As a recruiter or hiring manager, you're tasked with finding a Product Engineer who can bridge the gap between product vision and technical implementation. Many companies struggle to identify candidates who possess both the technical prowess and the product-centric mindset required for this role. The key is to look for individuals who not only excel in coding but also understand user needs and business objectives.
This guide will walk you through the process of hiring a top-notch Product Engineer, from defining the role to conducting effective interviews. We'll cover essential skills to look for, where to find qualified candidates, and how to assess their abilities accurately.
Table of contents
Why Hire a Product Engineer?
Product Engineers are key players in bridging the gap between product vision and technical implementation. They combine software engineering skills with product thinking to build user-centric solutions. If your company is struggling to align product features with technical feasibility, a Product Engineer can be a valuable addition to your team.
Consider hiring a Product Engineer when:
- You need to improve product development speed and quality
- There's a disconnect between your product and engineering teams
- You want to enhance user experience through technical innovation
Before committing to a full-time hire, you might want to start with a product engineer assessment test to evaluate potential candidates. This can help you gauge their skills and fit for your specific needs. If you're unsure about long-term requirements, working with a consultant initially can provide flexibility while you assess the role's impact on your business.
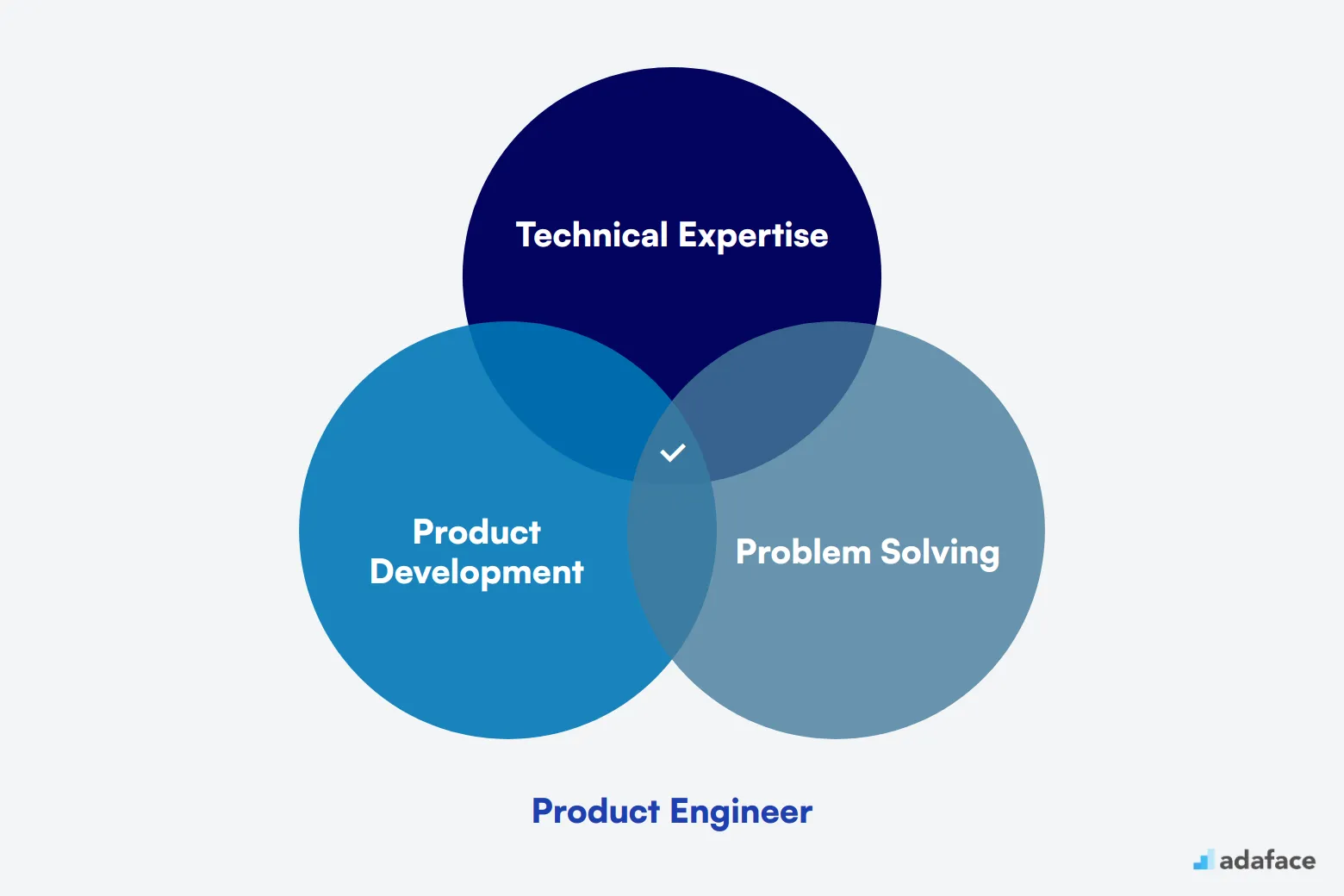
What Does a Product Engineer Do?
A Product Engineer is responsible for the design, development, and improvement of products. They work closely with cross-functional teams to ensure that a product meets both the company's standards and customers' needs.
Day-to-day tasks of a Product Engineer often involve a mix of design and technical responsibilities. They might include:
- Designing and prototyping new products or features.
- Collaborating with product managers and other engineers to define product specifications.
- Testing and iterating on prototypes to enhance product quality and performance.
- Troubleshooting product issues and suggesting improvements.
- Working closely with manufacturing teams to ensure seamless production.
For more insights on the skills required for this role, visit our skills required for product engineer page.
Product Engineer Hiring Process
Hiring a Product Engineer involves a well-structured process to ensure you find the right talent. Here's a quick overview to get you started.
