Hiring a Linux Administrator can be a challenging task for recruiters and hiring managers. Many companies underestimate the importance of this role in maintaining their IT infrastructure and ensuring smooth operations. A skilled Linux Administrator is key to managing servers, implementing security measures, and optimizing system performance. However, finding the right candidate requires a deep understanding of the technical skills and experience needed for the job.
This guide will walk you through the process of hiring a Linux Administrator, from identifying key skills to conducting effective interviews. We'll cover everything you need to know to find the best Linux Administrator for your organization.
Table of contents
Linux Administrator Hiring Process
The Linux Administrator hiring process typically spans 4-6 weeks. Here's a quick overview of the timeline and steps involved:
- Create and post a detailed job description on relevant platforms
- Review resumes and shortlist candidates (1-2 weeks)
- Conduct initial screening calls (3-5 days)
- Administer technical assessments (5-7 days)
- Schedule and conduct interviews (1-2 weeks)
- Make a job offer to the selected candidate
This process allows for thorough evaluation of candidates' skills and fit. In the following sections, we'll dive deeper into each step, providing checklists and resources to help you find the ideal Linux Administrator for your team.
Key Skills and Qualifications for a Linux Administrator
Hiring a Linux Administrator requires a clear understanding of the specific skills and qualifications necessary for the role. It can be tricky to differentiate between what is essential and what is simply nice to have, especially since different companies may prioritize these factors differently.
To aid your hiring process, it's beneficial to outline both required and preferred skills and qualifications. This clarity helps you attract candidates who not only meet your basic needs but also bring additional value to your team.
| Required skills and qualifications | Preferred skills and qualifications |
|---|---|
| Strong knowledge of Linux operating systems (e.g., Ubuntu, CentOS, Red Hat) | Certification in Linux administration (e.g., RHCSA, LPIC) |
| Experience with shell scripting (Bash, Python) | Experience with configuration management tools (Ansible, Puppet, Chef) |
| Proficiency in system administration tasks (user management, security, backups) | Knowledge of virtualization technologies (VMware, KVM) |
| Familiarity with networking concepts and protocols | Familiarity with cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP) |
| Troubleshooting and problem-solving skills | Understanding of containerization (Docker, Kubernetes) |
How to Write an Effective Linux Administrator Job Description
Once you've outlined the ideal candidate profile, the next step is crafting a job description that attracts top Linux talent. Here are some key tips to create a compelling Linux Administrator job description:
- Highlight key responsibilities: Clearly define the role's tasks, such as system maintenance, security management, and troubleshooting. Emphasize how the administrator's work impacts the organization's IT infrastructure.
- Balance technical requirements with soft skills: List specific Linux distributions, scripting languages, and certifications needed. Also mention desired soft skills like problem-solving and communication abilities.
- Showcase your company's unique aspects: Highlight what makes your organization stand out, such as cutting-edge projects or opportunities for professional growth. This helps attract candidates who align with your company culture.
Top Platforms to Source Linux Administrators
Now that you have a well-crafted job description, it's time to list it on job platforms to attract potential Linux Administrator candidates. The right platform can significantly boost your chances of finding qualified professionals. Let's explore some top sites for sourcing Linux Administrators.
A great platform for finding professional full-time Linux Administrators due to its extensive network and advanced search filters.
Indeed
Useful for listing both full-time and part-time job descriptions with a large audience reach.
Upwork
Ideal for hiring freelance Linux Administrators due to its global pool of freelancers and flexible hiring terms.
For freelance and remote positions, Upwork and Freelancer offer a global pool of talent with flexible hiring terms. FlexJobs specializes in remote work, making it ideal for distributed teams. Tech-specific platforms like Dice and GitHub Jobs cater to a specialized audience, while AngelList is perfect for startups looking to offer equity. These diverse platforms provide various options to match your specific hiring needs, whether you're seeking full-time, part-time, or contract Linux Administrators.
Keywords to Look for in Linux Administrator Resumes
Resume screening is a time-saver when hiring Linux Administrators. It helps you quickly identify candidates with the right skills and experience before moving to interviews.
