Hiring a Product Designer is a critical task for companies aiming to create user-centric products and services. Many organizations underestimate the impact a skilled Product Designer can have on their business outcomes. The right candidate brings a unique blend of creativity, technical know-how, and business acumen that can significantly enhance product development and user satisfaction.
This guide offers a step-by-step approach to hiring top-notch Product Designers. We'll cover everything from understanding the role to conducting effective interviews and assessments. For a deeper dive into evaluating design skills, check out our UI/UX Design Test.
Table of contents
Why Hire a Product Designer?
A Product Designer can solve various design challenges your company faces. They can improve user experience issues with your current products or create new designs for upcoming offerings. For example, if your app has a high drop-off rate during onboarding, a Product Designer can redesign the flow to make it more intuitive.
Product Designers also bring valuable skills to your team, such as:
- User research and analysis
- Prototyping and wireframing
- Visual design and branding
- Collaboration with developers and stakeholders
Consider hiring a full-time Product Designer if you have ongoing design needs or are scaling your product offerings. For short-term projects or to test the waters, you might start with a product design consultant before committing to a permanent hire.
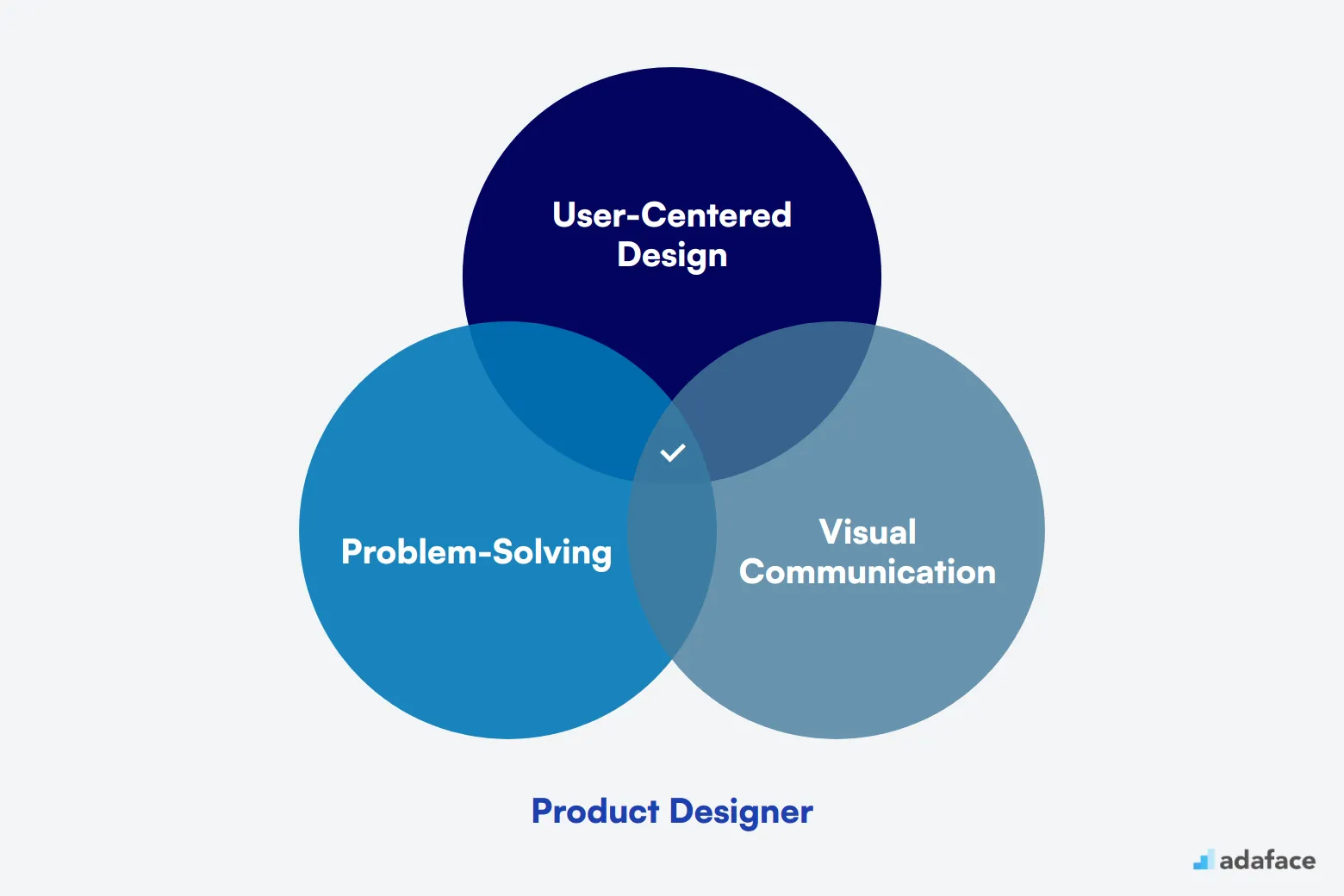
What Does a Product Designer Do?