- Begin by crafting a comprehensive job description that outlines the role's responsibilities and required skills. Post this on popular job boards for maximum visibility.
- Within the first week, you should start receiving resumes. Carefully screen these resumes to shortlist candidates that align with your needs.
- Next, move to the skill assessment phase. Use role-specific tests to evaluate the candidates' technical and problem-solving capabilities. This step typically takes about a week.
- Conduct interviews with the shortlisted candidates to assess their fit within your team and culture.
- Finally, select the best candidate and extend an offer.
Overall, the process can take 4-6 weeks, depending on your pace. Each step is crucial in ensuring you attract and hire the best talent. For additional guidance on conducting effective interviews, you can explore our interview questions resource.
Skills and qualifications for a Product Engineer
Crafting the ideal candidate profile for a Product Engineer can be tricky. It's important to distinguish between must-have skills and nice-to-have qualifications. This approach helps in conducting effective interviews and finding the right fit for your team.
Here's a quick overview of the key skills and qualifications to look for in a Product Engineer:
| Required skills and qualifications | Preferred skills and qualifications |
|---|---|
| Bachelor's degree in Computer Science, Engineering, or related field | Master's degree in Computer Science or related field |
| Three or more years of experience as a Product Engineer or similar role | Experience with cloud services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud |
| Proficient in programming languages such as Python, Java, or C++ | Knowledge of CI/CD tools and DevOps practices |
| Strong understanding of software development lifecycle and agile methodologies | Experience in building scalable web applications |
| Excellent problem-solving skills and attention to detail | Strong interpersonal and communication skills |
How to write a Product Engineer job description?
Crafting a well-structured Product Engineer job description is key to attracting the right talent for your team. Once you've defined your ideal candidate profile, the next step is to translate that into a compelling job description. Here's how:
- Detail key responsibilities and their impact: Clearly outline what the Product Engineer will be working on and how their contributions will drive the company's success. This could involve explaining the types of products they will develop or improve, and how these efforts align with broader company goals.
