Hiring a Problem Manager is like finding a skilled detective for your IT department. They're the ones who dig deep into recurring issues, preventing them from becoming major headaches down the line. Many companies overlook the importance of this role, focusing solely on putting out fires rather than preventing them. A good Problem Manager can save your organization time, money, and reputation by addressing the root causes of persistent problems.
This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to hire a top-notch Problem Manager. We'll cover everything from understanding the role to crafting an effective job description and conducting insightful interviews. For a deeper dive into the specific skills required for this position, check out our detailed skills breakdown for Problem Managers.
Table of contents
Why hire a Problem Manager?
To decide if you need a Problem Manager, start by identifying recurring issues that impact your business operations. For example, you might be experiencing frequent system outages that disrupt customer service and need someone to find and fix the root causes.
Consider hiring a Problem Manager when:
- You're facing complex, interconnected IT issues
- Incident resolutions are often temporary fixes
- You need to improve service quality and reduce downtime
If you're unsure about committing to a full-time role, consider starting with a consultant. They can assess your needs and help you determine if a permanent Problem Manager is necessary for your organization.
What Does a Problem Manager Do?
A Problem Manager is responsible for identifying, investigating, and resolving recurring issues within an organization's IT infrastructure. They work to minimize the impact of incidents and problems on business operations by finding and implementing long-term solutions.
The day-to-day tasks of a Problem Manager include:
- Analyzing incident patterns and trends to identify underlying problems
- Coordinating with various IT teams to investigate root causes
- Developing and implementing permanent fixes for recurring issues
- Maintaining a knowledge base of known errors and their resolutions
- Conducting problem reviews and post-implementation evaluations
- Providing regular updates to stakeholders on problem management activities
- Collaborating with Change Management to ensure smooth implementation of solutions
Problem Manager Hiring Process
The Problem Manager hiring process typically takes around 1-2 months, depending on the company's requirements and the availability of suitable candidates.
- Post the Job Description: Start by creating a clear and detailed job description for the Problem Manager role, highlighting the key responsibilities and qualifications required. Post the job on relevant job boards and your company's career page.
- Resume Screening: Within the first 3-4 days, you can expect to receive resumes from interested candidates. Carefully review and shortlist the resumes that align with the job requirements.
- Skill Assessment: Once you have a pool of qualified candidates, administer relevant skill assessments or case studies to evaluate their problem-solving abilities, critical thinking, and technical knowledge. This process may take a week or more.
- Interviews: Invite the top candidates for interviews, which may include a combination of technical, behavioral, and situational questions. This stage helps assess their communication skills, problem-solving approach, and overall fit for the role.
- Final Selection and Offer: After evaluating the interview performance, select the most suitable candidate and proceed with the hiring process, including reference checks and job offer negotiations.
Skills and qualifications to look for in a Problem Manager
Creating an ideal candidate profile for a Problem Manager can be tricky. Many recruiters focus too much on technical skills and overlook critical soft skills. It's important to strike a balance between required technical expertise and preferred attributes that can enhance the role.
Here are the key skills and qualifications to consider when hiring a Problem Manager:
Required Skills and Qualifications:
- Bachelor's degree in Computer Science, IT, or related field
- 5+ years of experience in IT service management or problem management
- Strong knowledge of ITIL framework and problem management processes
- Excellent analytical and problem-solving skills
- Proficiency in incident and problem management tools
Preferred Skills and Qualifications:
- ITIL certification
- Experience with root cause analysis techniques
- Knowledge of change management and release management processes
- Familiarity with project management methodologies
- Experience in a large enterprise environment
When evaluating candidates, focus on their ability to apply analytical tools like root cause analysis, Ishikawa diagrams, and 5 Whys. These skills are often more valuable than specific tool knowledge, which can be learned on the job.
| Required skills and qualifications | Preferred skills and qualifications |
|---|---|
| Bachelor's degree in Computer Science, IT, or related field | ITIL certification |
| 5+ years of experience in IT service management or problem management | Experience with root cause analysis techniques |
| Strong knowledge of ITIL framework and problem management processes | Knowledge of change management and release management processes |
| Excellent analytical and problem-solving skills | Familiarity with project management methodologies |
| Proficiency in incident and problem management tools | Experience in a large enterprise environment |
How to Write a Problem Manager Job Description
Once you've identified the ideal candidate profile for a Problem Manager, the next step is crafting a compelling job description. Here are some quick tips to help you attract top talent:
Highlight key responsibilities: Clearly outline the Problem Manager's role in identifying, tracking, and resolving IT issues. Mention their involvement in root cause analysis and implementing preventive measures.
