Database developers are the backbone of data management systems, ensuring that data is stored, retrieved, and managed efficiently. They design, implement, and maintain databases, making sure that data is organized and accessible for various applications. Their role is crucial in supporting data-driven decision-making processes within organizations.
The skills required for a database developer include proficiency in database languages such as SQL, knowledge of database management systems (DBMS) like MySQL, Oracle, or SQL Server, and an understanding of data modeling and database design. Additionally, problem-solving abilities and attention to detail are key attributes for success in this role.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Database Developer skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 8 essential Database Developer skills, 9 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
8 fundamental Database Developer skills and traits
The best skills for Database Developers include SQL Proficiency, Database Design, Data Modeling, Normalization, Performance Tuning, Data Security, Backup and Recovery and Transaction Management.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 8 essential skills of a Database Developer.
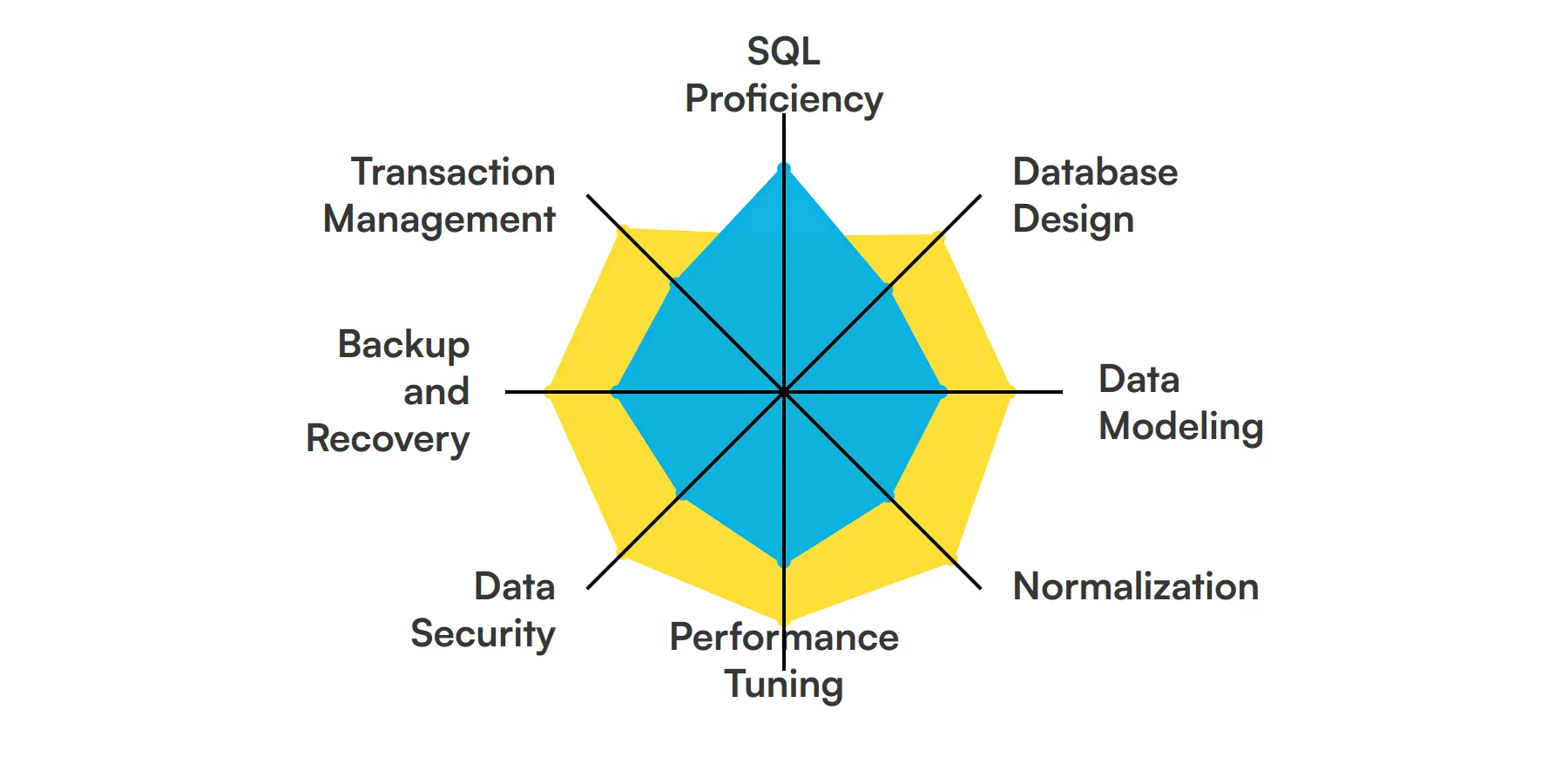
SQL Proficiency
SQL is the backbone of database development, enabling developers to retrieve and manipulate data efficiently. A database developer uses SQL to create complex queries that help in data analysis, reporting, and ensuring data integrity.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a SQL Developer Job Description.
