In today's digital landscape, a skilled webmaster is instrumental to maintaining and enhancing a company's online presence. Recruiters and hiring managers often find themselves on the hunt for webmasters who can manage websites, ensure server security, and improve user experience. However, identifying the right fit can be challenging, especially when companies don't fully understand the technical and strategic aspects the role encompasses.
This article will guide you through the intricacies of hiring a webmaster, including understanding their responsibilities, identifying key skills, and structuring an effective hiring process. You'll also learn about leveraging pre-employment assessments to evaluate potential candidates. For more insights, visit our in-depth guide on the skills required for webmasters.
Table of contents
What Does a Webmaster Do?
A webmaster is the guardian of a website, ensuring it runs smoothly and efficiently. They manage the day-to-day operations of a website, ensuring it's user-friendly, secure, and up-to-date.
Day-to-day tasks of a webmaster may include:
- Website Maintenance: Overseeing site health and conducting regular updates to ensure optimal performance.
- Content Management: Uploading new content and managing existing content to keep the site current and engaging.
- Technical Support: Troubleshooting issues and resolving any technical problems that arise.
- Security Management: Implementing and monitoring security measures to protect the website from threats.
To learn more about the skills required for a webmaster, check out this article.
Webmaster Hiring Process
The hiring process for a webmaster typically spans about 6-8 weeks. It involves several stages to ensure you find the right fit for your organization.
- Define the Role: Start by creating a clear job description outlining the skills and responsibilities. This step is critical as it sets the direction for your search.
- Posting the Job: Publish the job listing on relevant job boards and company websites. Expect to receive applications within a few days of posting.
- Screen Resumes: Review the resumes and shortlist candidates based on their experience and qualifications. Aim to finalize this step within a week.
- Skill Assessment: Conduct skill tests tailored to the webmaster role. This could include HTML, CSS, or SEO-related tasks. Allocate about a week for this assessment.
- Interviews: Organize interviews with shortlisted candidates. This often takes 1-2 weeks, allowing time for scheduling and discussions.
- Offer Stage: After identifying the best candidate, move to the offer stage. Factor in time for negotiation and onboarding.
Overall, the total process can take around 1-2 months. As we proceed, we'll discuss each step in detail and provide useful resources for a smoother hiring experience.
Skills and qualifications to look for in a Webmaster
Creating an ideal candidate profile for a Webmaster can be tricky due to the role's diverse responsibilities. It's important to distinguish between must-have skills and nice-to-have qualifications. This distinction helps you focus on candidates who can hit the ground running while still leaving room for growth and specialization.
When evaluating potential Webmasters, consider their proficiency in core web technologies and content management systems. Look for candidates with a solid foundation in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, as well as experience with popular CMS platforms. Additionally, knowledge of SEO best practices is often a key requirement for this role.
Remember that some skills may be more or less important depending on your specific needs. For example, while graphic design skills are often preferred, they might be essential if your team lacks a dedicated designer. Similarly, familiarity with server-side languages could be crucial if your website relies heavily on custom backend functionality.
| Required skills and qualifications | Preferred skills and qualifications |
|---|---|
| Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science or related field | Experience with graphic design tools such as Adobe Photoshop or Illustrator |
| Three or more years of experience in a webmaster role | Familiarity with server-side languages such as PHP, Ruby, or Python |
| Proficiency in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript | Understanding of web analytics tools like Google Analytics |
| Experience with web content management systems such as WordPress or Joomla | Experience with responsive and adaptive design |
| Knowledge of SEO best practices | Proven success in a collaborative, team-oriented environment |
How to Write an Effective Webmaster Job Description
Once you've identified the ideal candidate profile for your webmaster position, it's time to craft a compelling job description. A well-written JD is key to attracting top talent and setting clear expectations for the role.
Here are some tips to create an engaging webmaster job description:
- Highlight key responsibilities: Clearly outline the primary duties, such as website maintenance, content updates, and performance monitoring. Emphasize the webmaster's role in ensuring a smooth user experience and site functionality.
- Balance technical and soft skills: List required technical skills like HTML, CSS, and CMS experience, but also mention important soft skills such as problem-solving and communication. A webmaster needs both to excel in their role.
- Showcase your company culture: Describe your work environment, team dynamics, and any unique perks or benefits. This helps candidates envision themselves as part of your organization and can be a deciding factor for top talent.
- Include growth opportunities: Mention potential career paths or skill development opportunities. This attracts ambitious candidates who are looking for long-term career growth within your company.