A Product Designer is responsible for creating meaningful and functional user experiences. They work closely with cross-functional teams to design products that are both visually appealing and easy to use, aligning with business goals and user needs.
Day-to-day tasks of a Product Designer include:
- Collaborating with stakeholders to understand and define product requirements.
- Creating wireframes, prototypes, and visual designs to communicate design concepts.
- Conducting user research and usability testing to gather feedback and improve product designs.
- Working with developers to ensure that designs are implemented accurately.
To learn more about the skills needed for a Product Designer, you can explore our skills required for product designer guide.
Key skills and qualifications for a Product Designer
Creating an ideal candidate profile for a Product Designer can be tricky. It's important to distinguish between must-have skills and nice-to-have qualifications. This helps you focus on candidates who can truly drive your product's success.
Here's a quick overview of the skills and qualifications to consider when hiring a Product Designer:
Required skills and qualifications:
- Bachelor's degree in Design, HCI, or related field
- 3+ years of experience in product design or UX/UI design
- Proficiency in design tools (e.g., Figma, Sketch, Adobe Creative Suite)
- Strong portfolio demonstrating user-centered design process
- Experience with user research and usability testing
Preferred skills and qualifications:
- Master's degree in Design, HCI, or related field
- Experience in a fast-paced, agile environment
- Knowledge of front-end development (HTML, CSS, JavaScript)
- Experience with design systems and component libraries
- Familiarity with data visualization and information architecture
Remember, these are general guidelines. Tailor this list to your specific product and team needs for the best results.
| Required skills and qualifications | Preferred skills and qualifications |
|---|---|
| Bachelor's degree in Design, HCI, or related field | Master's degree in Design, HCI, or related field |
| 3+ years of experience in product design or UX/UI design | Experience in a fast-paced, agile environment |
| Proficiency in design tools (e.g., Figma, Sketch, Adobe Creative Suite) | Knowledge of front-end development (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) |
| Strong portfolio demonstrating user-centered design process | Experience with design systems and component libraries |
| Experience with user research and usability testing | Familiarity with data visualization and information architecture |
How to write a Product Designer job description?
Crafting an accurate Product Designer job description is key to attracting the right talent. Once you have identified the candidate profile, it's time to document these details effectively in the job description.
- Highlight key responsibilities and impact: Clearly define the role's responsibilities and the expected impact on product development and user experience. This attracts candidates who are eager to contribute significantly to your product's success.
- Balance technical skills with soft skills: While listing technical requirements like proficiency in design tools such as Sketch or Figma is important, don't forget to include soft skills like creativity and communication. A well-rounded description ensures you attract candidates who are not only technically sound but also adept at collaboration.
- Showcase unique selling points of your company: Emphasize what makes your company stand out, whether it's innovative projects, a strong team culture, or opportunities for professional growth. This can help differentiate your role from similar positions in the market.
For more details, explore our comprehensive Product Designer job description page to gather insights and examples.
10 Platforms to Hire Product Designers
Now that you have a job description ready, it’s time to list it on various job sites to attract suitable candidates. Using the right platforms can help you reach a broader audience and increase the chances of finding the perfect product designer for your team.
LinkedIn Jobs
Ideal for finding professional, full-time product designers due to its large professional network and recruitment tools.
Indeed
A comprehensive job listing platform suitable for hiring full-time product designers across various industries.
Dribbble Jobs
Great for finding freelance product designers, especially those with a strong focus on visual design.
Some of the most effective platforms include LinkedIn Jobs for professional full-time designers, Indeed for a comprehensive job listing experience, and Dribbble Jobs for creative freelance designers. These sites cater to different needs, whether you’re looking for full-time talent or freelancers with a strong visual design focus. Other notable platforms worth exploring include Upwork for versatile freelance arrangements, AngelList for startups, and Behance Jobs for access to a community of creative professionals.
How to Screen Product Designer Resumes?