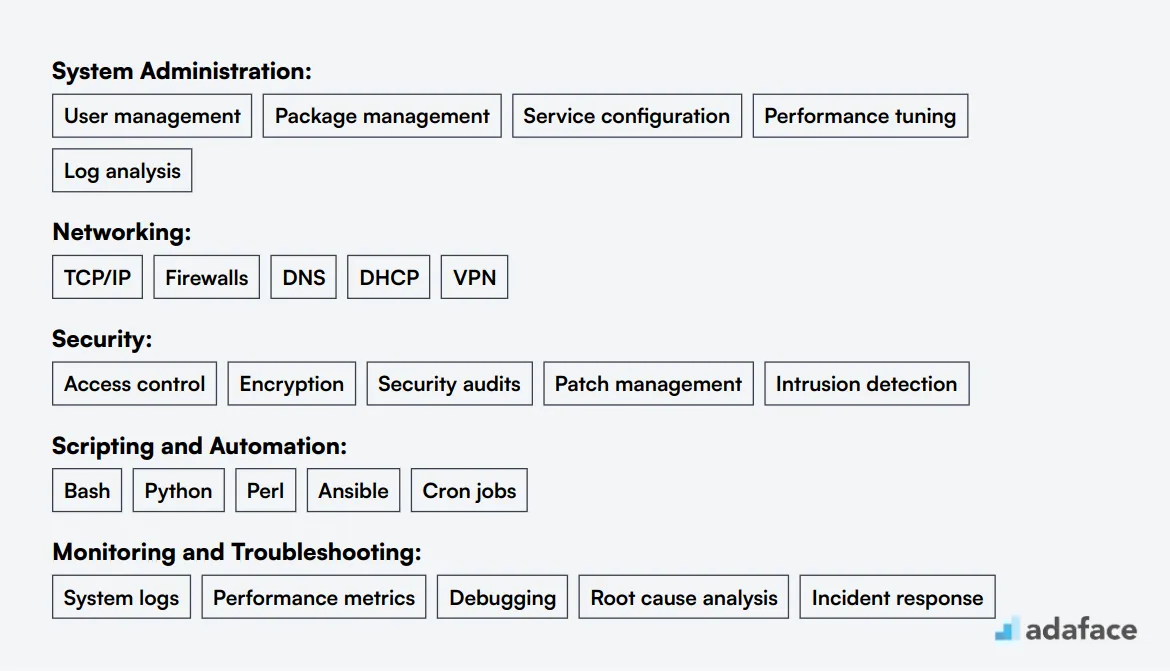
When manually screening resumes, focus on key technical skills. Look for Linux distributions (Ubuntu, CentOS, Red Hat), scripting languages (Bash, Python), and system administration tasks. Don't forget to check for networking knowledge and troubleshooting abilities.
AI tools can streamline the screening process. You can use ChatGPT or Claude by providing a prompt with your desired keywords and criteria. These tools can quickly analyze multiple resumes and provide recommendations.
TASK: Screen resumes for Linux Administrator role
INPUT: Resumes
OUTPUT:
- Email
- Name
- Matching keywords
- Score (out of 10)
- Recommendation
- Shortlist (Yes/No/Maybe)
KEYWORDS:
- Linux (Ubuntu, CentOS, Red Hat)
- Scripting (Bash, Python)
- System Administration
- Networking
- Security
- Automation
- Troubleshooting
- [Cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP)](https://www.adaface.com/assessment-test/cloud-computing-online-test)
- Containerization (Docker, Kubernetes)
Recommended Skills Tests to Screen Linux Administrators
Conducting skills tests is highly recommended when hiring Linux Administrators. These tests help ensure candidates have the necessary technical expertise to manage and maintain Linux systems effectively. Here are our top recommendations to assess the skills of Linux Administrators:
Linux Online Test is perfect for evaluating a candidate's grasp of Linux commands and system management skills. This test covers various aspects of Linux environments and helps identify candidates who can handle complex system tasks. Linux Online Test
System Administration Online Test focuses on broader system management skills that are essential for Linux Administrators. It evaluates their ability to manage user accounts, permissions, and system security. System Administration Online Test
Linux Bash Test checks the proficiency of candidates in using Bash scripting to automate tasks. This is crucial for managing repetitive tasks efficiently. Linux Bash Test
For assessing automation skills, the Ansible and Jenkins Online Test is a great choice. It evaluates a candidate's ability to use these tools for configuration management and continuous integration. Ansible and Jenkins Online Test
Finally, the DevOps Online Test provides insight into a candidate's understanding of the DevOps culture and practices, which are often intertwined with Linux system management. DevOps Online Test
Recommended Case Study Assignments to Hire Linux Administrators
Case study assignments can be a powerful tool for assessing a candidate's aptitude for a role, particularly for a technical position like a Linux Administrator. However, it's important to acknowledge that these assignments can be time-consuming and may result in lower candidate participation rates, potentially leading to the loss of talented individuals. Below, we have outlined some case study examples that balance depth and engagement.
Server Configuration and Management: This case study involves assessing a candidate's ability to configure Linux servers based on specific requirements. It tests their understanding of server setup, configuration, and maintenance, which are fundamental tasks for a Linux Administrator. This assignment reflects real-world scenarios that administrators often face, making it an effective tool for evaluation.
Troubleshooting and Problem Solving: Here, candidates are tasked with diagnosing and resolving issues in a pre-configured Linux environment. This case study highlights a candidate's troubleshooting skills, ability to quickly identify problems, and propose efficient solutions. For more insights on crafting such scenarios, you can refer to the Linux troubleshooting interview questions.
Security Audit and Enhancement: This assignment assesses a candidate's ability to audit a Linux system for potential security vulnerabilities and implement improvements. It gauges the candidate's knowledge of security protocols and their ability to safeguard systems against threats, which is critical for maintaining system integrity.
Structuring Technical Interviews for Linux Administrator Candidates
After candidates pass initial Linux Administrator skills tests, it's time for technical interviews to assess their practical abilities. While skills tests help filter out unqualified candidates, technical interviews are key to identifying the best fit for your team. Let's explore some effective interview questions to evaluate Linux Administrator candidates.