Top Platforms to Hire Webmasters
Once you've crafted a strong job description, the next step is to harness job listing sites to attract potential webmasters. Choosing the right platform helps reach the right talent pool, whether you're looking for local, remote, or project-based webmasters.
Upwork
Ideal for hiring freelancers for short-term or project-based webmaster tasks, offering a large pool of global talent.
Freelancer
Best for finding freelancers for specific webmaster projects, with options for both small and larger-scale tasks.
Use for hiring full-time webmasters with professional profiles and detailed resumes, suitable for building long-term teams.
For broader options, platforms like LinkedIn are great for full-time hires, providing professional profiles and detailed resumes. Indeed offers extensive job-posting tools for full-time roles, while Glassdoor can help recruit part-time webmasters by using company reviews to attract candidates. SimplyHired is another option for part-time listings with excellent resources. AngelList connects startups with eager talent, and We Work Remotely caters to those seeking location-independent opportunities. For local hiring, Craigslist offers straightforward listings. For tailored hiring processes, explore Adaface's online assessment platform, which can help streamline your recruitment process.
Keywords to Look for in a Webmaster Resume
Resume screening is a time-saver for recruiters dealing with numerous Webmaster applications. It helps quickly identify candidates with the right skills and experience before moving to interviews.
When manually screening resumes, focus on key technical skills like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and content management systems. Look for experience with SEO, web analytics, and responsive design. A bachelor's degree in Computer Science or related field is often preferred.
AI tools can streamline the resume screening process. You can use AI-powered assessment platforms to automatically scan resumes for relevant keywords and rank candidates based on their match to the job requirements.
Here's a sample prompt for AI-assisted resume screening:
TASK: Screen resumes for Webmaster role
INPUT: Resumes
OUTPUT:
- Email
- Name
- Matching keywords
- Score (out of 10)
- Recommendation
- Shortlist (Yes/No/Maybe)
KEYWORDS:
- Web Development (HTML, CSS, JavaScript)
- CMS (WordPress, Joomla)
- SEO
- Web Analytics
- Responsive Design
- Graphic Design
- Server-side languages (PHP, Ruby, Python)
Which skills tests should you use to assess Webmasters?
Skills tests are a great way to evaluate Webmaster candidates beyond their resumes. They provide objective insights into a candidate's technical abilities and practical knowledge. Here are five recommended tests to assess potential Webmasters:
Web Developer Test: This web developer assessment evaluates a candidate's proficiency in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and basic server-side concepts. It's ideal for gauging overall web development skills needed for managing websites.
SEO Assessment Test: An SEO test helps measure a candidate's understanding of search engine optimization principles. This is key for Webmasters who need to ensure website visibility and improve organic traffic.
JavaScript Online Test: JavaScript is essential for creating interactive websites. A JavaScript assessment can verify a candidate's ability to implement dynamic features and handle client-side scripting.
PHP Online Test: Many websites use PHP for server-side scripting. A PHP test can help assess a candidate's capability to work with databases, process forms, and manage server-side logic.
Technical Support Test: Webmasters often need to troubleshoot issues. A technical support assessment can evaluate a candidate's problem-solving skills and ability to handle common web-related challenges.
Recommended Case Study Assignments to Screen Webmasters
Case study assignments are a popular tool for hiring managers to assess a candidate's practical skills and problem-solving abilities in real-world scenarios. However, these assignments can be time-consuming, leading to lower participation rates among candidates. As a result, it's important to design assignments that are engaging yet concise to avoid losing talented candidates. Below are some carefully chosen case study assignments that can help you identify the right Webmaster for your team.
Website Performance Analysis: This case study involves evaluating a website's performance using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix. Candidates are asked to provide recommendations to enhance the site's load time and overall efficiency. This test is beneficial as it demonstrates the candidate's ability to analyze and improve website performance while also showcasing their understanding of optimization tools.
SEO & Content Strategy: In this assignment, candidates are tasked with developing an SEO strategy for a given website. This includes keyword research, on-page SEO recommendations, and content alignment to boost organic traffic. It is a valuable test to gauge a candidate's knowledge in SEO practices and their ability to create actionable strategies.
Cross-Browser Compatibility Testing: Here, candidates are required to ensure that a website functions seamlessly across various browsers and devices. They are asked to identify and resolve compatibility issues using tools like BrowserStack. This assignment helps assess the candidate's technical skills in maintaining website consistency and their ability to troubleshoot across different platforms.
Structuring the Interview Process for Webmaster Candidates
After candidates pass the initial skills tests, it's time for technical interviews to assess their hard skills in depth. While skills tests are great for initial screening, technical interviews are key to finding the best fit for your webmaster role. Let's look at some sample interview questions to help you evaluate candidates effectively.