- Balance technical skills with soft skills: While technical abilities such as proficiency in CAD software or experience with product lifecycle management are necessary, don't forget to emphasize soft skills like problem-solving and communication. This ensures you attract candidates who are not only technically competent but also collaborative and adaptable.
- Highlight the company's unique selling points: Differentiate your role by showcasing what makes your company special. It could be innovative projects, opportunities for career advancement, or a vibrant company culture. These details can be enticing to candidates and help your listing stand out on platforms like Adaface.
Where to Find Product Engineers?
Now that you have a job description ready, it's time to list your opening on job platforms to source candidates. Different platforms cater to various hiring needs, from full-time roles to freelance projects. Let's explore some popular options for finding product engineers.
LinkedIn is ideal for posting full-time positions due to its large professional network and job-seeking tools.
Indeed
Indeed is a comprehensive job listing platform suitable for reaching a wide audience for full-time roles.
AngelList
Best for startups looking to hire product engineers interested in startup environments.
Beyond these mainstream platforms, there are specialized sites for technical roles and remote work. Stack Overflow Jobs is great for reaching a technically skilled audience, while Remote.co focuses on remote workforce. HackerX offers networking opportunities through tech-specific job fairs. Remember to tailor your approach based on the type of role and work arrangement you're offering. Using a mix of these platforms can help you cast a wider net in your search for the ideal product engineer.
Keywords to Look for in Product Engineer Resumes
Resume screening is a key step in finding the right Product Engineer. It helps you quickly identify candidates with the most relevant skills and experience before moving to interviews.

When manually screening resumes, focus on primary keywords like Python, Java, or C++, and look for experience with agile methodologies. Keep an eye out for cloud services expertise (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) and knowledge of CI/CD tools.
To streamline the process, consider using AI language models for initial screening. These tools can quickly analyze resumes based on your specified criteria, saving time and ensuring consistency in your screening process.
Here's a sample prompt for AI-assisted resume screening:
TASK: Screen resumes for Product Engineer role
INPUT: Resumes
OUTPUT: For each resume, provide:
- Name
- Matching keywords
- Score (out of 10)
- Recommendation
- Shortlist (Yes, No, Maybe)
KEYWORDS:
- Programming: Python, Java, C++
- Cloud: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud
- DevOps: CI/CD, Docker, Kubernetes
- Web: React, Node.js, Angular
- Soft skills: Problem-solving, communication
Customize this prompt based on your specific Product Engineer job requirements.
Recommended skills tests for assessing Product Engineers
Skills tests are an effective way to evaluate Product Engineers beyond their resumes. They provide objective insights into a candidate's technical abilities and problem-solving skills. Here are five key tests we recommend for assessing Product Engineers:
Full Stack Developer Test: This full-stack developer test evaluates a candidate's proficiency in both front-end and back-end development. It assesses skills in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and server-side programming languages, which are important for Product Engineers who often work across the entire tech stack.
Problem Solving Test: A problem-solving test is valuable for assessing a Product Engineer's analytical and critical thinking abilities. It helps gauge how well candidates can approach complex issues and devise innovative solutions, which is a key aspect of product development.
Technical Aptitude Test: This technical aptitude test measures a candidate's overall technical knowledge and ability to learn new technologies quickly. It's particularly useful for evaluating a Product Engineer's adaptability and potential to work with various tools and platforms.
Backend Engineer Assessment Test: While Product Engineers need full-stack skills, a strong backend foundation is often critical. The backend engineer assessment helps evaluate their proficiency in server-side programming, database management, and API development.
Software Engineering Online Test: This comprehensive software engineering test covers a broad range of topics relevant to Product Engineers. It assesses coding skills, software design principles, and best practices in software development, providing a well-rounded evaluation of a candidate's technical capabilities.
