Auditors play a key role in ensuring the accuracy and integrity of financial records. They examine financial statements, assess internal controls, and provide insights that help organizations maintain compliance and improve operations.
Auditor skills include a strong understanding of accounting principles, attention to detail, and analytical thinking. Additionally, effective communication and ethical judgment are crucial for success in this role.
Candidates can write these abilities in their resumes, but you can’t verify them without on-the-job Auditor skill tests.
In this post, we will explore 8 essential Auditor skills, 10 secondary skills and how to assess them so you can make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
8 fundamental Auditor skills and traits
The best skills for Auditors include Analytical Thinking, Attention to Detail, Knowledge of Accounting Standards, Risk Assessment, Data Analysis, Communication Skills, Ethical Judgment and IT Proficiency.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 8 essential skills of a Auditor.
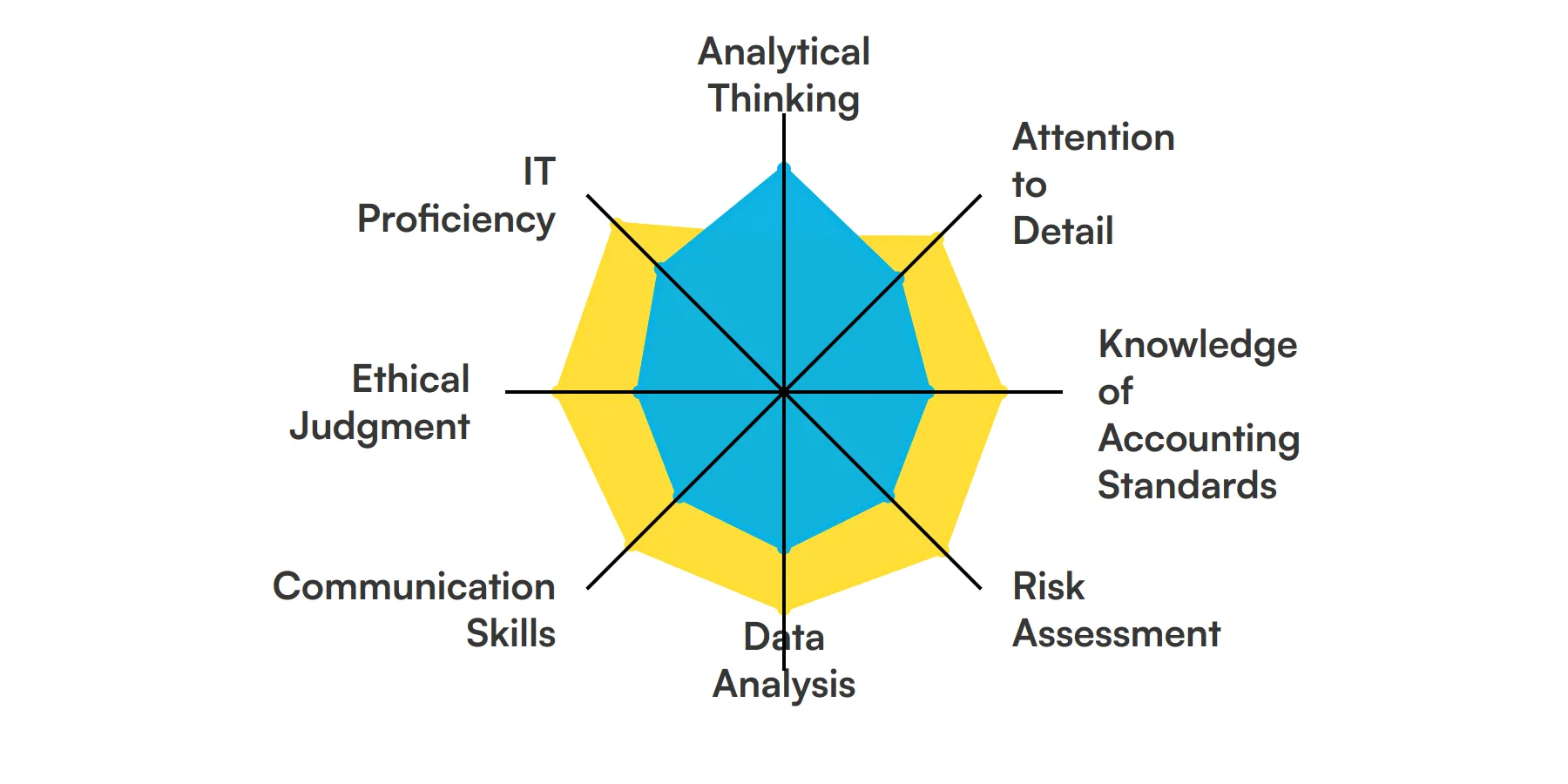
Analytical Thinking
Auditors need to dissect complex financial data and identify patterns or discrepancies. This skill helps in understanding the underlying trends and making informed decisions based on the data.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Data Analyst Job Description.