Consider asking: 'How do you approach website security?', 'What's your process for optimizing website performance?', 'How do you handle content management systems?', 'Can you explain your SEO strategy?', and 'How do you ensure cross-browser compatibility?'. These questions help assess a candidate's technical knowledge, problem-solving skills, and real-world experience in managing websites.
Understanding the Cost of Hiring a Webmaster
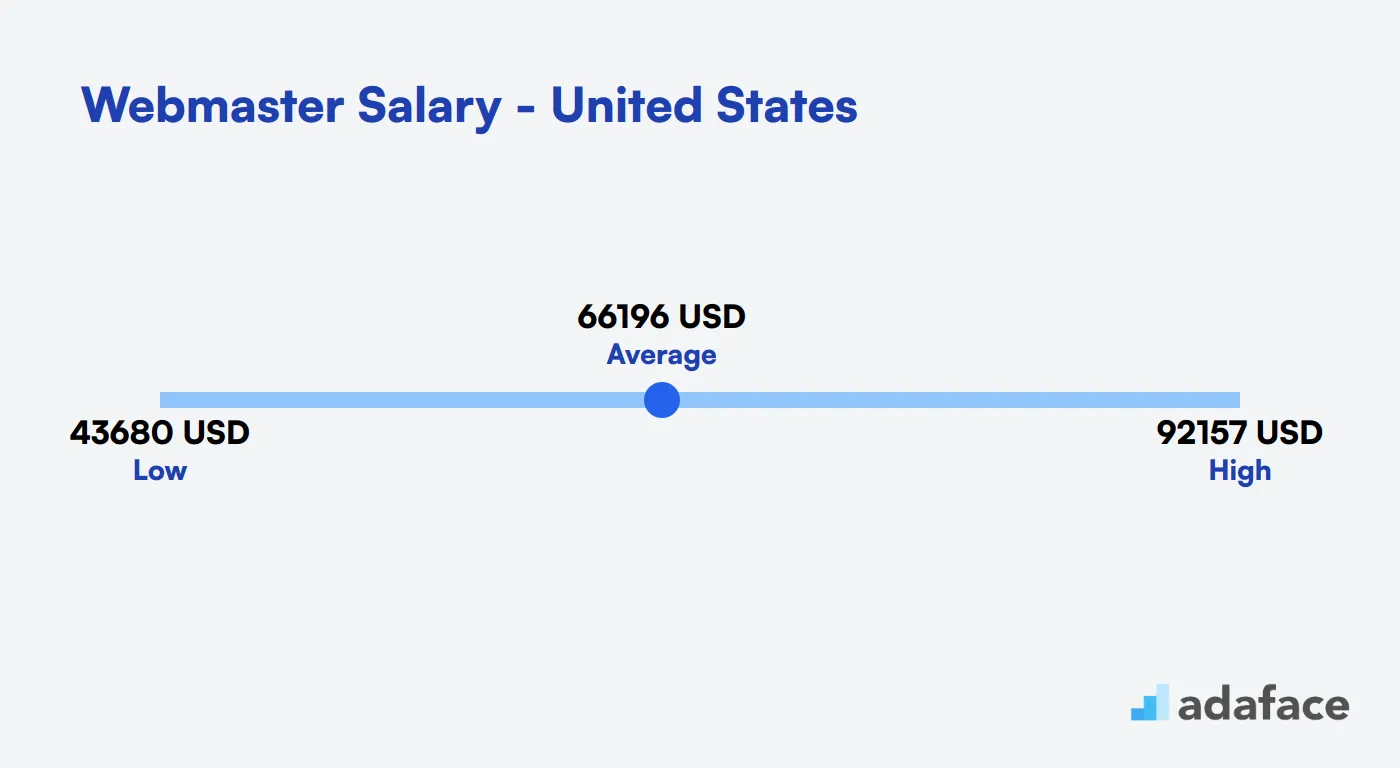
Hiring a webmaster can vary significantly based on location and experience. In the United States, the average salary hovers around $66,196 annually, with a range from $43,680 to $92,157 depending on various factors.