Case Study Assignments to Evaluate Product Engineers
Case study assignments can be valuable for assessing Product Engineers, but they come with drawbacks. They're often time-consuming, leading to lower candidate participation and potentially losing qualified applicants. Despite these challenges, well-designed case studies can provide insights into a candidate's problem-solving skills and approach to product development.
Product Feature Design: This assignment asks candidates to design a new feature for an existing product. They should outline the user problem, propose a solution, and explain their decision-making process. This task evaluates their ability to balance user needs with technical feasibility, a key skill for Product Engineers.
User Experience Improvement: Candidates are given a specific user flow or interface and asked to identify pain points and suggest improvements. This case study assesses their user empathy, attention to detail, and ability to create intuitive designs while considering technical constraints.
Technical Architecture Planning: This assignment involves designing a high-level architecture for a new product or feature. Candidates should explain their choice of technologies, data flow, and scalability considerations. It tests their technical knowledge and ability to make system-level decisions, crucial for Product Engineers who bridge the gap between product vision and technical implementation.
Structuring Technical Interviews for Product Engineers
After candidates pass the initial skills tests, it's crucial to conduct technical interviews to assess their hard skills in-depth. While skills tests help filter out unfit candidates, technical interviews are key to identifying the best talent for your Product Engineer role. Let's explore some sample interview questions to help you evaluate candidates effectively.
Consider asking questions like: 1) 'Describe a product feature you've implemented from concept to launch.' 2) 'How do you balance technical debt with new feature development?' 3) 'Explain your approach to writing maintainable code.' 4) 'How do you collaborate with designers and product managers?' 5) 'What metrics do you use to measure the success of a product feature?' These questions help assess a candidate's technical skills, product thinking, and teamwork abilities, which are essential for a Product Engineer role.
Understanding the Cost of Hiring a Product Engineer
Hiring a Product Engineer can vary significantly based on location and experience. In the United States, for example, the average salary hovers around $107,047, while entry-level positions can start at about $55,983. Other countries, such as India and Australia, have average salaries ranging from INR 969,041 to AUD 102,268, reflecting different economic factors and market demands.
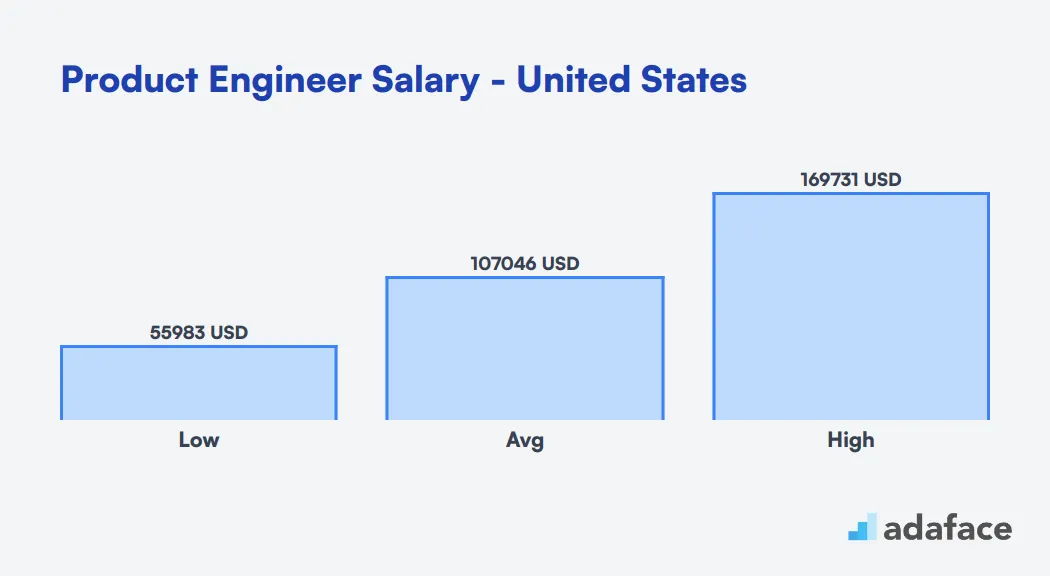
Product Engineer Salary United States
The average salary for Product Engineers in the United States is around $107,047. Entry-level positions start at about $55,983, while more experienced engineers can earn up to $169,731. Salaries vary significantly by location, with high-paying areas like Santa Clara, CA offering median salaries around $127,406, whereas other regions like Madison Heights, MI have median salaries closer to $61,998.
