In today's technology-driven world, hiring a software developer is a crucial step for companies looking to innovate and maintain a competitive edge. Software developers are the masterminds behind the applications and systems that businesses rely on daily. However, finding the right fit can be challenging. Many companies struggle because they don't fully understand the specific skill sets required or fail to assess candidates effectively.
This article provides a detailed guide on hiring a software developer. From crafting the ideal candidate profile and writing a clear job description to navigating the interview process, we cover it all. We also recommend using pre-employment screening tests found on platforms like Adaface to evaluate potential hires effectively.
Table of contents
Why Hire a Software Developer?
Software developers are key players in solving technical challenges and driving innovation. They can help your company create custom applications, improve existing systems, or develop new products that give you a competitive edge.
Consider hiring a software developer when:
- Your current tech stack isn't meeting business needs
- You're planning a digital transformation
- You need to automate processes or improve efficiency
Before committing to a full-time hire, assess your long-term needs. For short-term projects or to test the waters, you might start with a freelance developer or consulting firm. This can help you gauge the impact and decide if a permanent role is necessary.
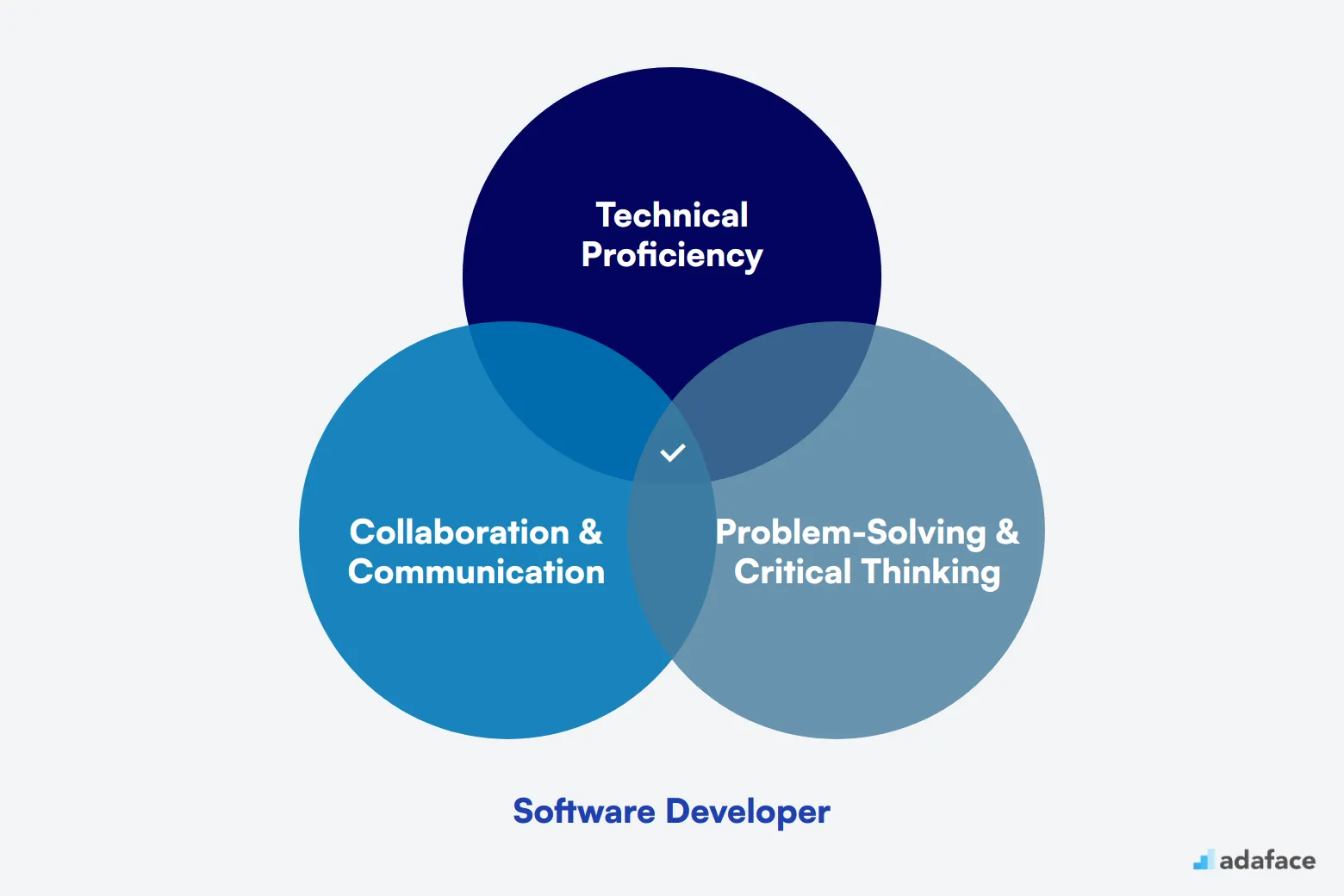
Software Developer Hiring Process
The software developer hiring process typically takes 4-6 weeks. Here's a quick overview:
- Define the role and create a detailed job description.