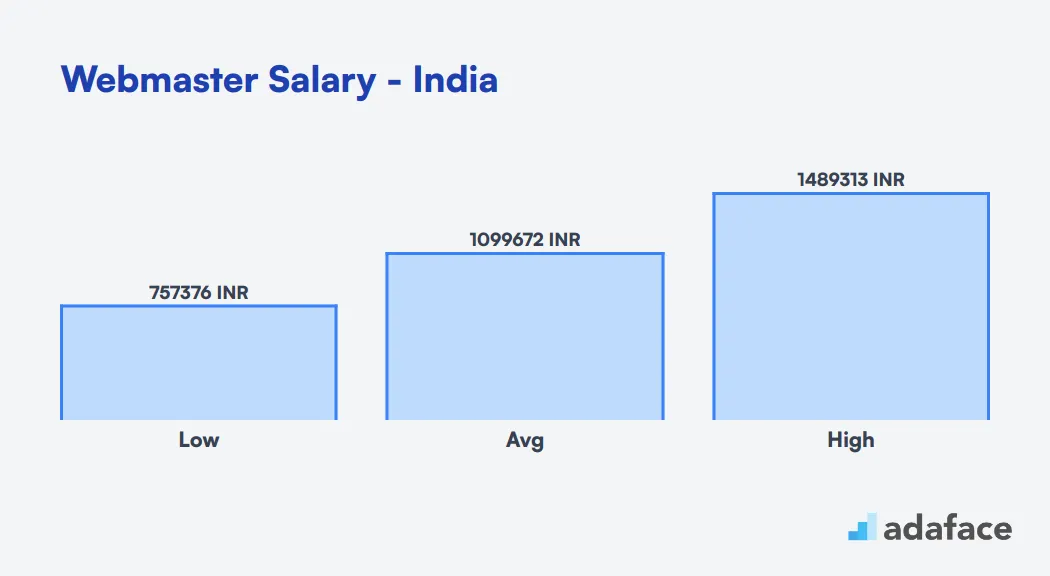
In other countries like India, webmasters earn an average of ₹10,99,672 per year, with a salary range between ₹7,57,376 and ₹14,89,314. These benchmarks are important for recruiters to attract skilled professionals in their respective markets.
Webmaster Salary in the United States
The average salary for a webmaster in the United States is approximately $66,196 per year. Salaries can range from a low of around $43,680 to a high of about $92,157, depending on factors such as experience, location, and company size.
For example, webmasters in cities like Tallahassee, FL, can earn between $106,151 and $236,590, while those in New York, NY, might see salaries ranging from $46,981 to $106,422. Understanding these salary benchmarks can be helpful in attracting top talent.
Webmaster Salary in the United Kingdom
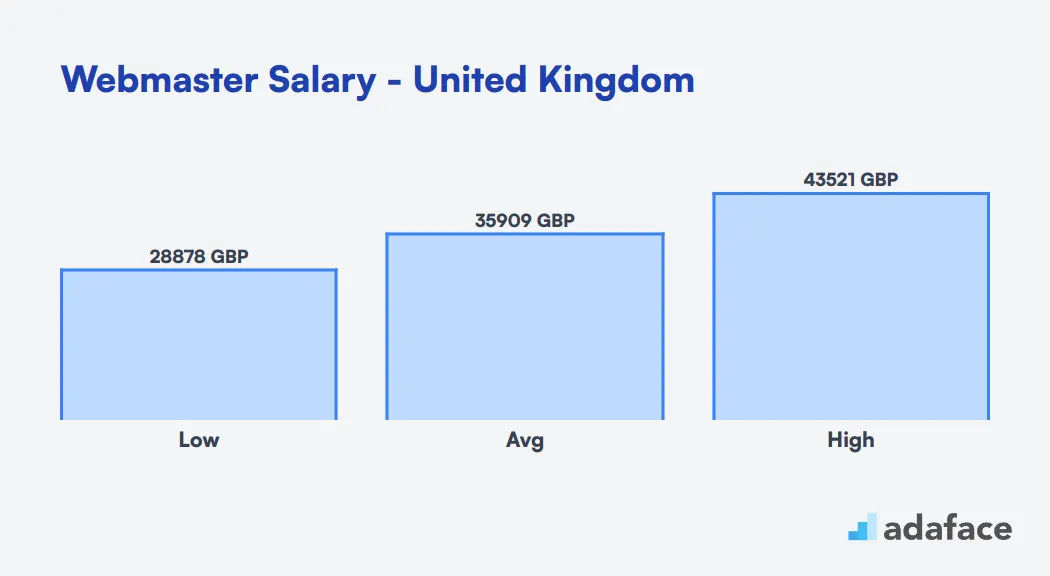
The average salary for Webmasters in the United Kingdom varies based on experience, location, and company size. While specific UK data is limited, we can draw insights from global trends. Generally, entry-level Webmasters can expect to earn around £20,000 to £25,000 per year, while more experienced professionals may command salaries of £35,000 to £50,000 or more.