Database Design
Understanding the principles of database design is critical for structuring data in ways that ensure scalability and performance. Database developers must design schemas that support the business requirements while optimizing for speed and efficiency.
Data Modeling
Data modeling involves creating visual representations of data systems, which are crucial for planning and improving database structures. This skill helps database developers in conceptualizing and implementing databases that effectively support user needs.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Normalization
Normalization is used to minimize data redundancy and dependency by organizing fields and table of a database. The proper use of normalization results in increased database efficiency and reduced data anomalies.
Performance Tuning
Performance tuning involves optimizing database speed and efficiency. A database developer must assess and modify indexes, queries, and server configurations to enhance performance and handle larger loads.
Data Security
Ensuring data security is paramount. Database developers implement security measures such as encryption and access controls to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Cyber Security Analyst Job Description.
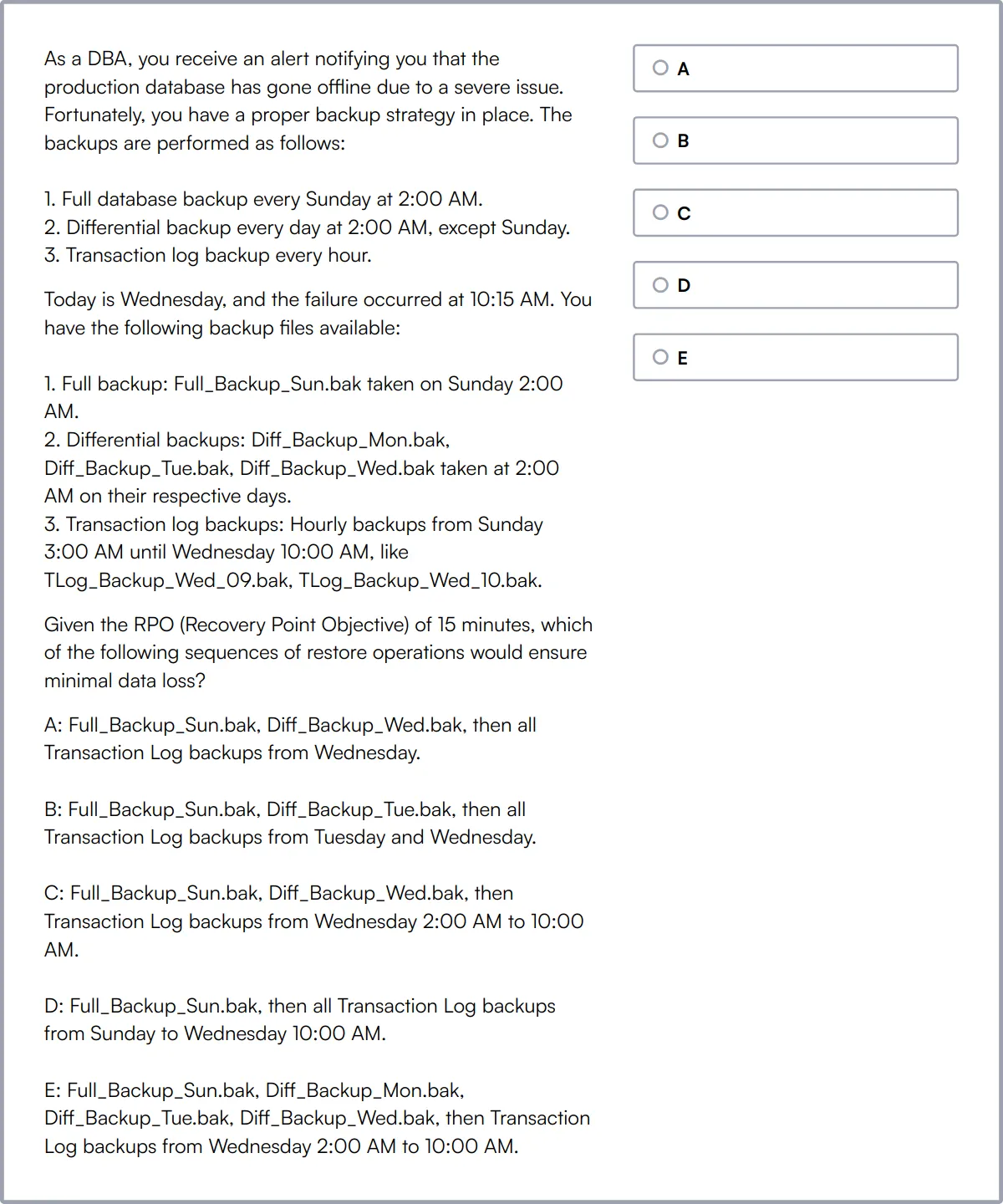
Backup and Recovery
Knowledge of backup and recovery techniques is essential to protect data against loss. Database developers must create and test backup strategies to ensure data integrity and availability during and after any failure.
