Hiring the right auditor is a critical task that many companies struggle with. As a recruiter or hiring manager, you're tasked with finding someone who not only has the technical skills to examine financial records but also possesses the analytical mindset to spot irregularities and the communication skills to report findings effectively. It's a balancing act that requires a keen eye for both hard and soft skills.
This guide will walk you through the process of hiring an auditor, from understanding the role to conducting effective interviews. We'll cover key aspects such as skills to look for in an auditor, recommended assessment methods, and strategies for evaluating candidates. Whether you're hiring for an internal audit team or seeking external audit services, this article will provide you with actionable insights to make informed hiring decisions.
Table of contents
Why Hire an Auditor?
To decide if you need an auditor, start by identifying financial challenges or compliance issues your organization faces. For example, you might be struggling with internal control weaknesses or need help preparing for an external audit.
Consider hiring an auditor if you're dealing with:
- Complex financial transactions
- Regulatory compliance requirements
- Need for improved financial reporting
If these issues are ongoing, a full-time auditor might be necessary. For one-time projects or smaller companies, hiring an independent consultant or working with an audit firm could be more cost-effective.
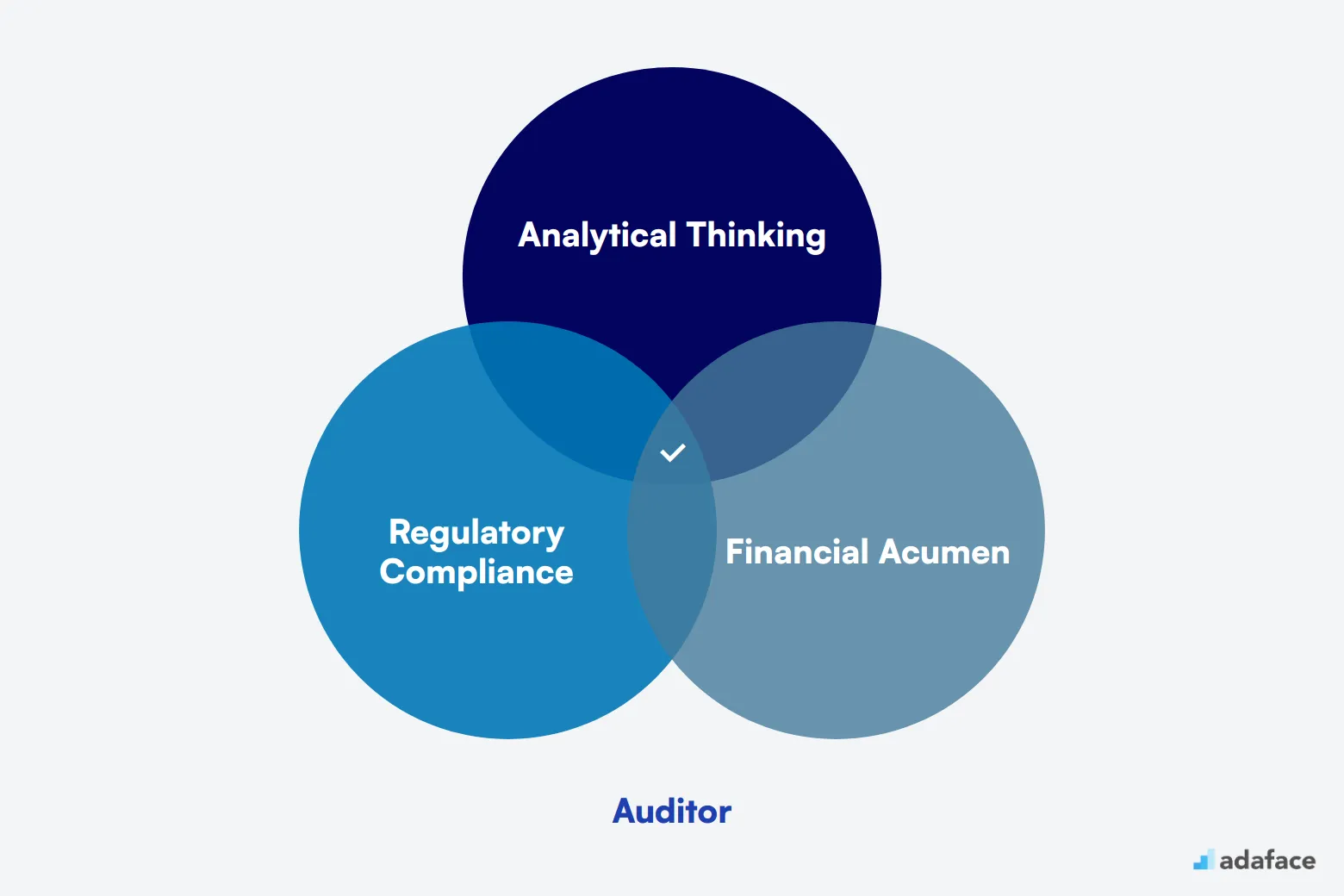
What does an Auditor do?