Attention to Detail
In the role of an auditor, missing even a small detail can lead to significant errors. This skill ensures that every aspect of financial records is thoroughly examined and accurately reported.
Knowledge of Accounting Standards
Auditors must be well-versed in accounting principles and standards like GAAP or IFRS. This knowledge is crucial for ensuring that financial statements are prepared correctly and comply with regulatory requirements.
Check out our guide for a comprehensive list of interview questions.
Risk Assessment
Identifying and evaluating potential risks is a key part of an auditor's job. This skill helps in determining areas that require more scrutiny and in developing strategies to mitigate those risks.
Data Analysis
Auditors often work with large datasets to identify trends, anomalies, and areas of concern. Proficiency in data analysis tools and techniques is essential for making sense of complex information.
Communication Skills
Auditors need to convey their findings clearly to stakeholders, including management and clients. Effective communication ensures that the insights and recommendations are understood and acted upon.
For more insights, check out our guide to writing a Communications Manager Job Description.
Ethical Judgment
Maintaining integrity and objectivity is paramount in auditing. Ethical judgment helps auditors navigate conflicts of interest and ensures that their work adheres to professional standards.
IT Proficiency
With the increasing use of technology in auditing, familiarity with auditing software and general IT skills are important. This helps in efficiently conducting audits and analyzing digital records.
10 secondary Auditor skills and traits
The best skills for Auditors include Time Management, Problem-Solving, Interpersonal Skills, Project Management, Critical Thinking, Adaptability, Negotiation Skills, Research Skills, Report Writing and Conflict Resolution.
Let’s dive into the details by examining the 10 secondary skills of a Auditor.
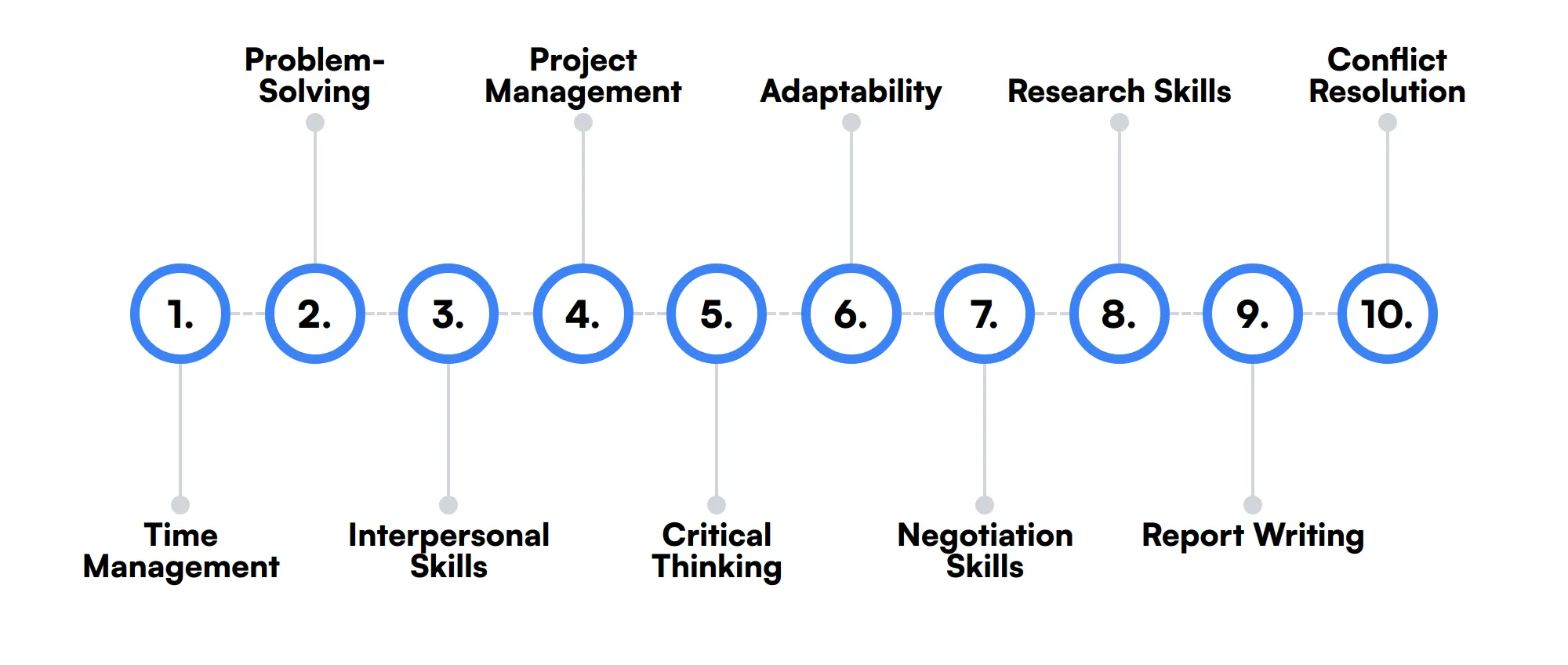
Time Management
Auditors often work on multiple projects with tight deadlines. Effective time management ensures that all tasks are completed within the required timeframe.
Problem-Solving
Auditors frequently encounter issues that require innovative solutions. Strong problem-solving skills help in addressing these challenges effectively.
Interpersonal Skills
Building good relationships with clients and team members is important for an auditor. Interpersonal skills facilitate better collaboration and smoother audit processes.
Project Management