Transaction Management
Managing database transactions is crucial for maintaining data accuracy and integrity across multiple operations. Database developers use transaction management to ensure that the database remains in a consistent state.
9 secondary Database Developer skills and traits
The best skills for Database Developers include Scripting Languages, NoSQL Databases, Cloud Services, Version Control, ETL Processes, Data Warehousing, API Integration, Agile Methodologies and Documentation Skills.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 9 secondary skills of a Database Developer.
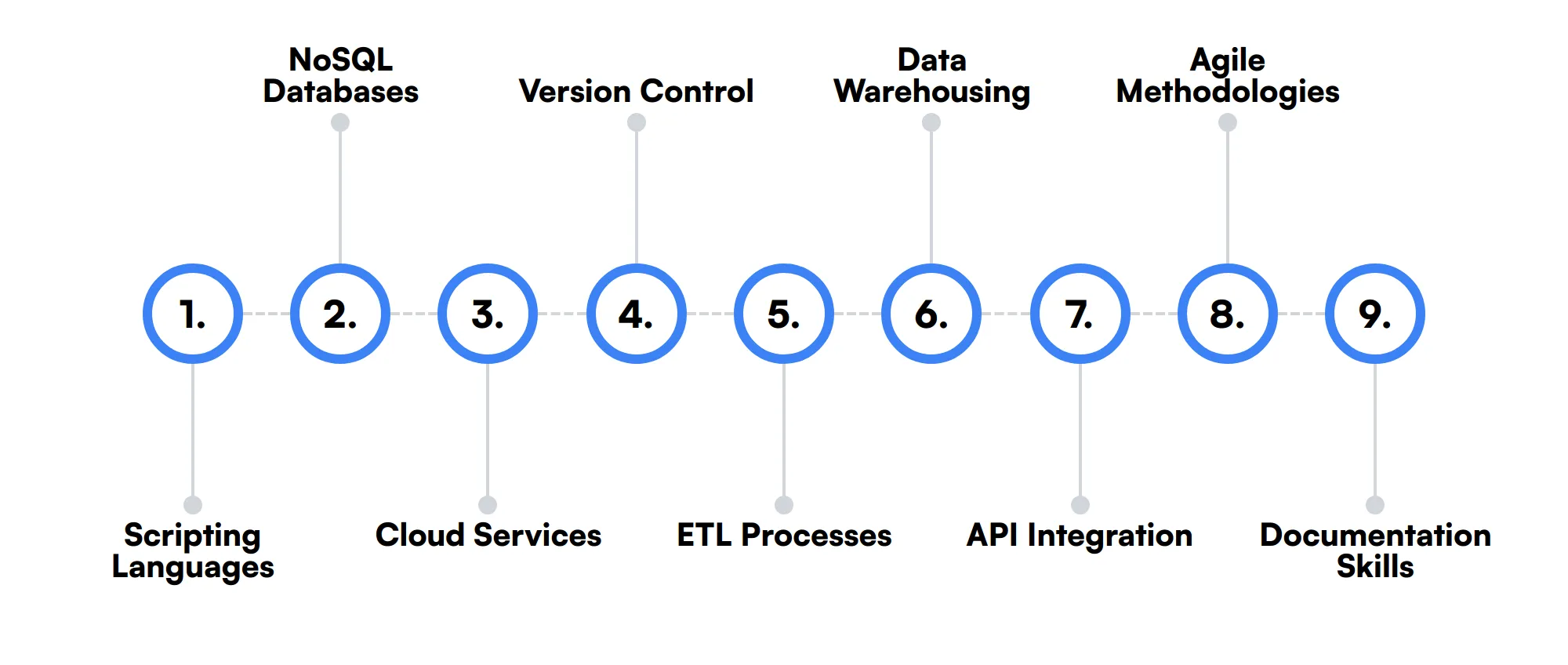
Scripting Languages
Familiarity with scripting languages like Python or Perl helps database developers automate tasks and manipulate data outside of SQL queries.
