In today's data-driven world, hiring a data analyst is crucial for businesses striving to gain insights that drive strategic decisions. Recruiters must identify candidates with proficiency in data analysis tools and techniques, as well as those who possess strong problem-solving skills. However, many companies struggle with building an effective hiring process, often focusing too much on technical skills and overlooking the candidate's ability to communicate findings to non-technical stakeholders.
This article offers recruiters and hiring managers a comprehensive guide to hiring data analysts. We will cover everything from identifying the right keywords on resumes to structuring the interview stage. Dive into top skills tests and case study assignments that help evaluate candidates effectively. For more insights, check our skills required for data analyst blog post.
Table of contents
Why Hire a Data Analyst?
Start by identifying business problems that could benefit from data-driven insights. For example, you might need to optimize your marketing budget allocation or improve customer retention rates. These are areas where a data analyst can make a significant impact.
Consider the following use cases:
- Analyzing sales trends to forecast future demand
- Evaluating the effectiveness of different marketing channels
- Identifying bottlenecks in your operational processes
If you're dealing with complex data challenges regularly, it's time to consider hiring a full-time data analyst. For occasional projects or to test the waters, working with a consultant might be a better option.
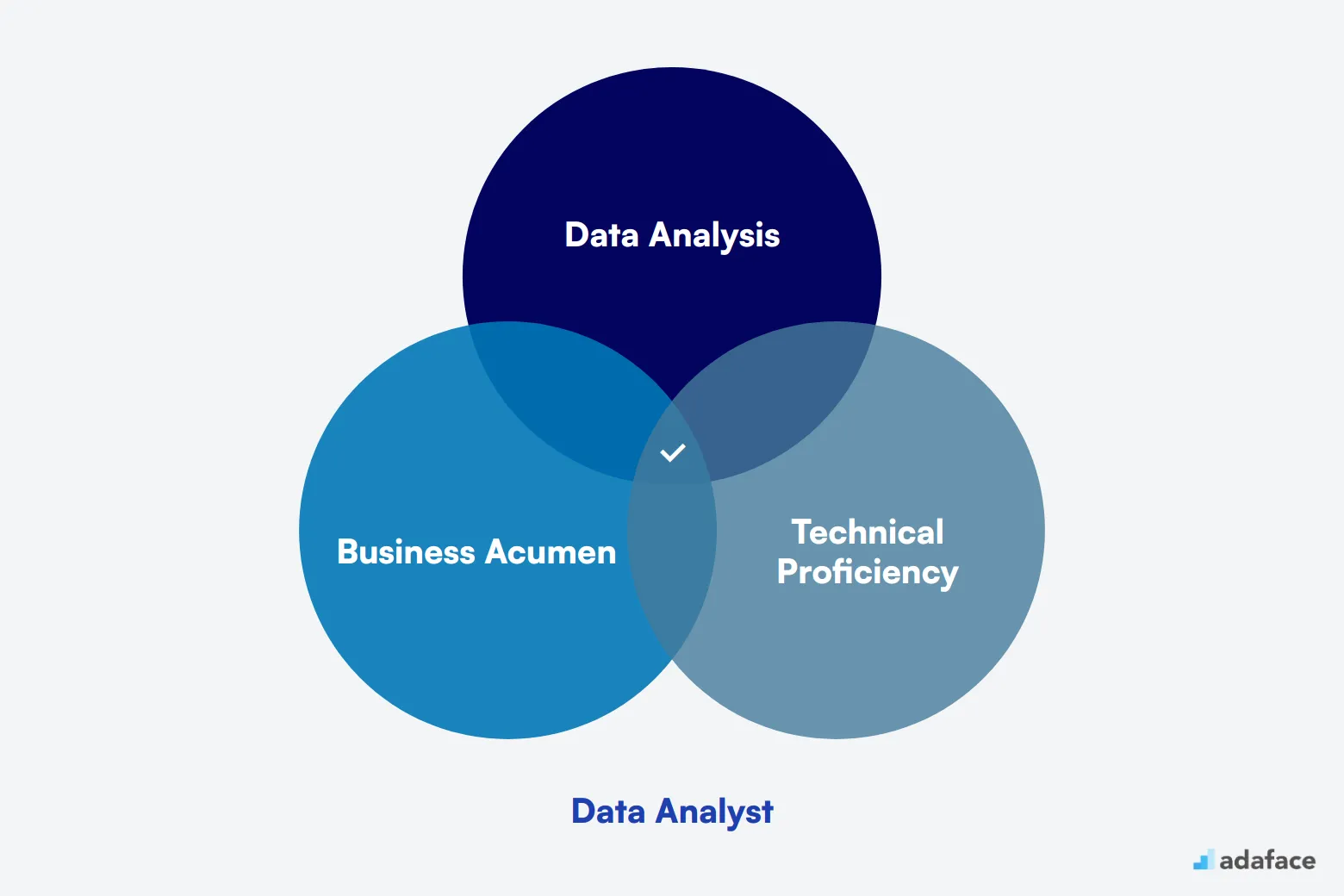
Skills and qualifications to look for in a Data Analyst
When hiring a Data Analyst, defining a candidate profile can be tricky. It's easy to mix up what is required and what is simply nice to have. A precise distinction between required and preferred skills will streamline your hiring process.
Essential qualifications for a Data Analyst include a Bachelor's degree in relevant fields and proficiency in SQL. In addition to these, strong analytical skills and the ability to present insights clearly to non-technical stakeholders are also crucial. Familiarity with data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI is also expected.
Preferred qualifications might include a Master's degree and experience with programming languages such as Python or R. Additionally, knowledge of machine learning techniques and big data technologies like Hadoop can be advantageous. Industry-specific experience, like in finance or healthcare, can be a bonus.