Resume screening is a fundamental step when hiring a Product Designer, given the number of applications a job posting can receive. It's your first filter to identify candidates whose skills and experiences align with your company's needs. This process helps you focus on the most promising applicants for further evaluation.
To manually screen resumes, familiarize yourself with key skills and qualifications. Look for primary keywords like 'User-Centered Design', 'Prototyping', or 'Figma'. A strong portfolio, proficiency in design tools, and experience in user research are also significant indicators of a good fit. This method enables you to swiftly eliminate those not meeting your core requirements.
Alternatively, you can leverage AI LLMs for resume screening, which can save time and enhance precision. By inputting the criteria you're seeking, AI tools can highlight resumes containing the right keywords, enhancing decision-making. Consider utilizing platforms that offer AI resume screening to streamline this process.
To aid in AI-assisted screening, here's a sample prompt you can use:
TASK: Screen resumes to match job description for Product Designer role
INPUT: Resumes
OUTPUT: For each resume, provide following information:
- Email id
- Name
- Matching keywords
- Score (out of 10 based on keywords matched)
- Recommendation (detailed recommendation of whether to shortlist this candidate or not)
- Shortlist (Yes, No, or Maybe)
RULES:
- If unsure, mark the candidate as Maybe instead of No
- Keep recommendations crisp.
KEYWORDS DATA:
- User-Centered Design, Figma, Adobe Creative Suite, User Research, Usability Testing
- Experience with design systems, HTML, CSS, JavaScript
Recommended Skills Tests for Assessing Product Designers
Skills tests are a great way to evaluate Product Designer candidates beyond their resumes. They provide objective insights into a candidate's abilities and help you make informed hiring decisions. Here are some key tests we recommend for assessing Product Designers:
UI/UX Design Test: This UI/UX Design test evaluates a candidate's proficiency in user interface and user experience design principles. It assesses their ability to create intuitive, visually appealing designs that enhance user satisfaction.
Graphic Design Test: A Graphic Design assessment helps gauge a candidate's visual design skills. It measures their ability to create compelling visuals, understand color theory, and effectively communicate through design.
Problem-Solving Test: Product Designers often face complex challenges. A Problem-Solving test evaluates their ability to analyze issues, think critically, and develop innovative solutions.
Visual Reasoning Test: This Visual Reasoning test assesses a candidate's ability to interpret and manipulate visual information. It's particularly useful for evaluating how well they can translate abstract concepts into concrete designs.
Attention to Detail Test: Product design requires precision. An Attention to Detail test helps identify candidates who can spot subtle design issues and maintain consistency across their work.
Structuring the Interview Stage for Product Designer Hiring
After candidates pass the initial skills tests, it's crucial to conduct technical interviews to further evaluate their hard skills. While skills tests are effective for initial screening, technical interviews help identify the best-suited candidates for the Product Designer role. Let's explore some sample interview questions to assess candidates effectively.
Consider asking these questions during the interview:
- Can you walk us through your design process for a recent project?
- How do you balance user needs with business requirements?
- What tools do you use for prototyping, and why?
- How do you handle feedback and iterate on your designs?
- Can you describe a situation where you had to make design trade-offs?
- How do you stay updated with the latest design trends and technologies?
These questions help evaluate the candidate's practical experience, problem-solving skills, and approach to design challenges.
How Much Does It Cost to Hire a Product Designer?