NoSQL Databases
Knowledge of NoSQL databases such as MongoDB or Cassandra is valuable as these databases are often used for handling big data and real-time web applications.
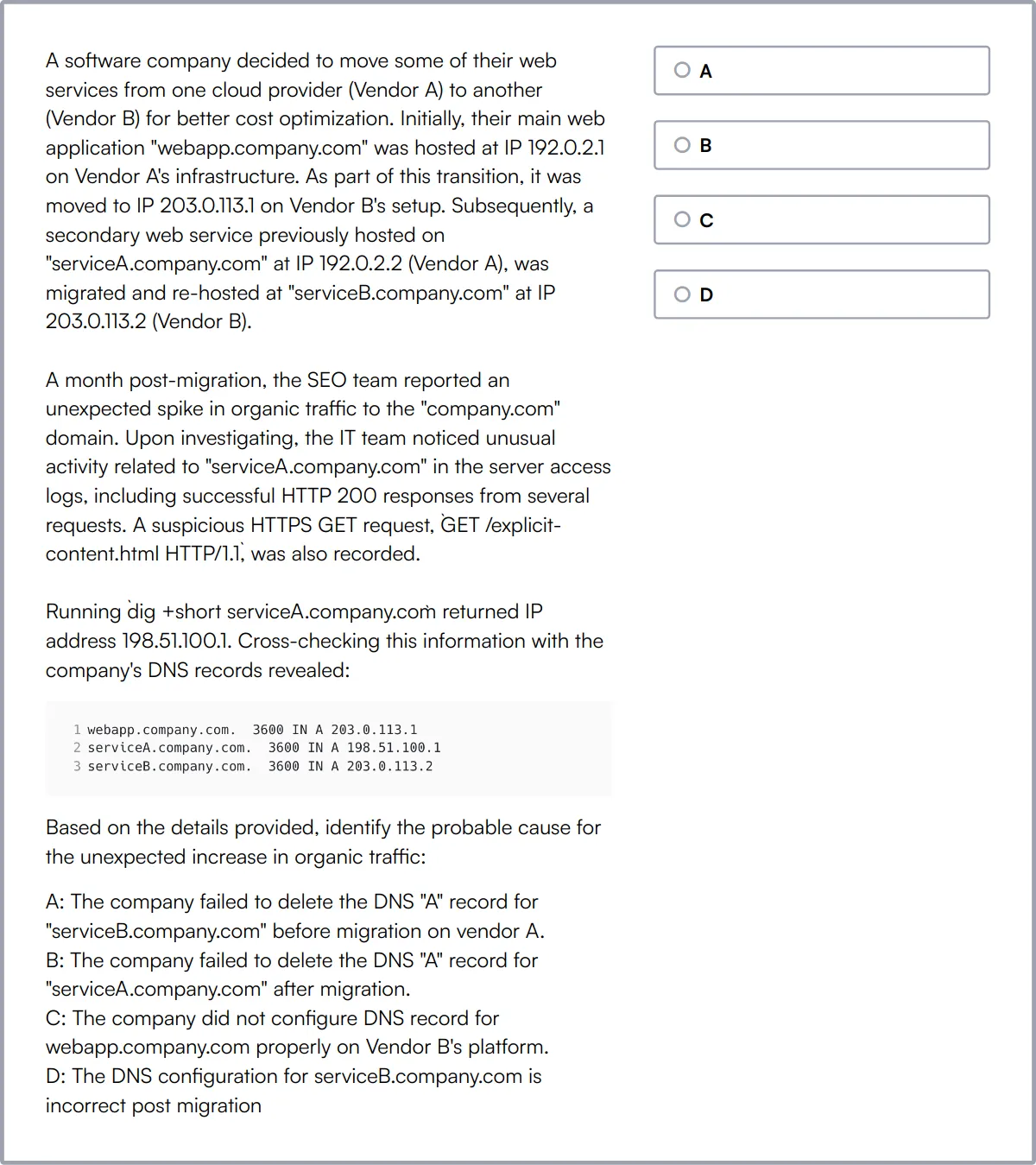
Cloud Services
Understanding cloud-based database services like AWS RDS or Azure SQL Database is beneficial as more organizations move their databases to the cloud.