For a deeper understanding of how to map these skills efficiently, our skill-mapping resource can be quite useful.
| Required skills and qualifications | Preferred skills and qualifications |
|---|---|
| Bachelor's degree in Statistics, Mathematics, Computer Science, or related field | Master's degree in a quantitative field |
| Proficiency in SQL and data manipulation | Experience with programming languages such as Python or R |
| Experience with data visualization tools (e.g., Tableau, Power BI) | Knowledge of machine learning techniques |
| Strong analytical and problem-solving skills | Familiarity with big data technologies (e.g., Hadoop, Spark) |
| Excellent communication skills for presenting insights to non-technical stakeholders | Experience in a specific industry (e.g., finance, healthcare, e-commerce) |
How to Write a Data Analyst Job Description
Once you've defined your ideal candidate profile, the next step is crafting a compelling job description to attract top talent. Here are some key tips for writing an effective Data Analyst job description:
- Highlight key responsibilities and impact: Clearly outline the role's main duties, expected outcomes, and how the analyst's work will contribute to business goals. This helps candidates understand their potential impact.
- Balance technical skills with soft skills: While emphasizing technical requirements like SQL, Python, and data visualization tools, don't forget to mention important soft skills such as communication, problem-solving, and teamwork.
- Showcase your company's unique selling points: Highlight what makes your organization and the role stand out. This could include exciting projects, growth opportunities, or a supportive work environment.
Best Platforms to Hire Data Analysts
Once you have crafted a detailed job description for a Data Analyst, the next step is to post it on various job listing sites to attract potential candidates. Selecting the right platforms can make a significant difference in sourcing high-quality applicants who meet your requirements.
Useful for finding candidates for full-time positions due to its large professional network and detailed profiles.
Indeed
A highly popular job board ideal for posting full-time job listings and attracting a large number of applicants.
Upwork
A platform specifically designed for hiring freelancers, suitable for short-term or project-based work.