An auditor is a professional responsible for examining and verifying a company's financial records to ensure they are accurate and comply with regulations. They play a critical role in maintaining the integrity of financial reporting, providing insights into financial practices, and identifying areas for improvement.
Day-to-day tasks of an auditor typically include:
- Reviewing financial statements and records to verify accuracy.
- Ensuring compliance with financial and legal regulations.
- Identifying financial risks and suggesting improvements.
- Preparing detailed audit reports and presenting findings to management.
Auditors are vital in safeguarding businesses against financial discrepancies. For more detailed insights, check out our auditor job description.
Key skills and qualifications for an Auditor
When creating a candidate profile for an Auditor, it's important to distinguish between must-have and nice-to-have qualifications. The role requires a mix of technical expertise, analytical skills, and professional certifications. Here's a breakdown of the skills and qualifications to consider when hiring an Auditor:
Required skills and qualifications:
- Bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, or related field
- Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or equivalent qualification
- Minimum of three years of auditing experience
- Strong knowledge of auditing standards and procedures
- Excellent analytical and problem-solving skills
Preferred skills and qualifications:
- Master's degree in accounting or finance
- Experience with financial software and accounting systems
- Strong project management skills
- Proven success in a collaborative environment
- Experience in industry-specific auditing (e.g., IT, healthcare)
To evaluate these skills effectively, consider using skills assessment tools that can provide objective insights into a candidate's abilities. This approach can help you identify top talent more accurately and streamline your hiring process.
| Required skills and qualifications | Preferred skills and qualifications |
|---|---|
| Bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, or related field | Master's degree in accounting or finance |
| Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or equivalent qualification | Experience with financial software and accounting systems |
| Minimum of three years of auditing experience | Strong project management skills |
| Strong knowledge of auditing standards and procedures | Proven success in a collaborative environment |
| Excellent analytical and problem-solving skills | Experience in industry-specific auditing (e.g., IT, healthcare) |
How to write an Auditor job description?
Creating an attractive job description for an auditor is the next step once you have a candidate profile ready. This document will be your tool to capture and engage the right candidates for the role.
- Highlight key responsibilities and impact: Clearly articulate the auditor's role in evaluating financial statements, advising on risk management, and ensuring legal compliance. Mention how their work directly influences organizational accountability and accuracy. For inspiration, visit the auditor job description page.
- Balance technical skills and certifications with soft skills: Specify required technical proficiencies like audit software knowledge and certifications such as CPA or CIA. Equally important is to emphasize soft skills like analytical thinking and attention to detail that are crucial in auditing.
- Showcase the unique selling points: Distinguish your role by highlighting unique aspects like exposure to diverse industries, opportunities for professional growth, or involvement in high-profile audits. These elements can attract top-tier candidates seeking engaging and challenging work environments.
10 platforms to hire Auditors
Now that you have your job description ready, it's time to post it on various job listing sites to attract the right candidates. Utilizing a range of platforms will help you broaden your reach and ensure you find the best auditors available in the market.
Indeed Auditor Jobs
Best for a wide range of auditor positions across industries. Offers a large pool of candidates and easy job posting process.
LinkedIn Auditor Jobs
Ideal for finding experienced auditors with established professional networks. Good for both active and passive candidate sourcing.