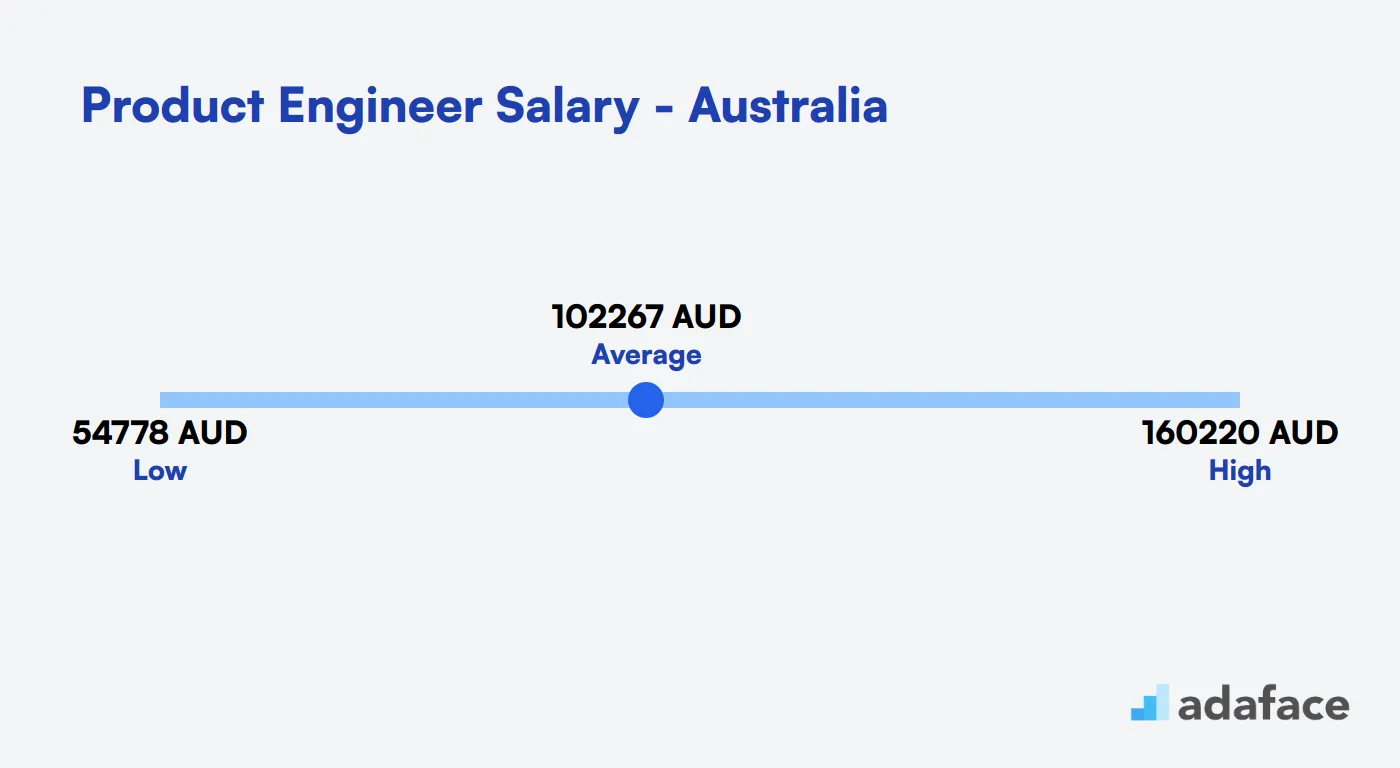
Product Engineer Salary in Australia
When considering hiring a Product Engineer in Australia, it's important to understand the salary landscape. The average salary nationwide is around AUD 102,268. In Melbourne, salaries range from AUD 88,993 to AUD 171,267, with a median of AUD 123,456. Meanwhile, in Sydney, typical salaries are between AUD 72,409 and AUD 144,333, with a median of AUD 102,230. These figures can help guide your budgeting and expectations when seeking the right candidate.