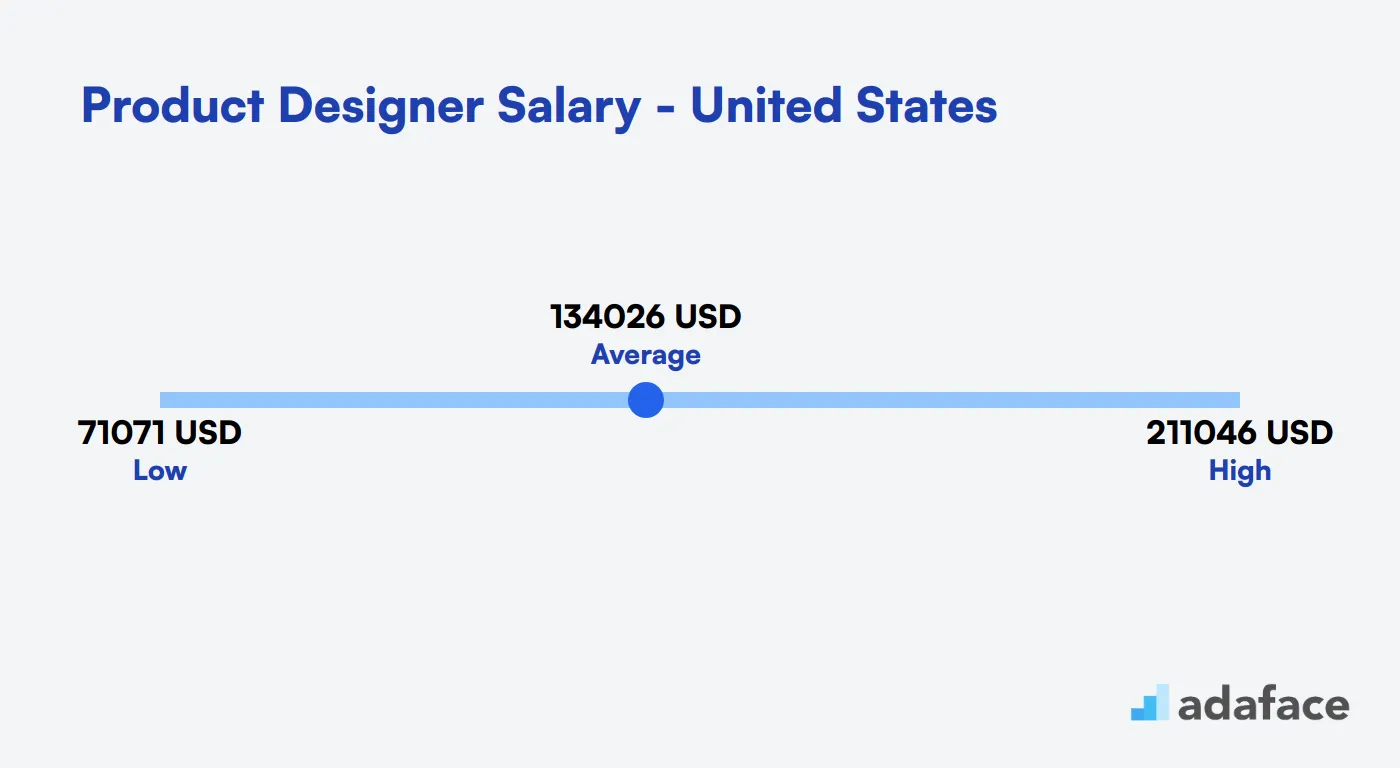
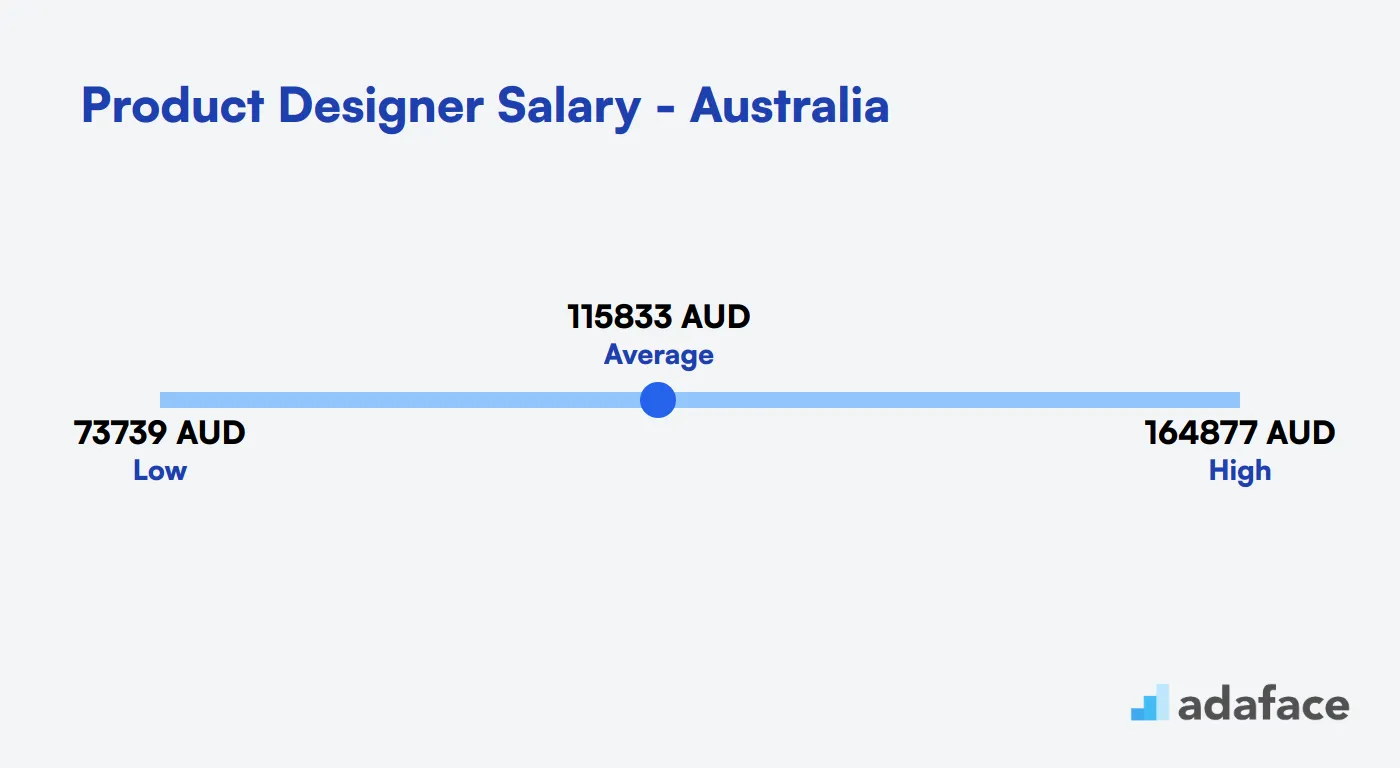
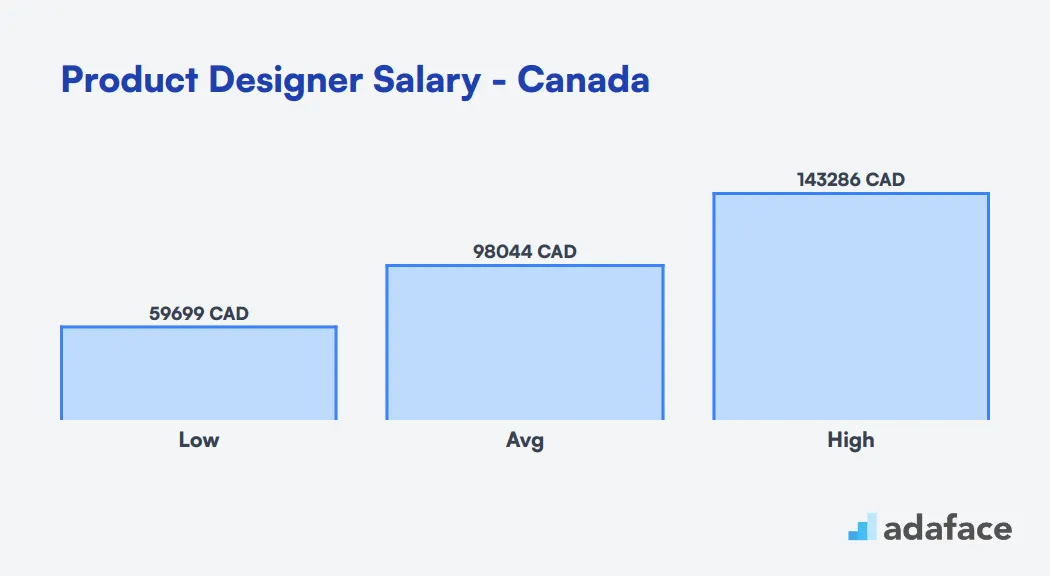
The cost to hire a Product Designer can vary widely based on location and experience. In the United States, average salaries hover around $134,027 annually, with tech hubs offering salaries up to $250,135. Meanwhile, in Australia, salaries range from $73,740 AUD to $164,877 AUD. In Canada, expect averages near $98,045 CAD. These figures highlight the importance of considering regional salary variations to attract top talent.
Product Designer Salary in the United States
Product Designer salaries in the United States vary widely based on location and experience. On average, a Product Designer can expect to earn around $134,027 annually. In tech hubs like Menlo Park and Cupertino, CA, salaries can range from $133,334 to $250,135, while places like Springfield, MO, offer a range of $56,865 to $92,839. The median salary overall is approximately $122,472.
Product Designer Salary Australia
In Australia, the average salary for a Product Designer varies significantly by location. For instance, in Sydney, the mean salary is approximately $128,879 AUD, while in Brisbane it stands at around $127,115 AUD. Salaries generally range from $73,740 AUD to $164,877 AUD across different regions. Understanding these variations can help in offering competitive salaries to attract top talent.