- Post the job opening on relevant job boards and your company's career page.
- Review resumes and conduct initial screening calls.
- Evaluate candidates' skills through coding tests and technical interviews.
- Conduct behavioral interviews to assess cultural fit.
- Make an offer to the top candidate.
The process involves multiple stages to ensure you hire the best talent. Let's dive deeper into each step.
Building the Ideal Candidate Profile for a Software Developer
When hiring a software developer, it's crucial to identify the right mix of skills and qualifications that match your company's specific needs. The challenge often lies in distinguishing between what's truly necessary and what's merely nice to have. For instance, one company might prioritize a specific programming language, while another might focus on collaboration skills.
To streamline your hiring process, it's helpful to clearly define and separate required skills from preferred qualifications. This not only helps in setting expectations but can also guide your interviews and technical assessments. For a deeper look at how to effectively screen candidates, explore our technical screening insights.
| Required skills and qualifications | Preferred skills and qualifications |
|---|---|
| Bachelor's degree in Computer Science, Information Technology, or related field | Master's degree in Computer Science or related field |
| Proficiency in at least one programming language (e.g., Java, Python, C++) | Experience with Agile or Scrum development processes |
| Strong understanding of software development methodologies and lifecycle | Knowledge of cloud services (AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud) |
| Experience with version control systems, like Git | Experience in developing software for multiple platforms |
| Solid problem-solving skills and attention to detail | Familiarity with DevOps practices |
How to write a Software Developer job description?
Once you have a candidate profile ready, the next step is to capture that information in the job description to attract the right candidates. A well-crafted job description can significantly impact your hiring success.
- Highlight key responsibilities and impact: Clearly outline the role's responsibilities, expected outcomes, and how the software developer's work will influence the organization. This clarity helps potential candidates understand their contribution to the team's success.
- Balance technical skills with soft skills: While it's vital to specify technical skills such as proficiency in programming languages like Java or Python, don't forget to include essential soft skills like teamwork and problem-solving abilities. A mix of both ensures you target well-rounded candidates.
- Showcase unique selling points: Mention what sets your company apart, such as innovative projects or a collaborative work environment. This information can entice top talent by giving them insight into the benefits of joining your team.
For more details, you can refer to this detailed software developer job description.
Top Platforms to Source Software Developers
Now that you have a well-crafted job description, it's time to list your opening on job platforms to attract potential candidates. The right platform can significantly impact the quality and quantity of applicants you receive. Let's explore some of the best options for sourcing software developers.
LinkedIn Jobs
Ideal for finding full-time software developers due to its vast professional network and detailed profiles.
Indeed
A comprehensive job site that attracts a large volume of applicants for full-time roles.
Upwork
Best for hiring freelance software developers due to its strong platform for temporary and project-based work.
For remote positions, Remote OK and FlexJobs are excellent choices, catering to developers seeking flexible work arrangements. AngelList is perfect for startups, while Dice specializes in tech-focused roles. Stack Overflow Jobs leverages its vast developer community, and Glassdoor offers candidates valuable company insights. Remember to tailor your hiring process to each platform for best results.
Keywords to Look for in Software Developer Resumes
Resume screening is a key step in finding the right software developer. It helps you quickly identify candidates with the skills and experience you need, saving time in the hiring process.

When manually screening resumes, focus on primary and secondary keywords related to the role. Look for technical skills like programming languages, frameworks, and databases. Also, check for soft skills such as problem-solving and teamwork.
AI tools can streamline the resume screening process. You can use ChatGPT or Claude with a custom prompt to analyze resumes based on your specific requirements. This approach can help you process a large number of applications more efficiently.