Version Control
Using version control systems such as Git helps database developers manage changes to the database scripts and collaborate more effectively with others.
ETL Processes
Experience with ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes is important for integrating and consolidating data from various sources into a centralized repository.
Data Warehousing
Skills in data warehousing are crucial for organizing large volumes of data for easy access and analysis, which is essential for business intelligence.
API Integration
Ability to integrate various APIs can enhance database functionality and enable interaction with other systems or third-party services.
Agile Methodologies
Familiarity with agile methodologies can help database developers adapt to changes quickly and deliver work in iterative cycles, aligning with modern development practices.
Documentation Skills
Effective documentation is necessary to ensure that the database setup and modifications are clearly understood and maintainable by others in the team.
How to assess Database Developer skills and traits
Assessing the skills and traits of a Database Developer involves more than just glancing at their resume. While a resume might highlight their experiences and certifications, it doesn't provide a clear insight into their hands-on skills like SQL Proficiency, Database Design, or Data Security.
To truly understand whether a candidate will thrive in your specific environment, you need a method that evaluates their practical abilities in areas such as Performance Tuning, Backup and Recovery, and Transaction Management. Skills-based assessments are the most effective way to measure these competencies.
Using tools like Adaface assessments, you can create customized tests that focus on the key skills required for a Database Developer, such as Data Modeling and Normalization. These assessments help streamline the hiring process, ensuring that you not only save time but also significantly improve the quality of your hires. For more information on creating a tailored assessment, visit Adaface.
Let’s look at how to assess Database Developer skills with these 4 talent assessments.
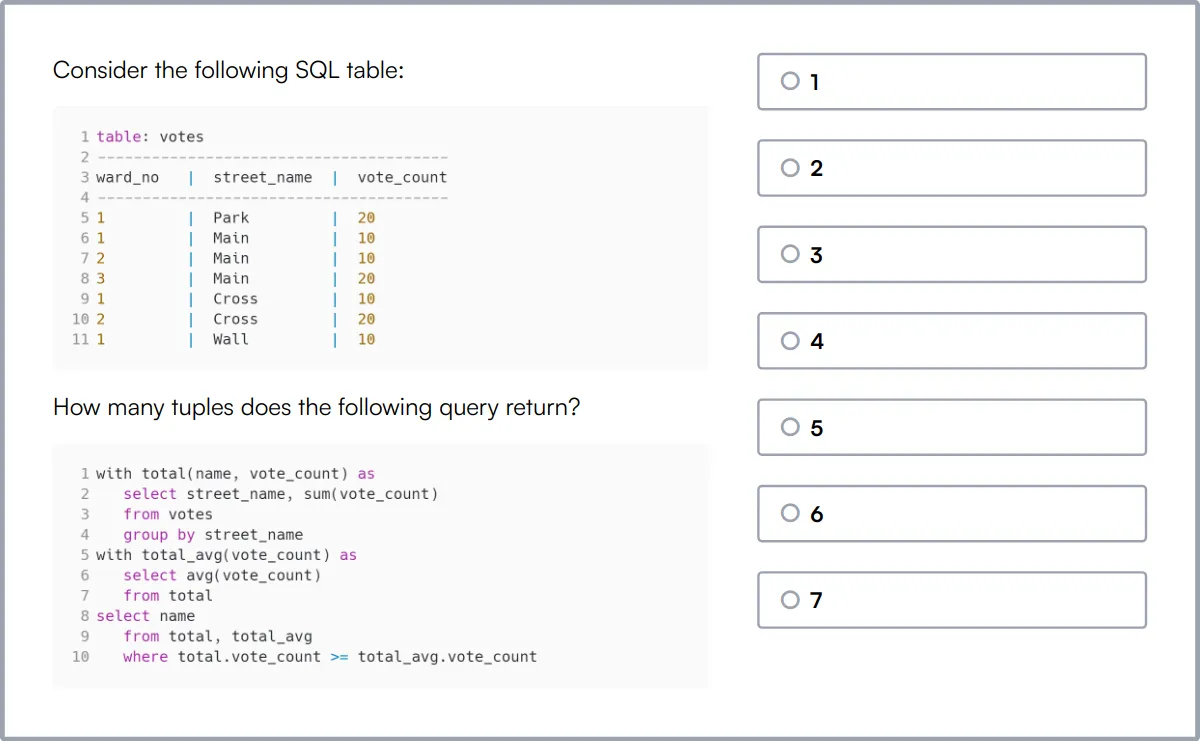
SQL Online Test
Our SQL Online Test evaluates a candidate's ability to design and build relational databases, perform CRUD operations, and write efficient queries including joins and subqueries.