Balance technical and soft skills: While technical expertise is important, emphasize soft skills like communication, leadership, and stakeholder management. Include any required Problem Manager certifications or industry experience.
Showcase your company culture: Highlight what makes your IT department unique, such as cutting-edge technologies or opportunities for professional growth. This helps candidates envision themselves in the role and your organization.
Top Platforms to Hire Problem Managers
Now that you have crafted a compelling job description, the next step is to list your open Problem Manager position on job listing sites. This approach will help you source qualified candidates efficiently and expand your reach in finding the ideal match for your organization.
LinkedIn Jobs
Ideal for posting full-time Problem Manager positions. Offers extensive reach and professional networking capabilities.
Indeed
Versatile platform suitable for posting various job types. Offers wide reach and easy application process for candidates.
Glassdoor for Employers
Effective for established companies looking to hire Problem Managers. Provides company reviews and salary insights.
For the remaining platforms, Dice Hiring is perfect for tech-focused roles, while ZipRecruiter offers AI-powered matching suitable for small to medium businesses. Monster for Employers provides access to a diverse candidate pool, and Upwork and Toptal are excellent for freelance opportunities. AngelList Talent caters to startups, and FlexJobs for Employers specializes in remote and flexible positions, offering various options to match your hiring need. For more insights on hiring effectively, explore our guide on attracting top technical talent.
How to Screen Problem Manager Resumes
Resume screening is a key step in the hiring process, allowing you to efficiently narrow down the pool of applicants to those who truly fit the role. With numerous applications, it becomes vital to quickly identify the candidates who meet the basic requirements and have the potential to thrive in the position.
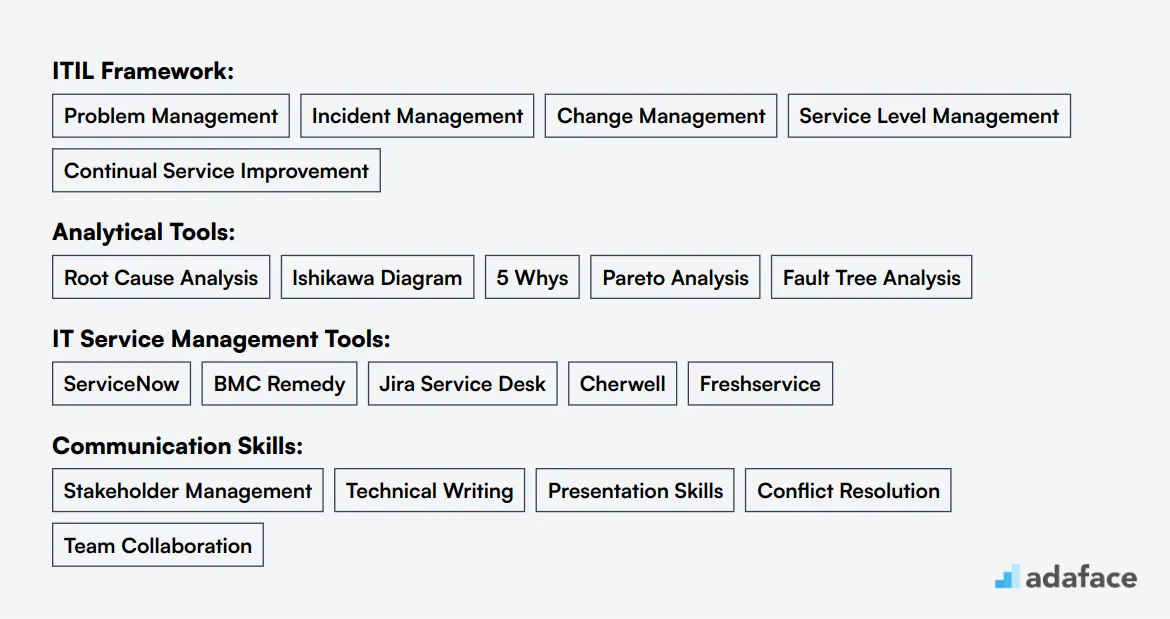
When manually screening resumes, it's important to focus on specific keywords related to the Problem Manager role. Look for terms such as ITIL framework, problem management processes, and tools like ServiceNow or Jira Service Desk. Highlight candidates with a Bachelor's degree in Computer Science or a related field, and those possessing strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
Leveraging AI-powered tools like LLMs (Language Model Machines) can streamline the resume screening process. By inputting your desired keywords, these tools can scan through resumes and match candidates to your job description. This helps save time and ensures a more objective review by focusing purely on the content.