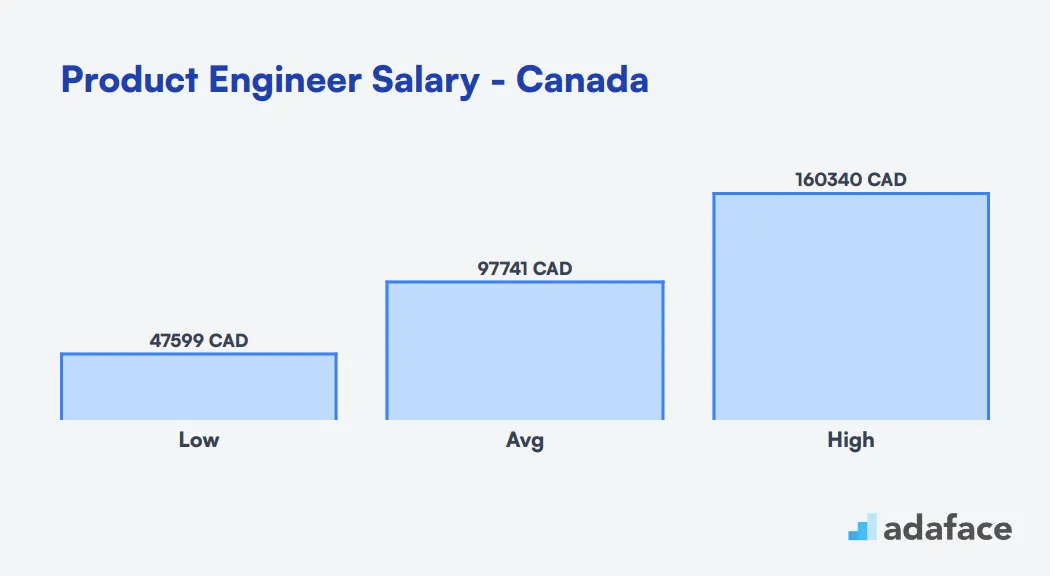
Product Engineer Salary in Canada
In Canada, the average salary for a Product Engineer varies significantly depending on the location. On a country-wide level, the average salary is about CAD 97,741. In Toronto, Product Engineers earn between CAD 83,150 and CAD 233,523, with a median of CAD 139,347. Meanwhile, in Ottawa, the range is from CAD 71,043 to CAD 149,681, and the median salary is CAD 103,120. These figures illustrate that salaries can fluctuate widely based on the city and demand for product engineers in that area.