Managing audit projects from start to finish requires good project management skills. This includes planning, executing, and closing audits while ensuring all objectives are met.
Critical Thinking
Auditors need to evaluate information critically to make sound judgments. This skill helps in assessing the validity of data and the reliability of financial statements.
Adaptability
The auditing landscape is constantly evolving with new regulations and technologies. Being adaptable allows auditors to stay current and effectively handle changes.
Negotiation Skills
Sometimes, auditors need to negotiate findings or recommendations with clients. Good negotiation skills help in reaching mutually agreeable solutions.
Research Skills
Auditors often need to research new regulations, industry standards, and best practices. Strong research skills ensure they are well-informed and up-to-date.
Report Writing
Creating clear and comprehensive audit reports is a key part of an auditor's role. Good report writing skills ensure that findings are documented accurately and professionally.
Conflict Resolution
Auditors may face disagreements with clients or team members. Conflict resolution skills help in addressing and resolving these issues constructively.
How to assess Auditor skills and traits
Auditors play a critical role in ensuring the financial integrity of an organization. Their ability to scrutinize financial statements and processes is paramount. However, assessing the skills and traits of an auditor goes beyond just looking at their resume. It involves understanding how well they can apply their knowledge and skills in real-world scenarios.
To effectively assess an auditor's skills, one must consider a comprehensive approach that evaluates both technical abilities and soft skills. This includes their analytical thinking, attention to detail, and proficiency in IT, among others. Each skill contributes uniquely to their overall capability to perform audits efficiently and accurately.
Incorporating practical assessments into the hiring process can significantly enhance the quality of hires. Tools like Adaface assessments offer a tailored approach to evaluating the key competencies of auditors. By simulating real-world challenges, these assessments provide a clear picture of a candidate's abilities in risk assessment, data analysis, and ethical judgment. Learn more about Adaface assessments here.
Let’s look at how to assess Auditor skills with these 6 talent assessments.
Analytical Skills Test
The Analytical Skills Test evaluates a candidate's ability to comprehend scenarios, identify key information, apply logic, find patterns, and draw conclusions.