The test assesses skills in creating and managing views, implementing indexes for query optimization, and handling database security and transactional integrity.
Candidates who score well demonstrate a strong grasp of SQL functionalities such as string and mathematical functions, and the ability to manage database scale and security effectively.
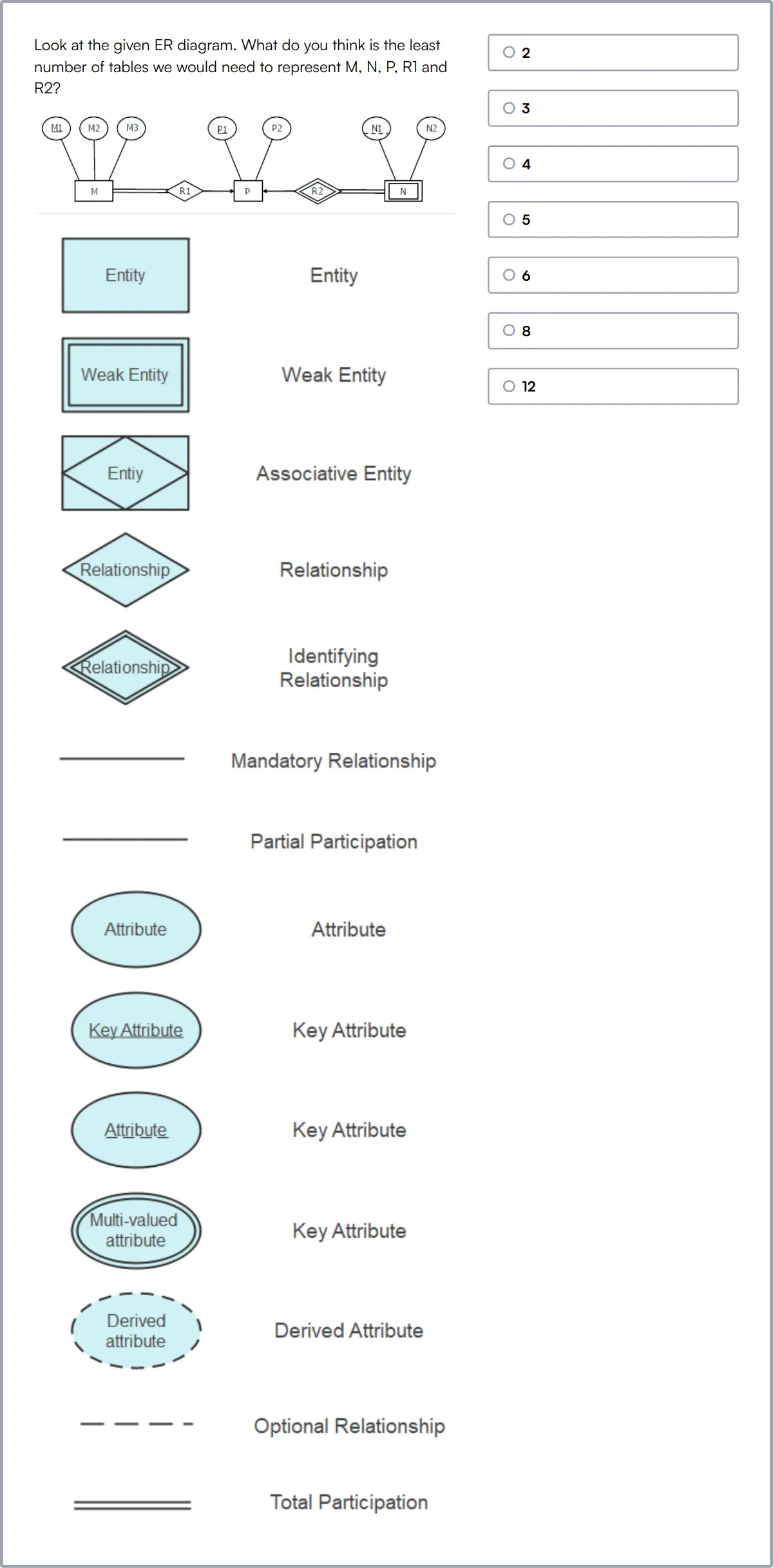
Data Modeling Skills Test
Our Data Modeling Skills Test measures a candidate's proficiency in database design principles, including ER diagrams, normalization, and SQL.