In addition to the top platforms like LinkedIn, Indeed, and Upwork, there are numerous other sites to consider. Glassdoor is excellent for reaching candidates who value company culture, while AngelList caters to those interested in startup environments. For remote roles, FlexJobs and Remote Global are specialized platforms offering a great talent pool. If you’re seeking tech-savvy analysts, Dice stands out as an ideal choice. Lastly, Toptal provides access to top-tier freelance talent with their stringent vetting process. Utilize skills assessment tools to further filter and evaluate candidates effectively.
Keywords to Look for in Data Analyst Resumes
Resume screening is a key step in finding the right Data Analyst for your team. It helps you quickly identify candidates with the most relevant skills and experience before moving to the interview stage.
When manually screening resumes, focus on key Data Analyst skills like SQL, data visualization tools, and statistical analysis. Look for specific tools and technologies mentioned, such as Tableau, Python, or R. Also, pay attention to quantifiable achievements and industry-specific experience.
AI-powered tools can streamline the resume screening process. These tools can quickly scan multiple resumes, identify relevant keywords, and even rank candidates based on your specified criteria. This approach can save time and reduce bias in the initial screening phase.
Here's a sample prompt for AI-assisted resume screening:
TASK: Screen resumes for Data Analyst role
INPUT: Resumes
OUTPUT:
- Candidate Name
- Matching keywords
- Score (out of 10)
- Recommendation
- Shortlist (Yes/No/Maybe)
KEYWORDS:
- SQL
- Python or R
- Data Visualization (Tableau, Power BI)
- Statistical Analysis
- Excel
- Machine Learning (optional)
Customize this prompt based on your specific requirements and use it with AI tools to efficiently screen candidates.
Top skills tests to assess Data Analysts
Skills tests are an effective way to evaluate Data Analyst candidates beyond their resumes. They provide objective insights into a candidate's abilities and help you make informed hiring decisions. Here are our recommended tests for assessing Data Analyst skills:
Data Analysis Test: This test evaluates a candidate's ability to interpret data, identify patterns, and draw meaningful conclusions. It covers key areas like statistical analysis, data visualization, and problem-solving techniques.
Excel Data Interpretation Test: Excel proficiency is often a requirement for Data Analysts. This test assesses a candidate's skills in using Excel for data manipulation, analysis, and creating insightful reports.
SQL Test: SQL is a fundamental skill for Data Analysts to query and manage databases. A SQL test helps you gauge a candidate's ability to write efficient queries and extract relevant information from databases.
Python Test: Python is widely used in data analysis for its versatility and powerful libraries. This test evaluates a candidate's proficiency in using Python for data manipulation, analysis, and visualization tasks.
Business Intelligence Analyst Test: This test assesses a candidate's ability to transform raw data into actionable insights. It covers areas like data modeling, dashboard creation, and business metrics understanding.
Case Study Assignments to Evaluate Data Analyst Candidates
Case study assignments can be valuable for assessing Data Analyst skills, but they come with drawbacks. They're often time-consuming, leading to lower completion rates and potentially losing good candidates. However, when used judiciously, they can provide insights into a candidate's problem-solving approach and analytical abilities.
Data Cleaning and Visualization: This assignment involves providing candidates with a messy dataset and asking them to clean, analyze, and visualize the data. It tests their proficiency in data analysis tools and their ability to derive meaningful insights from raw data.
Customer Churn Analysis: Candidates are given a dataset of customer information and asked to predict which customers are likely to churn. This case study evaluates their skills in predictive modeling, data interpretation, and presenting actionable recommendations.
Sales Trend Forecasting: This assignment requires candidates to analyze historical sales data and forecast future trends. It assesses their ability to use time series analysis, identify patterns, and communicate findings effectively to non-technical stakeholders.