The test assesses their understanding of Logical Reasoning, Data Visualization, Data Sufficiency, Verbal Reasoning, Numerical Reasoning, Critical Thinking, and Problem Solving.
Successful candidates demonstrate strong analytical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and the capacity to interpret and visualize data effectively.
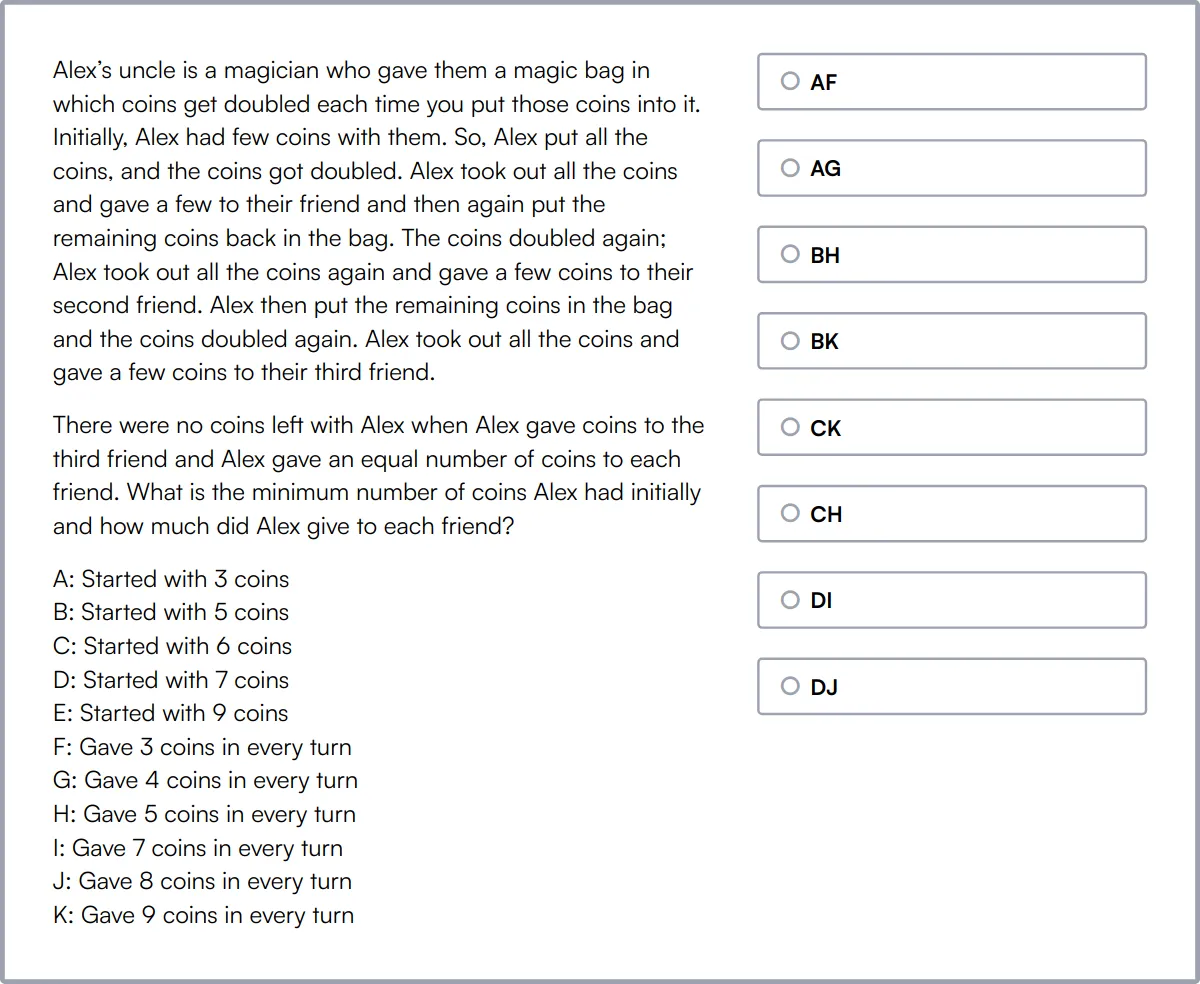
Attention To Detail Test
The Attention to Detail Test evaluates a candidate's ability to focus on tasks and their willingness to be thorough for detail-oriented work.