Robert Half Finance & Accounting
Specialized in finance and accounting roles. Excellent for finding qualified auditors with specific industry experience.
Some of the top platforms to consider include Indeed Auditor Jobs, known for its extensive reach, and LinkedIn Auditor Jobs, where you can tap into professional networks for experienced candidates. Other worthwhile options are Robert Half Finance & Accounting, which specializes in finance roles, and Glassdoor Auditor Jobs, where you can attract candidates interested in company culture and transparency. As you explore additional platforms, consider those that cater to specific needs, such as freelance opportunities or specialized accounting roles.
Keywords to Look for in Auditor Resumes
Resume screening is a critical first step in the auditor hiring process. It helps you quickly identify candidates with the right skills and experience, saving time and resources in your recruitment efforts.

When manually screening resumes, focus on key qualifications like a Bachelor's degree in accounting or finance, CPA certification, and relevant auditing experience. Look for specific skills such as knowledge of GAAP, IFRS, and experience with audit tools like ACL or IDEA.
AI-powered screening tools can streamline this process. You can use AI language models to analyze resumes based on predefined criteria, helping you shortlist candidates more efficiently.
Here's a sample prompt for AI-assisted resume screening:
TASK: Screen resumes for auditor role
INPUT: Resumes
OUTPUT: For each resume, provide:
- Email id
- Name
- Matching keywords
- Score (out of 10)
- Recommendation
- Shortlist (Yes, No, or Maybe)
KEYWORDS:
- Accounting degree (CPA, ACCA)
- Auditing experience
- GAAP, IFRS
- Audit tools (ACL, IDEA)
- [Financial analysis](https://www.adaface.com/assessment-test/financial-accounting-test)
- Regulatory knowledge (SOX, industry regulations)
- Communication skills
Recommended skills tests for assessing Auditors
Skills tests are an effective way to evaluate auditor candidates beyond their resumes. They provide objective insights into a candidate's abilities and knowledge. Here are five key tests we recommend for assessing auditor skills:
Aptitude Test for Auditors: This test evaluates critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills specific to auditing roles. It helps gauge a candidate's ability to handle complex auditing tasks.
Financial Accounting Test: Use this assessment to measure a candidate's understanding of financial statements, accounting principles, and reporting standards. It's important for auditors to have a strong foundation in these areas.
Excel Test: Excel proficiency is a must for auditors. This test assesses a candidate's ability to work with spreadsheets, perform data analysis, and create financial models.
Attention to Detail Test: Auditors need to be meticulous in their work. This test evaluates a candidate's ability to spot errors, inconsistencies, and anomalies in financial data.
Critical Thinking Test: Critical thinking skills are essential for auditors to analyze complex financial information and make sound judgments. This test assesses a candidate's ability to evaluate evidence and draw logical conclusions.
Case Study Assignments to Evaluate Auditor Candidates
Case study assignments can be valuable tools for assessing auditor candidates, but they come with drawbacks. These assignments often lead to lower completion rates and may cause qualified candidates to drop out due to their time-consuming nature. However, when used judiciously, they can provide insights into a candidate's practical skills.
Financial Statement Analysis: This case study involves reviewing a company's financial statements to identify discrepancies or areas of concern. Candidates are asked to analyze financial data, spot irregularities, and propose audit procedures.
Internal Control Evaluation: Candidates are presented with a scenario describing a company's internal control systems. They must identify weaknesses, assess risks, and recommend improvements to strengthen the control environment.
Fraud Detection Scenario: This assignment presents a complex business situation with potential fraud indicators. Auditor candidates need to recognize red flags, outline investigative steps, and suggest ways to prevent similar issues in the future.
How to structure interviews for hiring Auditors?
Candidates who successfully pass the skills tests should proceed to the technical interview stage, where their hard skills are further evaluated. While skills tests are effective in filtering out unfit candidates, they don't always identify the best-suited individuals for the role. The technical interview is your opportunity to assess candidates' practical knowledge and problem-solving abilities before making a hiring decision.