Factors influencing Webmaster salaries include technical skills, project management abilities, and understanding of SEO and digital marketing. London-based positions typically offer higher salaries compared to other UK regions. As the digital landscape evolves, Webmasters with a broad skill set and ability to adapt to new technologies are likely to command higher salaries.
Webmaster Salary in India
In India, webmasters can expect a competitive salary range. Based on recent data, the average annual salary for webmasters in India is approximately ₹10,99,672. The salary range typically falls between ₹7,57,376 and ₹14,89,314, with the median at ₹10,62,060.
Location can impact earnings. For instance, in Gurgaon, Haryana, webmasters earn an average of ₹9,40,000 annually. This regional variation highlights the importance of considering location when evaluating webmaster salaries in India.
What's the difference between a Front-End Webmaster and a Back-End Webmaster?
It's common to see confusion between Front-End and Back-End Webmasters, but these roles focus on very different aspects of web development. While Front-End Webmasters are concerned with what users see and interact with, Back-End Webmasters work behind the scenes to ensure server-side functionality and database management are up to par.
The Front-End Webmaster primarily focuses on the user interface and experience, utilizing languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. They are skilled in UI/UX design and often work with tools such as Photoshop and React to create visually appealing and responsive designs. In contrast, the Back-End Webmaster handles server-side functionality, relying on languages like PHP, Python, and Ruby, and uses tools like MySQL and AWS for database management.
Key differences include their main focus areas: Front-End Webmasters tackle client-side rendering and performance optimization, while Back-End Webmasters prioritize server response times and database queries. Security concerns also differ; the Front-End Webmaster is focused on preventing cross-site scripting, while the Back-End Webmaster addresses SQL injection prevention and authentication issues.
| Front-End Webmaster | Back-End Webmaster | |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | User interface and experience | Server-side functionality and databases |
| Core Languages | HTML, CSS, JavaScript | PHP, Python, Ruby, Java |
| Key Skills | UI/UX design, responsive design | Database management, server configuration |
| Tools | Photoshop, Sketch, React, Angular | MySQL, Apache, Node.js, AWS |
| Performance Optimization | Client-side rendering, asset optimization | Server response time, database queries |
| Security Focus | Cross-site scripting prevention | SQL injection prevention, authentication |
| Testing | Browser compatibility, usability testing | Unit testing, integration testing |
| Typical Challenges | Cross-browser compatibility, responsive layouts | Scalability, data integrity |
What are the ranks of Webmasters?
Many people confuse webmasters with other web-related roles due to overlapping responsibilities. However, webmasters have distinct ranks and career progression paths within their field.
- Junior Webmaster: Entry-level position responsible for basic website maintenance, content updates, and troubleshooting minor issues. They often work under the guidance of more experienced team members.
- Webmaster: Mid-level role managing website operations, implementing new features, and ensuring site functionality. They may also handle some SEO tasks and content management.
- Senior Webmaster: Experienced professionals overseeing multiple websites or complex web properties. They lead teams, make strategic decisions, and often collaborate with other departments on web-related projects.
- Web Operations Manager: High-level position responsible for overall web strategy, budgeting, and team management. They often report directly to executive leadership and coordinate with various stakeholders.
- Director of Web Services: Top-tier role in larger organizations, overseeing all web-related operations, setting long-term goals, and aligning web strategies with business objectives.
Hire the Best Webmasters for Your Team
We've covered the key aspects of hiring webmasters, from understanding their role to crafting effective job descriptions and conducting thorough interviews. The hiring process involves assessing technical skills, communication abilities, and problem-solving aptitude.
The most important takeaway is to use accurate job descriptions and appropriate skills tests to ensure a precise hiring process. Consider using a web developer online test to evaluate candidates' technical proficiency. Remember, finding the right webmaster is crucial for maintaining and improving your organization's online presence.
Web Developer Test
FAQs
A webmaster is responsible for managing and maintaining a website, ensuring optimal performance and security, handling updates and technical aspects, and often improving user experience.
Key skills include proficiency in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, understanding of web analytics, SEO knowledge, and experience with web hosting and server management.
Utilize skills tests and practical assignments to evaluate a candidate's technical abilities. You can find relevant tests on platforms like Adaface.
Some popular platforms for hiring webmasters include LinkedIn, Upwork, and specialized tech job boards.
Front-end webmasters focus on the website's user interface and design, while back-end webmasters work on server-side functionality and integration.
Begin with a preliminary screening to evaluate their experience and skills, followed by technical assessments and problem-solving exercises, and conclude with behavioral and cultural fit interviews.
Yes, webmasters can range from junior to senior levels, depending on their experience and expertise in managing complex and large-scale web projects.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