The test assesses skills such as Following Instructions, Verifying Data, Checking Consistency, Proof-reading, Identifying Mistakes, and Detecting Typos.
Candidates who excel in this test are meticulous, ensuring high-quality work by paying close attention to details and maintaining consistency.
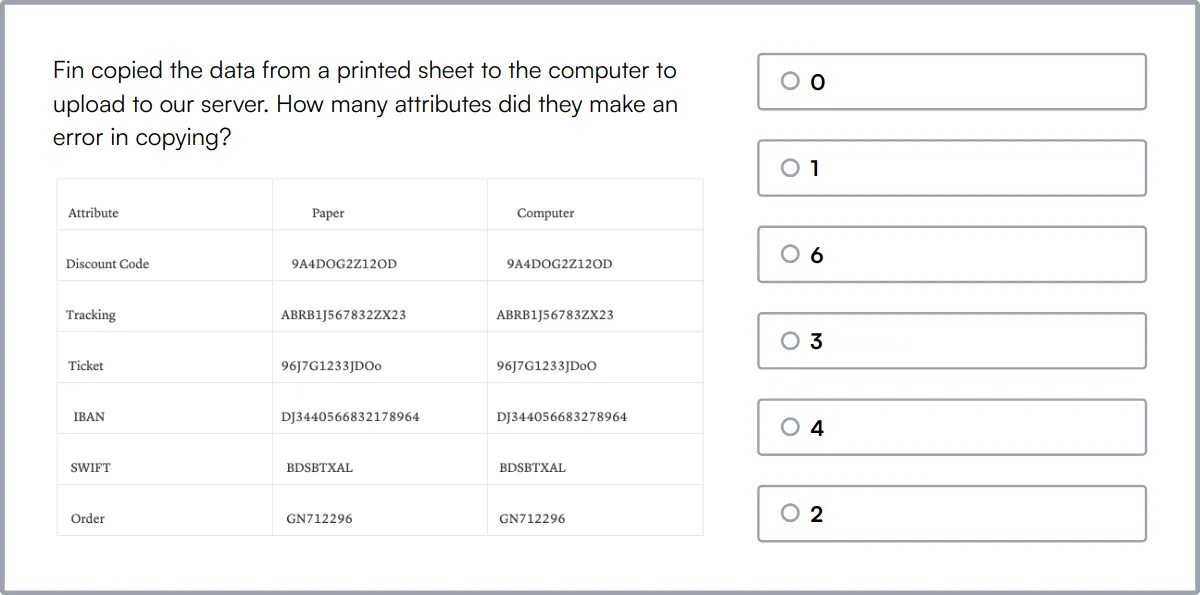
Financial Accounting Online Test
The Financial Accounting Test uses scenario-based multiple-choice questions to evaluate a candidate's knowledge and skills related to financial statements and reporting.
The test covers Financial Statements, Accounting Principles, Double-Entry Bookkeeping, Assets and Liabilities, Income and Expense Recognition, Financial Ratios, Cash Flow Statement, Inventory Valuation, Depreciation and Amortization, and Financial Analysis.
Candidates are evaluated on their ability to interpret and analyze financial data, apply accounting standards, and communicate financial information effectively to stakeholders.
Aptitude Test for Auditors
The Aptitude Test for Auditors uses scenario-based MCQs to evaluate candidates on their aptitude for auditing, risk assessment, and compliance.
The test assesses understanding of Auditing Principles, Financial Statements Analysis, Internal Controls and Risk Management, Fraud Detection and Prevention, International Auditing Standards, and Accounting Regulations and Laws.
Candidates are evaluated on their ability to identify risks, evaluate audit evidence, communicate audit findings, and ensure compliance with regulations and accounting principles.