Here's a handy AI prompt to use for screening Problem Manager resumes:
TASK: Screen resumes to match job description for Problem Manager role
INPUT: Resumes
OUTPUT: For each resume, provide the following information:
- Email id
- Name
- Matching keywords
- Score (out of 10 based on keywords matched)
- Recommendation (detailed recommendation of whether to shortlist this candidate or not)
- Shortlist (Yes, No, or Maybe)
RULES:
- If unsure about a candidate's fit, list as Maybe instead of No
- Keep recommendation crisp and to the point
KEYWORDS DATA:
- ITIL framework
- Problem management
- Root cause analysis
- Analytical tools
- Incident management tools like ServiceNow
To gain more insights into crafting job descriptions for this role, visit our Problem Manager job description page. Also, explore our skills assessment tools to further refine your screening process.
Recommended skills tests for assessing Problem Managers
Skills tests are an effective way to evaluate Problem Manager candidates beyond their resumes. They provide objective insights into a candidate's abilities and readiness for the role. Here are five key tests we recommend for assessing Problem Managers:
Problem-solving test: This problem-solving test evaluates a candidate's ability to analyze complex situations and develop effective solutions. It's particularly relevant for Problem Managers who need to tackle diverse challenges daily.
Critical thinking test: A critical thinking assessment measures a candidate's ability to evaluate information objectively and make sound judgments. This skill is essential for Problem Managers when prioritizing issues and making decisions under pressure.
Attention to detail test: Problem Managers must be meticulous in their work. An attention to detail test helps identify candidates who can spot small but significant details that might impact problem resolution.
Logical reasoning test: A logical reasoning assessment evaluates a candidate's ability to draw valid conclusions from given information. This skill is valuable for Problem Managers when analyzing root causes and developing action plans.
Management trainee test: While not specific to problem management, a management trainee test can assess a candidate's potential for leadership and coordination. These skills are important for Problem Managers who often need to lead cross-functional teams during incident resolution.
Case Study Assignments to Evaluate Problem Managers
Case study assignments can be effective for assessing Problem Manager candidates, but they come with drawbacks. These assignments often have low completion rates due to their length and may result in losing qualified candidates. Despite these challenges, well-designed case studies can provide valuable insights into a candidate's problem-solving abilities.
IT Service Disruption Scenario: This case study presents a complex IT service outage affecting multiple departments. Candidates must analyze the situation, identify root causes, and propose both short-term fixes and long-term solutions. This assignment tests their problem-solving skills and ability to manage critical incidents.
Process Improvement Challenge: Candidates are given a fictional company with inefficient problem management processes. They must review the current procedures, identify bottlenecks, and suggest improvements to streamline operations. This case study evaluates their process optimization abilities and strategic thinking.
Stakeholder Communication Exercise: This assignment focuses on a sensitive problem affecting high-profile clients. Candidates must create a communication plan to address stakeholders at various levels, demonstrating their ability to manage expectations and communicate effectively in challenging situations.
