assessment skills?
Use scenario-based questions to see how candidates identify and mitigate risks. Reviewing past experiences in risk management is also effective.
How does IT proficiency benefit Financial Auditors?
IT proficiency allows auditors to use auditing software and tools efficiently, enhancing data analysis and reporting capabilities.
What are some ways to assess communication skills in Financial Auditor candidates?
Conduct role-playing exercises or ask candidates to explain complex financial concepts. Reviewing written reports can also provide insights.
Why is ethical judgment critical for Financial Auditors?
Ethical judgment ensures auditors act with integrity, maintaining trust and credibility in financial reporting and auditing processes.
How can adaptability be evaluated during the hiring process?
Ask candidates about past experiences where they had to adapt to changes. Situational questions can also reveal their flexibility and problem-solving skills.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