How to structure interview stage for hiring Data Analysts
After candidates successfully pass the skills tests, it's time to move them to the technical interview stage where their hard skills are thoroughly assessed. Skills tests are excellent for filtering out unfit candidates, but technical interviews help identify the best-suited individuals for the role. This stage should be designed to evaluate a candidate's analytical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and specific technical expertise, such as in SQL or data visualization tools.
- How do you approach data cleaning in a project, and what tools do you commonly use? This question helps gauge their practical understanding of managing messy datasets.
- Explain the difference between a left join and an inner join in SQL. Use this to test their comprehension of database management.
- Describe a time when you used data visualization to influence decision-making. This is to assess their ability to communicate findings effectively.
- What statistical methods do you find most useful for analyzing data and why? This checks their knowledge of statistical techniques.
- How do you stay updated with the latest developments in data analysis? It's important to know if they are proactive in learning and evolving with the industry.
Understanding the Costs of Hiring a Data Analyst
The cost of hiring a Data Analyst varies widely based on factors such as location, experience, and industry. In general, salaries can range from $50,161 to over $128,687 in the United States, while in India, they can vary from INR 310,225 to INR 1,280,532.
It's essential to benchmark salaries against your target market to attract the right talent. Be prepared to offer competitive packages that reflect the skills and experience you require.
Data Analyst Salary in the United States