This test evaluates their ability to maintain data integrity, perform data mapping and transformation, and utilize relational schemas effectively.
High-scoring individuals are adept at creating accurate data models that ensure efficient data validation and transformation processes.
SQL Server Online Test
The SQL Server Online Test is designed to assess a candidate's expertise in managing SQL Server environments, from installation to data synchronization and security.
Candidates are tested on their ability to handle transaction logs, perform database monitoring and maintenance, and implement backup and recovery strategies.
Successful candidates will demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of SQL Server configurations, including SAN storage solutions and database object management.
Cyber Security Assessment Test
Our Cyber Security Assessment Test evaluates knowledge in network security, cyber attacks, and cryptography, including practical defenses against common threats.
The test covers a wide range of cybersecurity topics, from understanding network protocols and firewalls to handling cyber attacks like SQL injections and XSS.
Candidates excelling in this test are well-versed in implementing effective cybersecurity measures and risk assessment strategies.
Summary: The 8 key Database Developer skills and how to test for them
| Database Developer skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. SQL Proficiency | Evaluate a candidate's ability to write and optimize SQL queries. |
| 2. Database Design | Assess understanding of structuring database schemas effectively. |
| 3. Data Modeling | Review proficiency in creating accurate data models. |
| 4. Normalization | Check for ability to organize data to reduce redundancy. |
| 5. Performance Tuning | Gauge skills in enhancing database speed and efficiency. |
| 6. Data Security | Determine knowledge of implementing secure database systems. |
| 7. Backup and Recovery | Test strategies for data backup and disaster recovery. |
| 8. Transaction Management | Examine handling of database transactions and concurrency. |
BI Developer Test
Database Developer skills FAQs
What are the key SQL skills a Database Developer should have?
A Database Developer should be proficient in writing complex SQL queries, understanding joins, subqueries, and set operations. They should also be skilled in creating and managing database objects like tables, views, and stored procedures.
How important is data modeling in the role of a Database Developer?
Data modeling is critical as it involves designing data systems that are scalable and maintainable. It includes defining relationships between data points and structuring database schemas to support business processes.
What should a Database Developer know about performance tuning?
Performance tuning involves optimizing SQL queries and database configuration to improve the efficiency of data retrieval and storage. Skills include indexing, query optimization, and understanding the database's execution plan.
Can you explain the significance of data security for Database Developers?
Data security is key for protecting sensitive information. Database Developers need to implement security measures such as encryption, access controls, and SQL injection prevention to safeguard data integrity and privacy.
What is the role of NoSQL databases in modern database development?
NoSQL databases offer flexibility with schema-less data models, making them suitable for big data and real-time web apps. Understanding when to use NoSQL over traditional relational databases is important for modern development projects.
How do cloud services enhance the capabilities of Database Developers?
Cloud services provide scalable and cost-effective solutions for database management. Skills in cloud platforms like AWS RDS or Azure SQL Database enable developers to deploy, manage, and scale databases more effectively.
What is the importance of version control in database development?
Version control is important for managing changes to database scripts and collaboration among team members. It helps in tracking revisions, restoring previous versions, and minimizing conflicts in multi-developer environments.
Why are ETL processes relevant to Database Developers?
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes are essential for integrating data from multiple sources into a centralized repository. Understanding ETL tools and techniques is important for data consolidation and warehousing projects.
Assess and hire the best Database Developers with Adaface
Assessing and finding the best Database Developer is quick and easy when you use talent assessments. You can check out our product tour, sign up for our free plan to see talent assessments in action or view the demo here:

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