Structuring Technical Interviews for Problem Manager Candidates
After candidates pass initial skills tests, it's important to conduct technical interviews to thoroughly assess their hard skills. While skills tests are great for filtering out unfit candidates, they may not always identify the best fit for the role. Technical interviews allow for a deeper evaluation of a candidate's problem-solving abilities and domain knowledge.
Some key questions to ask in a Problem Manager interview include: 'Can you describe a complex problem you've managed and how you approached it?', 'How do you prioritize multiple ongoing issues?', 'What metrics do you use to measure problem management effectiveness?', 'How do you handle stakeholder communication during critical problems?', and 'Can you explain your process for root cause analysis?'. These questions help assess the candidate's problem-solving skills, prioritization abilities, analytical thinking, communication skills, and technical knowledge - all crucial for a Problem Manager role.
What's the difference between a Problem Manager and an Incident Manager?
It's easy to confuse Problem Managers and Incident Managers since both roles deal with IT issues. However, their approaches and end goals are quite distinct. While an Incident Manager focuses on immediate resolution and restoration, a Problem Manager aims to identify and prevent root causes of issues.
Problem Managers work with a long-term perspective. Their primary responsibilities include trend analysis and problem prevention, with the goal of reducing recurring incidents. They use tools like root cause analysis and knowledge bases and interact with cross-functional teams and management.
Incident Managers, on the other hand, concentrate on short-term fixes. They handle incidents to minimize service disruptions, ensuring quick service restoration. Their key responsibilities involve incident handling and maintaining SLA compliance using ticketing systems and monitoring tools. They primarily interact with end-users and support teams.
For a deeper understanding of the skills required for a Problem Manager, you can explore our skills blog.
| Problem Manager | Incident Manager | |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Root cause analysis and prevention | Immediate resolution and restoration |
| Time Perspective | Long-term | Short-term |
| Key Responsibilities | Trend analysis, problem prevention | Incident handling, service restoration |
| Primary Goal | Reduce recurring incidents | Minimize service disruption |
| Metrics | Problem resolution time, recurrence rate | Incident resolution time, SLA compliance |
| Interaction with Stakeholders | Cross-functional teams, management | End-users, support teams |
| Tools Used | Root cause analysis tools, knowledge bases | Ticketing systems, monitoring tools |
| ITIL Process Alignment | Problem Management | Incident Management |
Hire the Best Problem Managers
We've covered the role of Problem Managers, their responsibilities, and the hiring process. We've also discussed key skills, qualifications, and how to write an effective job description. The importance of resume screening, skills tests, and structured interviews has been highlighted to help you find the right candidate.
If there's one key takeaway, it's the importance of using accurate job descriptions and skills tests to make your hiring process more precise. By implementing these strategies, you'll be well-equipped to identify and hire Problem Managers who can drive your organization's success in resolving complex issues.
Problem Solving Test
FAQs
While both roles deal with IT issues, an Incident Manager focuses on restoring service quickly after an incident occurs. A Problem Manager, on the other hand, investigates the root causes of recurring incidents to prevent them from happening again in the future.
Key skills for a Problem Manager include analytical thinking, ITIL knowledge, communication skills, and experience with problem-solving methodologies. Technical expertise in relevant IT systems is also valuable.
Use a combination of problem-solving tests, case studies, and scenario-based interview questions. This approach helps evaluate how candidates approach complex issues and their ability to implement effective solutions.
Include key responsibilities such as root cause analysis, trend identification, and process improvement. Highlight required qualifications like ITIL certification, relevant experience, and specific technical skills. Our Problem Manager job description template can provide a comprehensive starting point.
ITIL certification is highly valuable for a Problem Manager as it ensures they understand best practices in IT service management. However, practical experience and problem-solving skills can sometimes outweigh certification, especially for candidates with a strong track record.
Use a mix of behavioral and situational questions focused on past experiences with problem-solving, process improvement, and stakeholder management. Our Problem Manager interview questions guide offers a comprehensive list to help you evaluate candidates effectively.
Look for candidates with strong collaboration skills and experience working across different IT functions. During the interview, ask about their approach to team communication and how they've handled conflicts or resistance to change in previous roles.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