Here's a sample prompt for AI-assisted resume screening:
TASK: Screen resumes for a software developer role
INPUT: Resumes
OUTPUT:
- Candidate name and email
- Matching keywords
- Score (out of 10)
- Recommendation
- Shortlist decision (Yes/No/Maybe)
KEYWORDS:
- Programming languages (Java, Python, C++)
- Web frameworks (React, Angular, Django)
- Database management (MySQL, MongoDB)
- Version control (Git)
- [Software development methodologies](https://www.adaface.com/blog/how-to-interview-software-engineers/)
Recommended Skills Tests to Assess Software Developers
Assessing the technical capabilities of software developers is a key component of the hiring process. Using skills tests helps ensure candidates are well-suited for your team, providing a reliable measure of their proficiency and potential. Our recommendations include a selection of tests tailored to evaluate various aspects of software development skills.
Software Engineering Online Test: This test focuses on evaluating the practical knowledge and problem-solving skills necessary in software engineering roles. It's ideal for verifying candidates' understanding of software development principles and methodologies. Learn more at Software Engineering Online Test.
Full Stack Developer Test: Designed to assess knowledge in both front-end and back-end technologies, this test evaluates a candidate's ability to work across the full technology stack. Useful when hiring for roles demanding versatile development skills. Explore more with our Full Stack Developer Test.
Technical Aptitude Test: This test measures a developer's ability to solve complex problems using logical reasoning and technical knowledge. It helps identify individuals with the potential to learn and adapt to technological advancements. Discover more on the Technical Aptitude Test.
Coding and Data Structures Test: Perfect for assessing a candidate's proficiency in algorithms and data structures, which are fundamental to writing optimal code. This test is great for screening candidates' ability to implement and manipulate various data structures. Check out the Coding Data Structures Arrays Test and Coding Data Structures Strings Test.
Problem Solving Test: This test gauges a candidate's ability to approach complex software challenges and devise effective solutions. It's an excellent choice to ensure your candidates can think critically and solve real-world problems. Learn more at Problem Solving Test.
Case Study Assignments to Evaluate Software Developers
Case study assignments can be valuable tools for assessing software developers' skills. However, they come with drawbacks like lengthy completion times, low participation rates, and the risk of losing promising candidates. Let's explore some effective case studies that balance thoroughness with practicality.
Bug Fixing Simulation: This assignment involves presenting candidates with a codebase containing intentional bugs. Developers must identify and fix these issues, demonstrating their debugging skills and code comprehension abilities. This coding test simulates real-world scenarios software developers often face.
Feature Implementation Challenge: Candidates are tasked with adding a new feature to an existing application. This assignment tests their ability to understand requirements, write clean code, and integrate new functionality seamlessly. It's particularly useful for assessing how well developers can work within established codebases.
API Design and Implementation: This case study requires candidates to design and implement a RESTful API for a given set of requirements. It evaluates their understanding of API best practices, data modeling, and backend development skills. This assignment is especially relevant for roles involving backend development.
Structuring the Interview Stage for Software Developer Hiring
Once candidates pass the initial skills tests, it's time for technical interviews to assess their hard skills in-depth. While skills tests are great for filtering out unqualified candidates, they're not always the best at identifying top talent. Technical interviews allow you to dive deeper into a candidate's abilities and problem-solving skills.
Consider asking these interview questions: 1) 'Describe a challenging project you've worked on and how you overcame obstacles.' 2) 'How do you approach debugging a complex issue?' 3) 'Explain your process for optimizing code performance.' 4) 'How do you stay updated with new technologies and best practices?' 5) 'Can you walk me through your thought process for designing a scalable system?' These questions help evaluate problem-solving skills, technical knowledge, and communication abilities crucial for software developers.
What's the difference between a Frontend Developer and a Backend Developer?
Frontend and backend developers are often confused due to their overlapping roles in web development. While both are essential for creating functional websites and applications, they focus on different aspects of the development process.
Frontend developers specialize in creating the user interface and experience. They work with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build the visual elements users interact with directly. Their toolkit includes popular frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js for crafting responsive and dynamic web pages.
Backend developers, on the other hand, focus on server-side logic and databases. They use languages like Java, Python, or Ruby to build the core functionality that powers the application. Backend developers work with frameworks such as Spring, Django, or Ruby on Rails to handle data processing, API design, and server management.