The average salary for a Data Analyst in the United States is approximately $85,959 per year. Salaries can range from around $50,161 at the lower end to about $128,687 at the higher end, depending on factors like location, experience, and industry.
For instance, Data Analysts in San Jose, CA can earn between $88,916 and $156,819, while those in Washington, DC see salaries from $62,528 to $135,421. Understanding these salary benchmarks can help you make informed offers to attract top talent.
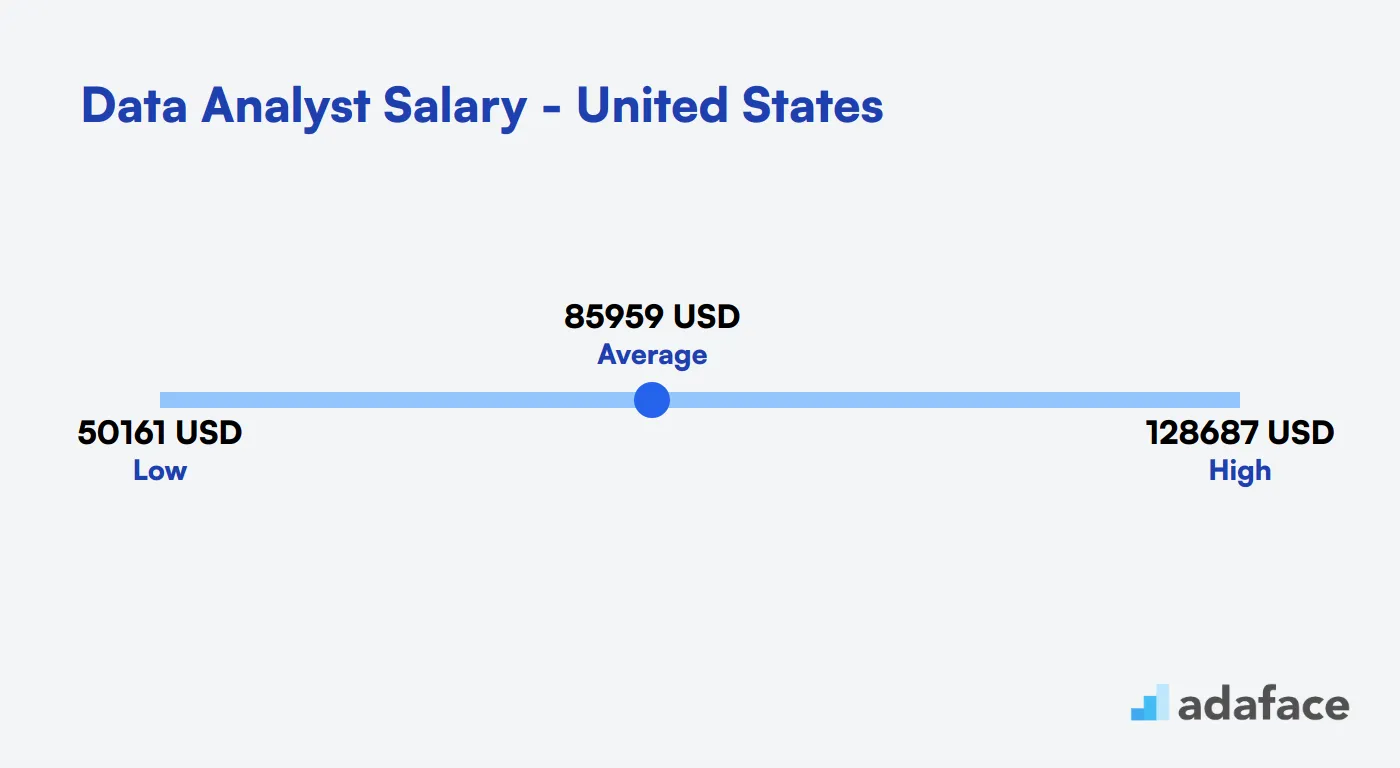
Data Analyst Salary in Australia
In Australia, Data Analysts earn competitive salaries across major cities. The national median salary is AUD 91,892, with a range typically between AUD 67,873 and AUD 124,409.
Top-paying locations include Parramatta and Sydney CBD, where median salaries reach AUD 130,000+. Other cities like Melbourne, Brisbane, and Perth offer median salaries ranging from AUD 87,000 to AUD 98,000.
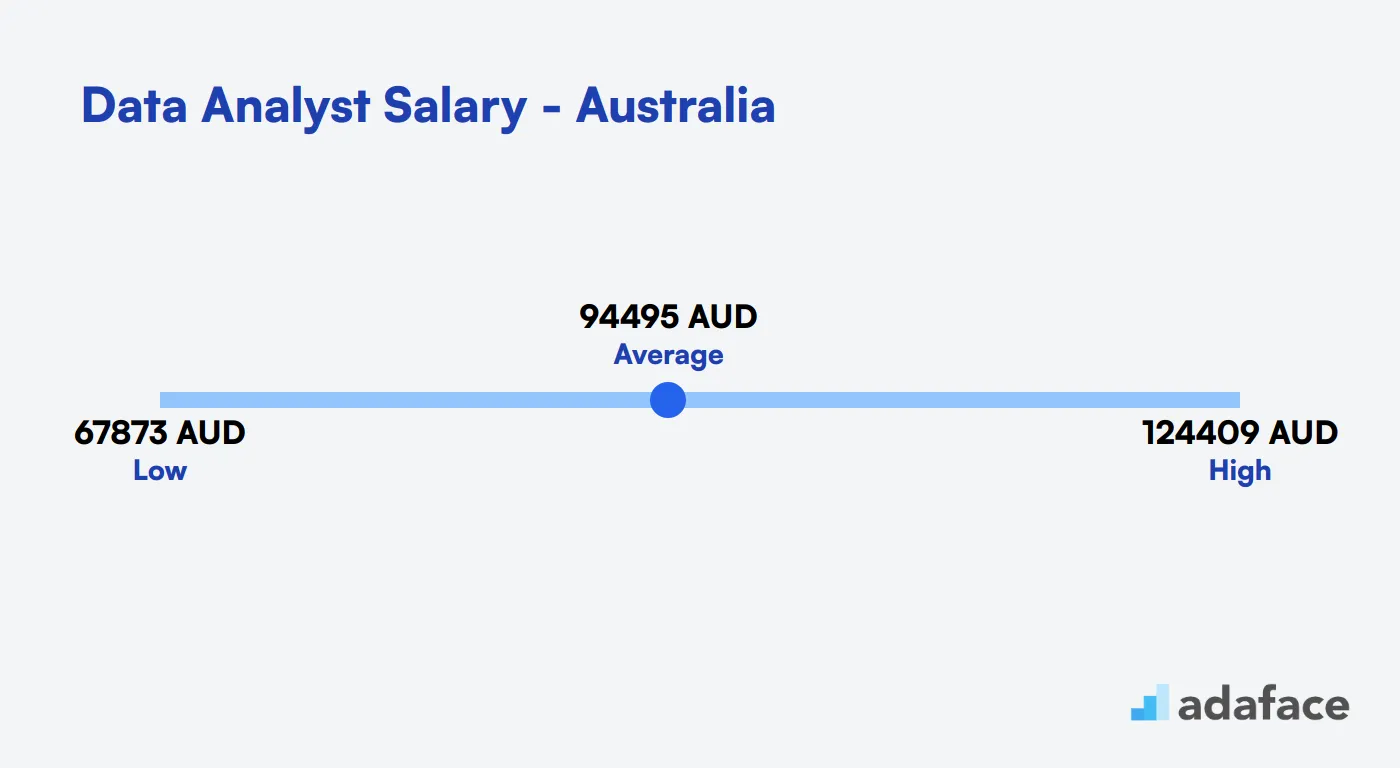
Data Analyst Salary in the Philippines