Consider asking: 'How would you troubleshoot a server that's running out of disk space?', 'Explain the process of setting up a LAMP stack', 'What's your experience with containerization and Docker?', 'How do you approach system security and user management?', and 'Describe a complex Linux issue you've solved recently'. These questions help assess problem-solving skills, technical knowledge, and real-world experience in Linux administration.
What's the difference between a Linux Systems Administrator and a DevOps Engineer?
While Linux Systems Administrators and DevOps Engineers both operate within IT, their roles differ significantly. Recruiters often confuse the two because both involve managing system environments and require technical skills. However, their core responsibilities and focus areas set them apart.
A Linux Systems Administrator focuses on system maintenance, ensuring that servers and networks are stable and running smoothly. Their primary goal is to ensure system stability by managing servers and monitoring uptime. They often work with tools like Shell, Nagios, and Puppet, and possess skills in troubleshooting and configuration. Typically, they operate in server and network environments and hold certifications like RHCSA or CompTIA Linux+.
On the other hand, a DevOps Engineer is involved in automating and deploying software. Their main aim is to streamline software delivery, making processes more fluid and agile. They work extensively with tools such as Docker, Jenkins, and Ansible, focusing on scripting and continuous integration. DevOps Engineers usually work in both cloud and on-premises environments and often come with certifications like AWS Certified DevOps Engineer.
For a deeper understanding of the skills required for a Linux Administrator, you can explore this detailed guide.
| Linux Systems Administrator | DevOps Engineer | |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Area | System Maintenance | Automation and Deployment |
| Primary Goal | Ensure System Stability | Streamline Software Delivery |
| Tools Used | Shell, Nagios, Puppet | Docker, Jenkins, Ansible |
| Key Skills | Troubleshooting, Configuration | Scripting, Continuous Integration |
| Typical Environment | Servers and Networks | Cloud and On-premises |
| Experience Level | Associate or Mid-Level | Mid-Level or Senior |
| Work Responsibilities | Manage servers, Monitor uptime | Automate pipelines, Optimize deployments |
| Certifications | RHCSA, CompTIA Linux+ | AWS Certified DevOps Engineer |
What are the ranks of Linux Administrators?
Linux administration roles often have varying titles and responsibilities across organizations. This can make it challenging for recruiters to distinguish between different levels of expertise. Let's break down the common ranks of Linux Administrators:
- Junior Linux Administrator: Entry-level position for those with basic Linux knowledge. They handle routine tasks, user management, and basic troubleshooting under supervision.
- Linux Administrator: Mid-level role with 2-5 years of experience. They manage system configurations, perform backups, and handle more complex troubleshooting independently.
- Senior Linux Administrator: Experienced professionals with 5+ years in the field. They design system architectures, implement security policies, and lead projects. Senior admins often tackle complex Linux troubleshooting scenarios.
- Linux Systems Architect: Top-tier position focusing on enterprise-level system design. They make high-level decisions about infrastructure and often have a say in company-wide IT strategies.
- Linux DevOps Engineer: Specialized role combining Linux administration with development practices. They automate processes, manage CI/CD pipelines, and bridge the gap between operations and development teams.
Hire the Best Linux Administrators
Throughout this guide, we've explored each step of the Linux Administrator hiring process, from understanding key skills and qualifications to crafting effective job descriptions and conducting technical interviews. These insights are designed to aid you in building a solid foundation for attracting and assessing potential candidates.
The most crucial takeaway is to use accurate job descriptions and skills tests to ensure you hire the right person for the role. Utilize Linux online tests and system administration online tests to assess candidates effectively. These tools help streamline the process, ensuring you find the best Linux Administrator for your team's needs.
Linux Online Test
FAQs
Key skills include proficiency in Linux operating systems, shell scripting, networking, security management, and troubleshooting. Experience with cloud platforms and containerization technologies is also valuable.
Use a combination of technical assessments, coding tests, and practical problem-solving exercises. Consider using platforms that offer specialized Linux and system administration tests.
Ask about their experience with specific Linux distributions, server management, automation tools, and security practices. Include scenario-based questions to assess problem-solving skills. Check our Linux Administrator interview questions for more ideas.
Focus on specific technical requirements, daily responsibilities, and required certifications. Highlight opportunities for growth and the technologies they'll work with. You can find a template and tips in our Linux Administrator job description guide.
Look on tech-focused job boards, professional networking sites, and Linux community forums. Consider attending tech meetups or conferences. Don't forget to leverage employee referrals and partnerships with tech schools.
Senior candidates typically have more extensive experience with complex environments, advanced troubleshooting skills, and leadership abilities. They should be able to design and implement large-scale solutions and mentor junior staff.
Valuable certifications include RHCE (Red Hat Certified Engineer), LPIC (Linux Professional Institute Certification), and CompTIA Linux+. Cloud certifications like AWS Certified SysOps Administrator or Google Cloud Professional Cloud Architect are also beneficial.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