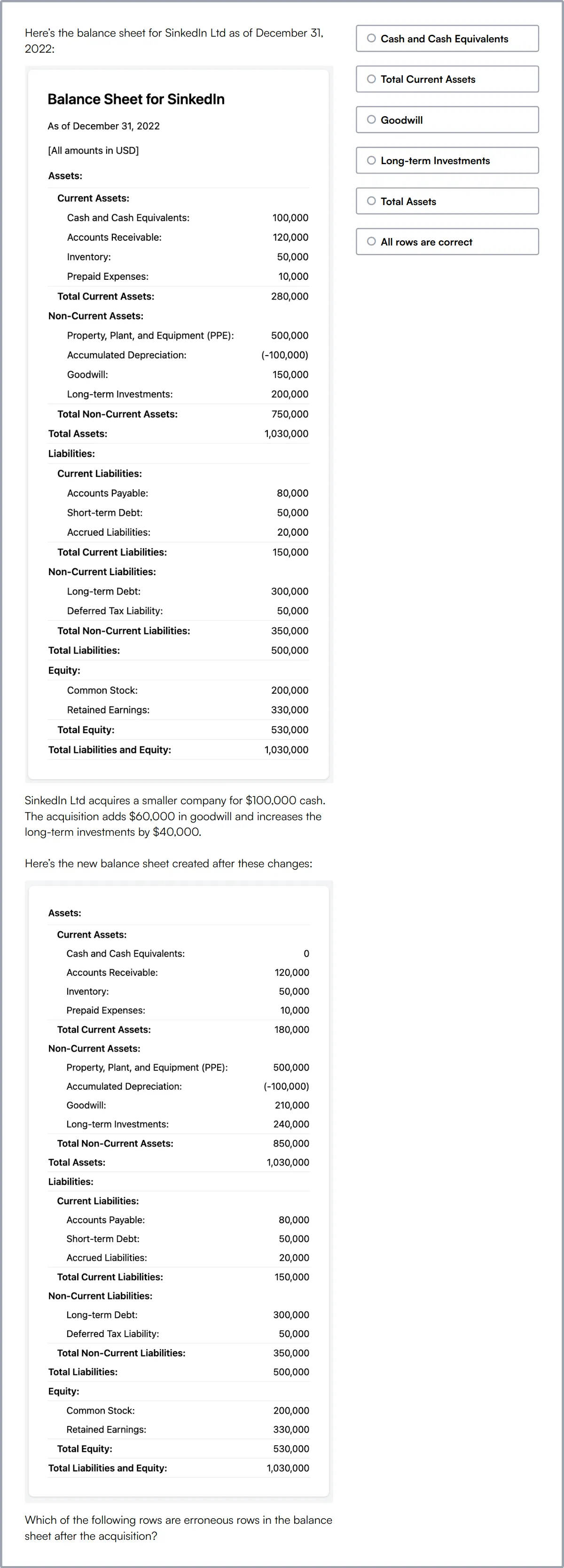
Data Analysis Test
The Data Analysis Test assesses a candidate's ability to handle, modify, analyze, and interpret data.
The test covers Data Modelling, Data Analysis, Business Analysis Fundamentals, Data Interpretation, Data Queries and Databases (SQL), Data Operations, Data Investigations, and Popular Data Tools (Excel).
Candidates are evaluated on their ability to analyze data to find outcomes, detect anomalies, extract insights, project estimates, and visualize data using charts and graphs.