In the Philippines, Data Analyst salaries vary significantly by location. In major cities like Taguig and Makati, the average annual salary ranges from approximately PHP 299,041 to PHP 1,038,836, with a median of around PHP 557,364 and PHP 477,733, respectively. Meanwhile, in Caloocan, the average salary dips to between PHP 217,932 and PHP 290,839. On a national level, Data Analysts in the Philippines earn a median salary of PHP 303,932, reflecting a diverse and dynamic job market across regions.
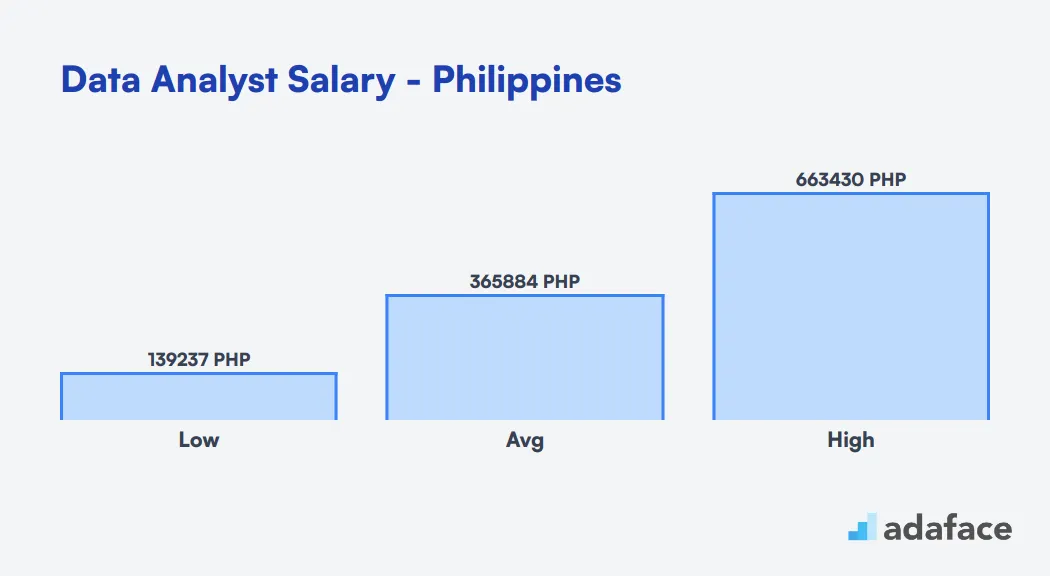
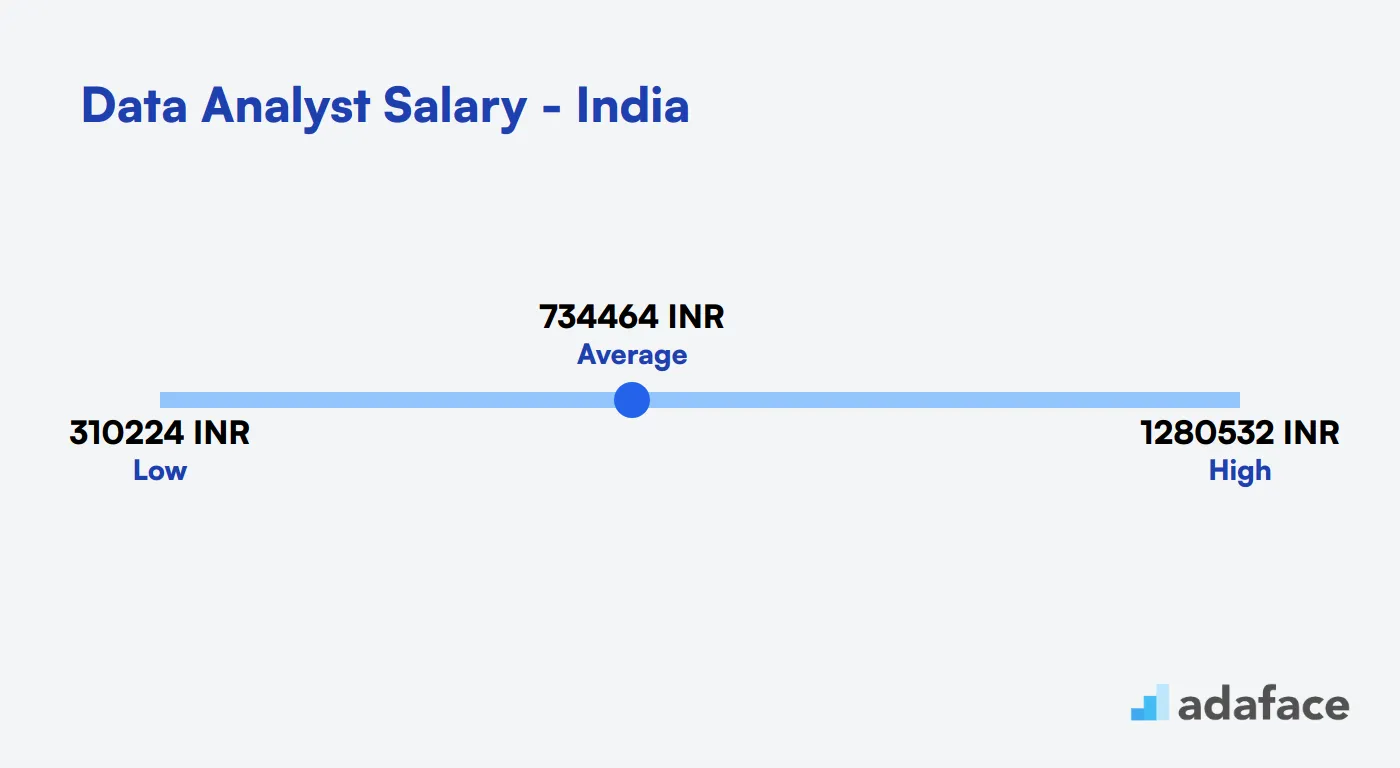
Data Analyst Salary in India
The average salary for a Data Analyst in India is approximately INR 734,464 per year. Salaries can range significantly depending on the location and experience, with overall figures varying from INR 310,225 to INR 1,280,532. In cities like Bengaluru, the median salary is around INR 756,960, while in Delhi, it is lower at INR 351,843. Understanding these differences can help recruiters set competitive offers.