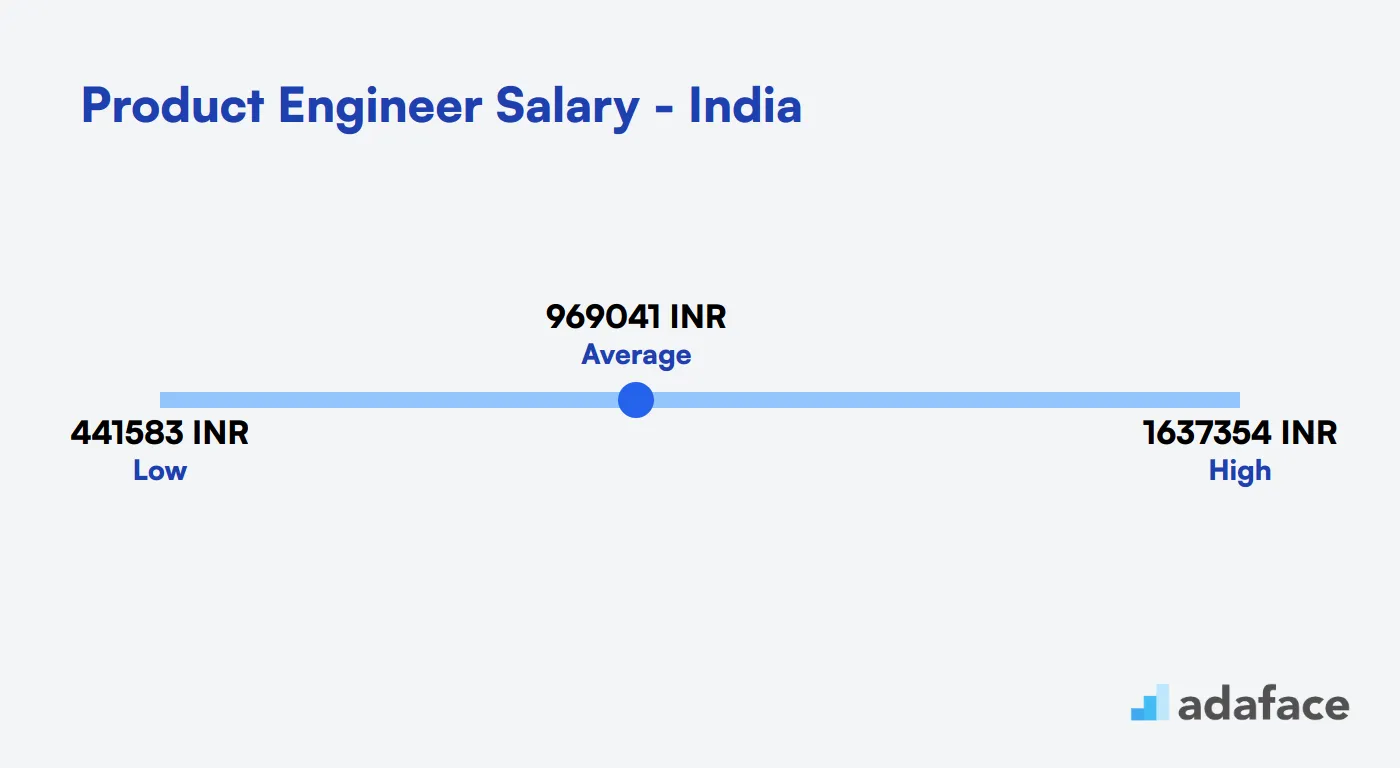
Product Engineer Salary in India
The average salary for a Product Engineer in India is approximately INR 969,041 per year. This varies widely across cities, with Bengaluru typically offering salaries between INR 440,058 and INR 1,655,746. In Delhi, the range is from INR 321,614 to INR 1,667,593. While in Mumbai, you can expect figures from INR 809,134 to INR 1,341,899. These numbers reflect the diverse economic landscape and demand across different regions.
What's the difference between a Product Engineer and a Software Engineer?
Many hiring managers often confuse the roles of Product Engineer and Software Engineer due to the overlap in their technical skills. However, each role has distinct responsibilities and focuses, making it essential to understand their differences when hiring.
A Product Engineer is primarily focused on user-centric product development. They work closely with product managers, designers, and stakeholders to create products that resonate with users. Their key skills include UX/UI design, prototyping, and product strategy, which guide their decision-making towards enhancing user experience and product features. They measure their success through user engagement and product adoption metrics.
In contrast, a Software Engineer emphasizes technical implementation. They collaborate with other developers, QA, and DevOps to ensure high-quality code and system performance. Their core competencies lie in programming, algorithms, and system design, which are instrumental in developing reliable and scalable applications. Success for them is often gauged through code quality, performance, and scalability metrics.