Product Designer Salary in Canada
The average salary for a Product Designer in Canada is approximately $98,045 CAD. Salaries can vary widely by province, with the lowest average around $66,100 CAD in Winnipeg and the highest reaching $113,929 CAD in Ottawa. When hiring, it's important to consider these regional differences to attract the right talent.
What's the difference between a UX Designer and a UI Designer?
People often confuse a UX Designer with a UI Designer because both aim to create enjoyable digital experiences. However, their roles, skills, and focus areas are distinct.
A UX Designer is primarily concerned with the user's experience and behavior. They engage heavily in user research, wireframing, and prototyping, delivering outputs like user flows, personas, and journey maps. Their toolkit often includes Figma, Sketch, and UserTesting, and they have strong analytical skills with frequent interaction with users.
On the other hand, a UI Designer focuses on the visual elements of digital interfaces—such as aesthetics and layout. They specialize in visual design, typography, and color theory, and their deliverables include visual mockups and UI kits. Tools like the Adobe Creative Suite and Sketch are staples for them, and while a basic understanding of coding is helpful, it is not typically required.
For more insights into the skills required for a product designer, you can explore the Adaface blog on skills required for designers.
| UX Designer | UI Designer | |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | User experience and behavior | Visual design and aesthetics |
| Primary Skills | User research, wireframing, prototyping | Visual design, typography, color theory |
| Deliverables | User flows, personas, journey maps | Visual mockups, style guides, UI kits |
| Tools | Figma, Sketch, UserTesting | Adobe Creative Suite, Sketch, Figma |
| Research Involvement | High | Low to moderate |
| Interaction with Users | Frequent | Limited |
| Analytical Skills | Strong | Moderate |
| Coding Knowledge | Basic understanding helpful | Not typically required |
What are the ranks of Product Designers?
Product design roles can often be confusing due to the overlap with similar positions like UI and UX design. Understanding the various ranks of product designers can help recruiters and hiring managers identify the right talent for their teams.
• Junior Product Designer: This is typically an entry-level position. Junior Product Designers assist in designing products and may focus on specific areas like user interface or user experience under the guidance of more experienced designers.
• Product Designer: At this level, designers are expected to have a solid understanding of the design process and can manage projects independently. They are responsible for creating user-centered designs that meet business objectives.
• Senior Product Designer: A Senior Product Designer has extensive experience and often leads design projects. They provide strategic direction and mentor junior designers, ensuring that design solutions align with user needs and business goals.
• Lead Product Designer: This role involves overseeing a team of designers and coordinating design efforts across multiple projects. Lead Product Designers set the design vision and ensure consistency in user experience across products.
• Product Design Manager: A Product Design Manager focuses on team leadership and project management. They are responsible for hiring, training, and guiding the design team while collaborating with other departments to achieve strategic objectives.
Hire the Right Product Designers for Your Team
Throughout this guide, we have explored various aspects of hiring a Product Designer, from understanding their role to screening resumes and structuring interviews. We also covered key skills and how to write effective job descriptions that attract top talent.
The key takeaway for hiring managers and recruiters is to use detailed job descriptions and appropriate skills tests to identify the right candidates. By incorporating tailored assessments like the UI/UX Design Test, you can ensure that the candidates not only fit the role but also your company's culture. Making use of these tools will streamline your hiring process, helping you find the best fit for your team.
UI/UX Design Test
FAQs
Key skills for a Product Designer include user experience (UX) design, user interface (UI) design, prototyping, user research, and problem-solving. They should also have knowledge of design tools, understand business goals, and possess strong communication skills.
When reviewing a Product Designer's portfolio, look for diverse projects, clear problem-solving processes, attention to user needs, and the impact of their designs. Ask for detailed explanations of their role in each project and the outcomes achieved.
Ask about their design process, how they handle user feedback, their experience with design tools, how they collaborate with other teams, and examples of challenges they've overcome in previous projects. For more ideas, check our Product Designer Interview Questions.
While industry experience can be beneficial, it's not always necessary. Look for transferable skills and a candidate's ability to adapt to new domains. A diverse background can often bring fresh perspectives to product design challenges.
Yes, design tests can be valuable in assessing a candidate's practical skills. Consider using a combination of take-home assignments and on-site design challenges. Our UI/UX Design Test can help evaluate key competencies.
An effective job description should clearly outline the role's responsibilities, required skills, and your company's design philosophy. Be specific about the types of products they'll work on and the team structure. For guidance, refer to our Product Designer Job Description template.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