The key differences between frontend and backend developers include:
- Focus Area: Frontend developers prioritize user interface and experience, while backend developers concentrate on server-side logic and databases.
- Languages and Tools: Frontend developers use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript with browser DevTools, while backend developers work with server-side languages and tools like Docker and Jenkins.
- Database Knowledge: Frontend developers typically have basic database knowledge, whereas backend developers possess advanced skills in this area.
- API Interaction: Frontend developers consume APIs, while backend developers design and implement them.
- Security Focus: Frontend developers deal with client-side security issues like cross-site scripting, while backend developers handle data protection, authentication, and authorization.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for recruiters and hiring managers when building a balanced development team. For a comprehensive overview of the skills required for software developers, including both frontend and backend roles, check out our detailed guide.
| Frontend Developer | Backend Developer | |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Area | User Interface and Experience | Server-side Logic and Databases |
| Primary Languages | HTML, CSS, JavaScript | Java, Python, Ruby, PHP |
| Frameworks/Libraries | React, Angular, Vue.js | Spring, Django, Ruby on Rails |
| Database Knowledge | Basic | Advanced |
| API Interaction | Consumption | Design and Implementation |
| Performance Optimization | Client-side | Server-side |
| Security Focus | Cross-site Scripting, CSRF | Data Protection, Authentication, Authorization |
| Typical Tools | Browser DevTools, Webpack | Docker, Jenkins, Kubernetes |
What are the ranks of Software Developers?
In the tech industry, understanding the different ranks of software developers can be a bit confusing, especially when roles seem to overlap. However, each rank comes with its own set of responsibilities and expectations, making it important for recruiters to know the distinctions.
Junior Software Developer: Generally an entry-level position, a junior software developer focuses on learning the ropes of software development. They typically work under the guidance of more experienced developers, performing coding tasks and assisting in larger projects. Their primary goal is to develop their programming skills and familiarize themselves with best practices in the industry.
Software Developer: As a standard role, software developers are responsible for writing, testing, and maintaining code. They work on a variety of projects and are expected to handle more complex tasks with less supervision. This position requires a solid understanding of programming languages and development tools.
Senior Software Developer: With more experience, senior software developers take on leadership responsibilities, such as mentoring junior developers and leading project teams. They work on high-level architectural design and ensure that projects meet the desired specifications and quality standards. Their role is critical in shaping the technical direction of a project.
Lead Developer: Often seen as a bridge between management and development teams, lead developers are tasked with overseeing the entire development process. They collaborate with stakeholders to define project goals and ensure the team stays on track. Their role involves a mix of technical expertise and interpersonal skills.
For more tailored information on each role, such as job descriptions, you can explore the Software Developer Job Description section on our site.
Hire the Best Software Developers for Your Team
Throughout this guide, we've explored various steps in the software developer hiring process, including crafting detailed job descriptions, sourcing candidates from top platforms, and evaluating them through interviews and assessments. Understanding the ranks and roles, from frontend to backend developers, is also important to make informed decisions.
If there's one takeaway, it is the importance of using precise job descriptions and skills assessments to identify the right candidates. Consider utilizing targeted skills tests, such as Adaface's software engineering online test, to make informed decisions and enhance your hiring accuracy. The right tools and strategies ensure you build a talented development team efficiently.
Software Engineering Online Test
FAQs
Look for skills such as proficiency in programming languages, problem-solving abilities, teamwork, and communication skills. Depending on the role, domain-specific knowledge may also be important.
You can find qualified software developers on platforms such as LinkedIn, GitHub, Stack Overflow, and specialized job boards like Adaface.
To write an effective job description, clearly define the role's responsibilities, required skills, and qualifications. Use specific language and focus on the traits that differentiate the role from others.
Frontend developers focus on the user interface and client-side logic, while backend developers handle server-side logic, database interactions, and application integration.
You can assess a software developer's skills through coding tests, technical interviews, and case study assignments. Platforms like Adaface offer tailored coding assessments.
Software developers often progress through ranks such as junior, mid-level, senior, lead, and principal developer. Each level represents increased experience and responsibility.
An effective interview process includes screenings, technical assessments, and behavioral interviews. Use real-world problem-solving scenarios to gauge candidates' expertise and fit.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