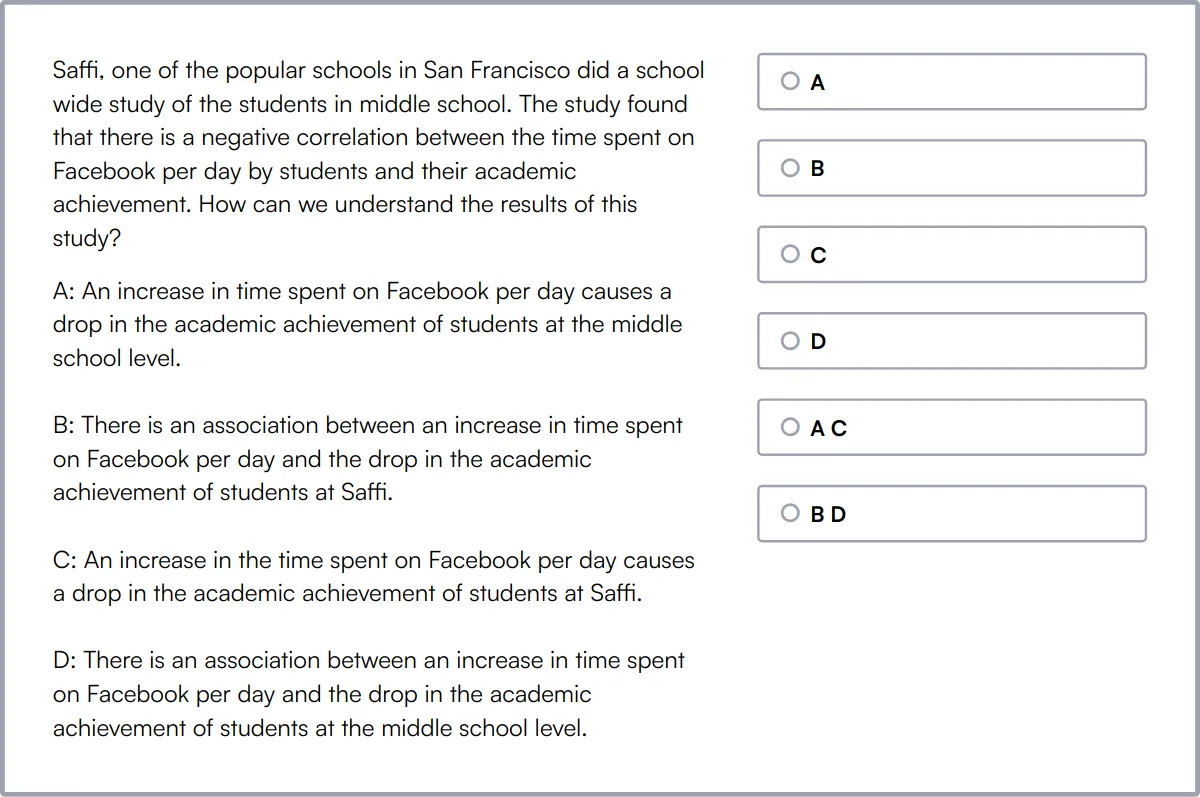
Communication Skills Test
The Communication Skills Test evaluates candidates' communication skills, including verbal and written communication, active listening, and interpersonal skills.
The test assesses Communication Skills, Situational Judgement, Attention to Detail, Critical Thinking, and Verbal Reasoning.
Candidates are evaluated on their ability to effectively communicate with customers, colleagues, and stakeholders in various professional scenarios.
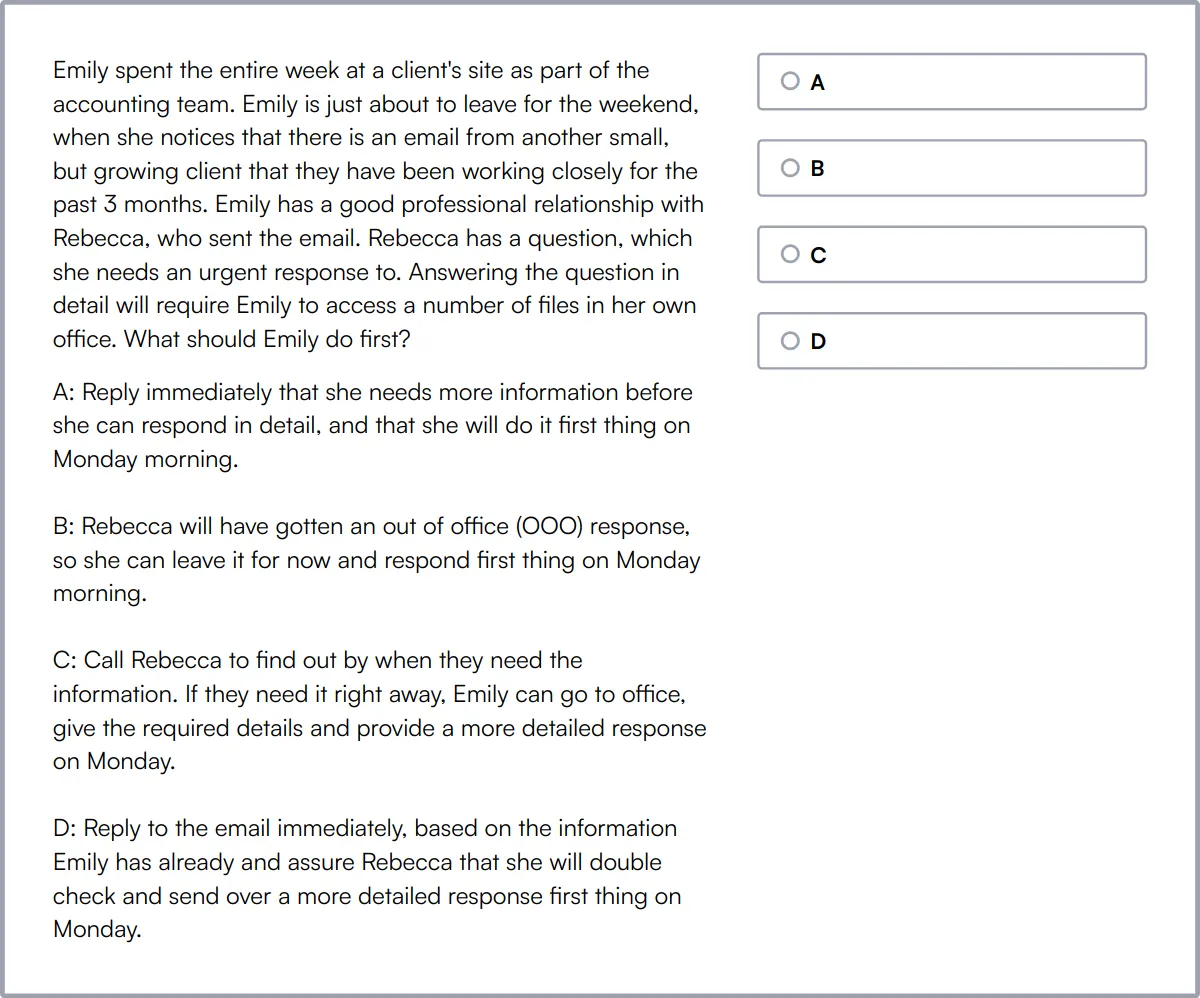
Summary: The 8 key Auditor skills and how to test for them
| Auditor skill | How to assess them |
|---|---|
| 1. Analytical Thinking | Evaluate how well a candidate analyzes complex information systematically. |
| 2. Attention to Detail | Assess accuracy and thoroughness in completing tasks. |
| 3. Knowledge of Accounting Standards | Test understanding and application of relevant accounting frameworks. |
| 4. Risk Assessment | Check ability to identify and evaluate risks effectively. |
| 5. Data Analysis | Review proficiency in interpreting and leveraging data. |
| 6. Communication Skills | Observe clarity, effectiveness, and adaptability in communication. |
| 7. Ethical Judgment | Examine decision-making in ethically ambiguous scenarios. |
| 8. IT Proficiency | Test for competence with relevant software and systems. |
Aptitude Test for Auditors
Auditor skills FAQs
What are the key skills required for an auditor role?
Key skills include analytical thinking, attention to detail, knowledge of accounting standards, risk assessment, data analysis, and communication skills.
How can recruiters assess an auditor's analytical thinking?
Recruiters can use case studies or problem-solving exercises to evaluate an auditor's ability to analyze complex data and draw meaningful conclusions.
Why is attention to detail important for auditors?
Attention to detail helps auditors identify discrepancies, errors, and potential fraud in financial records, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
What methods can be used to evaluate an auditor's knowledge of accounting standards?
Interviews, technical tests, and reviewing past work experience or certifications can help assess an auditor's understanding of accounting standards.
How do communication skills impact an auditor's effectiveness?
Strong communication skills enable auditors to clearly present findings, collaborate with team members, and interact with clients effectively.
What role does ethical judgment play in auditing?
Ethical judgment ensures auditors adhere to professional standards, maintain integrity, and make unbiased decisions, which is critical for trust and credibility.
How can IT proficiency benefit auditors?
IT proficiency allows auditors to use auditing software, analyze large datasets, and improve efficiency in conducting audits.
What are effective ways to assess an auditor's time management skills?
Recruiters can ask about past project timelines, use situational questions, or review how candidates prioritize tasks to gauge their time management abilities.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