What's the difference between a Data Analyst and a Business Analyst?
People often confuse data analysts and business analysts because both roles involve working with data to aid decision-making. However, their areas of focus and expertise differ significantly.
A data analyst is primarily data-centric, with skills in statistical analysis and data manipulation. They use tools like SQL, Python, and R to clean data and build predictive models. Typically, data analysts have degrees in fields like statistics or computer science. Their deliverables include data insights and dashboards, usually reporting to a data science manager.
In contrast, a business analyst is business-centric, focusing on business process analysis and requirements gathering. They use tools such as Excel, PowerBI, and Jira to improve processes and manage stakeholders. Business analysts often have backgrounds in business administration or economics and report to a business unit manager. Their work results in business recommendations and process maps.
For more insights into the skills required for data analysts, you can explore our detailed guides.
| Data Analyst | Business Analyst | |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Data-centric | Business-centric |
| Primary Skills | Statistical analysis, Data manipulation | Business process analysis, Requirements gathering |
| Tools | SQL, Python, R, Tableau | Excel, PowerBI, Jira, Visio |
| Key Responsibilities | Data cleaning, Predictive modeling | Process improvement, Stakeholder management |
| Typical Degree | Statistics, Computer Science | Business Administration, Economics |
| Technical Depth | Deep technical knowledge | Broad business acumen |
| Deliverables | Data insights, Dashboards | Business recommendations, Process maps |
| Reporting To | Data Science Manager | Business Unit Manager |
What are the ranks of Data Analysts?
Navigating the world of data analytics can be challenging for recruiters and hiring managers, especially when differentiating between various roles and ranks. While the positions of data analysts may overlap in some responsibilities, there is a structured hierarchy that helps in understanding their scope of work.
• Junior Data Analyst: Often considered an entry-level role, junior data analysts assist in basic data collection and analysis tasks. They are usually responsible for cleaning data, creating reports, and supporting senior team members with simpler data requests.
• Data Analyst: As standard data analysts, these professionals work independently on various data projects. They analyze complex datasets, provide actionable insights, and collaborate with other departments to meet organizational goals. A data analyst job description typically includes proficiency in tools like SQL and Excel.
• Senior Data Analyst: With more experience, senior data analysts handle larger datasets and lead data projects. They mentor junior analysts, develop advanced models, and often work closely with business stakeholders to influence strategic decisions.
• Lead Data Analyst: At the top of the hierarchy, lead data analysts oversee the entire data analysis function within a team. They set the analytical direction, manage complex projects, and ensure that the insights generated align with the company's objectives.
Hire the Best Data Analysts for Your Team
Throughout this guide, we've covered the importance of data analysts, key skills to look for, writing effective job descriptions, and various stages of the hiring process. We've also explored different platforms for sourcing candidates and discussed the costs associated with hiring top talent in this field.
The key takeaway is to use well-crafted job descriptions and skill-based assessments to make your hiring process more accurate and efficient. By focusing on candidates' practical abilities and problem-solving skills, you'll be better equipped to find the right data analyst who can drive value for your organization.
Data Analysis Test
FAQs
Focus on keywords like SQL, Python, data visualization, and experience with data analysis tools. Look for candidates with strong problem-solving skills and the ability to communicate complex data insights effectively.
Key skills include proficiency in statistical analysis, data mining, SQL, data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI, and the ability to interpret data patterns and trends.
Utilize targeted skills tests and practical case study assignments to evaluate a candidate's ability to analyze data and derive actionable insights.
Ask about their experience with specific data tools, how they handle data cleaning, their process for interpreting data, and how they present findings to stakeholders.
Begin with a phone screening focusing on technical skills, followed by a practical case study assignment, and conclude with an in-person or virtual interview that assesses both technical and soft skills.
A data analyst helps interpret complex data, providing valuable insights that can guide strategic decisions and improve overall business performance.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