In summary, while both roles share overlapping skills, they focus on different aspects of product development and engineering. Understanding these differences can help in making better hiring decisions, ensuring that the right talent is brought on board for the respective roles.
| Product Engineer | Software Engineer | |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | User-centric product development | Technical implementation |
| Primary Skills | UX/UI, prototyping, product strategy | Programming, algorithms, system design |
| Collaboration | Product managers, designers, stakeholders | Other developers, QA, DevOps |
| Metrics | User engagement, product adoption | Code quality, performance, scalability |
| Tools | Prototyping tools, analytics platforms | IDEs, version control, CI/CD tools |
| Decision Making | Product features, user experience | Technical architecture, implementation details |
| Business Impact | Direct influence on product strategy | Indirect through technical excellence |
| Career Path | Product management, CTO | Technical lead, software architect |
What are the ranks of Product Engineers?
Product Engineers often have a career progression that spans multiple levels of expertise and responsibility. Understanding these ranks can help both job seekers and hiring managers navigate the career ladder in this field.
- Junior Product Engineer: This entry-level position is for those new to the field. They work on smaller features or components under close supervision, learning the ropes of product development and engineering practices.
- Product Engineer: At this level, engineers take on more complex projects independently. They contribute significantly to product features and may lead small teams on specific tasks.
- Senior Product Engineer: These experienced professionals lead major product initiatives. They mentor junior team members and play a key role in technical decision-making and architecture design.
- Lead Product Engineer: Lead engineers oversee entire product lines or large-scale projects. They balance technical leadership with people management, often guiding teams of 5-10 engineers.
- Principal Product Engineer: This high-level position focuses on strategic technical direction. Principal engineers influence product roadmaps, set engineering standards, and often work across multiple teams or departments.
- Director of Product Engineering: At this executive level, the role involves setting the overall technical strategy for product development. They manage multiple teams and collaborate closely with other department heads.
Each rank brings new challenges and responsibilities, requiring a mix of technical skills and soft skills. When hiring, it's important to assess candidates not just on their technical abilities but also on their leadership and problem-solving skills.
Hire the Best Product Engineers for Your Team
We've covered the role of Product Engineers, their key responsibilities, and the skills they need. We've also discussed how to write effective job descriptions, where to find candidates, and how to assess them through various methods including skills tests and interviews.
If there's one key takeaway, it's the importance of using well-crafted job descriptions and skills tests to make your hiring process more accurate. By focusing on these elements, you'll be better equipped to identify and attract the Product Engineers who can truly drive innovation and success for your company.
Product Manager Online Test
FAQs
Product Engineers focus on building features that directly impact user experience and business goals, while Software Engineers typically concentrate more on technical implementation. Product Engineers often have a broader skill set that includes both technical expertise and product strategy understanding.
Key skills for a Product Engineer include strong coding abilities, product sense, user empathy, problem-solving skills, and effective communication. They should also have experience with agile methodologies and be comfortable working closely with product managers and designers.
You can use coding tests and technical interviews to evaluate their programming skills. Additionally, consider giving them a small product-related problem to solve, which can help assess their ability to balance technical and product considerations.
Look for candidates on professional networking sites, tech job boards, and at industry events. Employee referrals can also be valuable. Consider partnering with universities or coding bootcamps that offer product engineering courses.
Start with a phone screen, followed by a technical assessment. Then conduct in-person or video interviews that include both technical discussions and product-focused scenarios. Consider including a take-home project that mimics real-world product engineering challenges.
Ask about their experience balancing technical and product needs, how they've contributed to product strategy, and examples of features they've built that improved user experience. Also, inquire about their approach to collaboration with product managers and designers. For more ideas, check our Product Engineer interview questions.
Besides technical skills, assess their communication style, teamwork abilities, and cultural fit. Consider including team members in the interview process and potentially have a trial period or project to ensure compatibility.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