Here are some sample interview questions to consider: What auditing software are you proficient with? This helps gauge their comfort with the tools your organization uses. Can you walk us through your process for conducting an audit? This question assesses their methodological knowledge. How do you handle discrepancies found during an audit? This provides insight into their problem-solving skills. What steps would you take to ensure compliance with financial regulations? This evaluates their understanding of regulatory requirements. Lastly, how do you maintain accuracy and attention to detail under tight deadlines? This examines their ability to perform under pressure. Assessing a candidate's responses to these questions alongside results from skills tests for auditors can significantly enhance your hiring process.
How much does it cost to hire an Auditor?
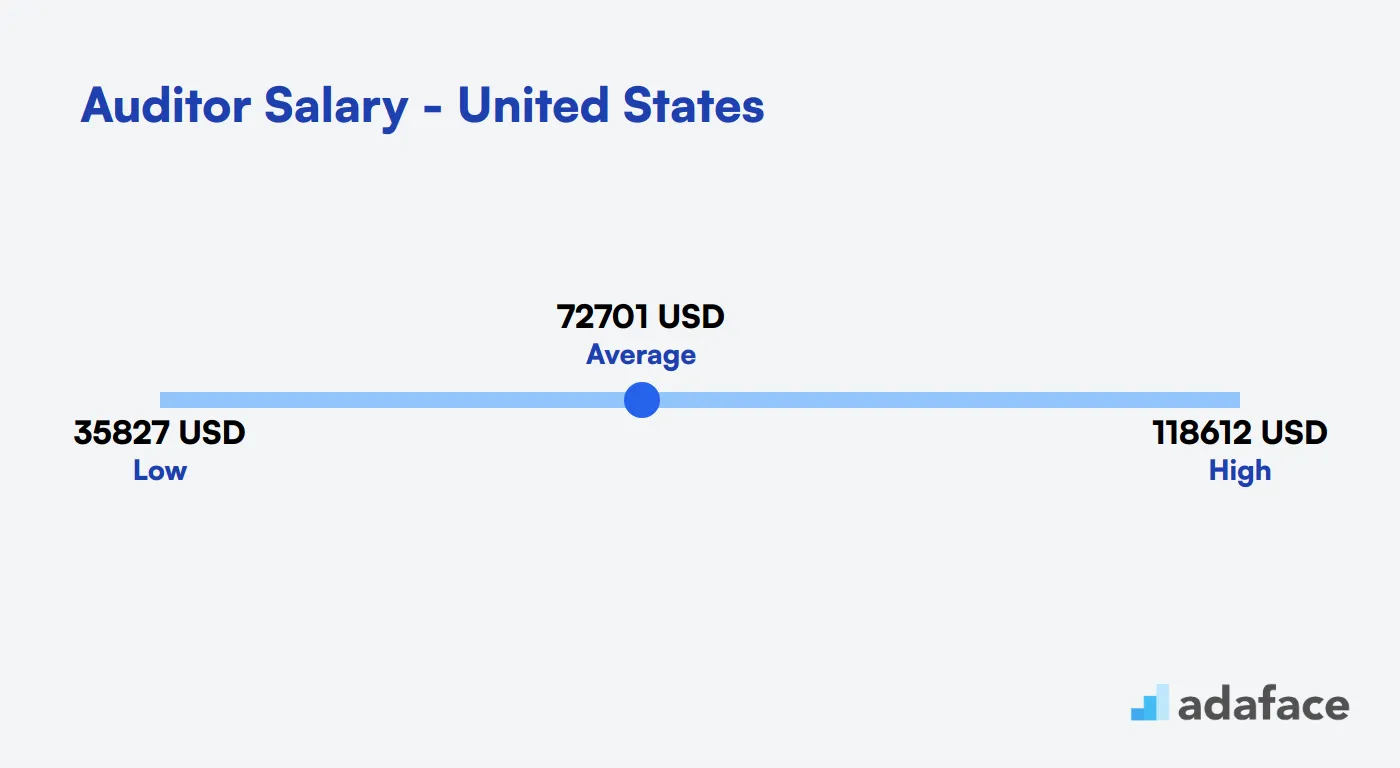
The cost of hiring an auditor varies widely based on location, experience, and industry. On average, an auditor in the United States earns about $72,701 per year. However, this figure can range from $38,294 to $184,300 depending on factors like city and specialization.
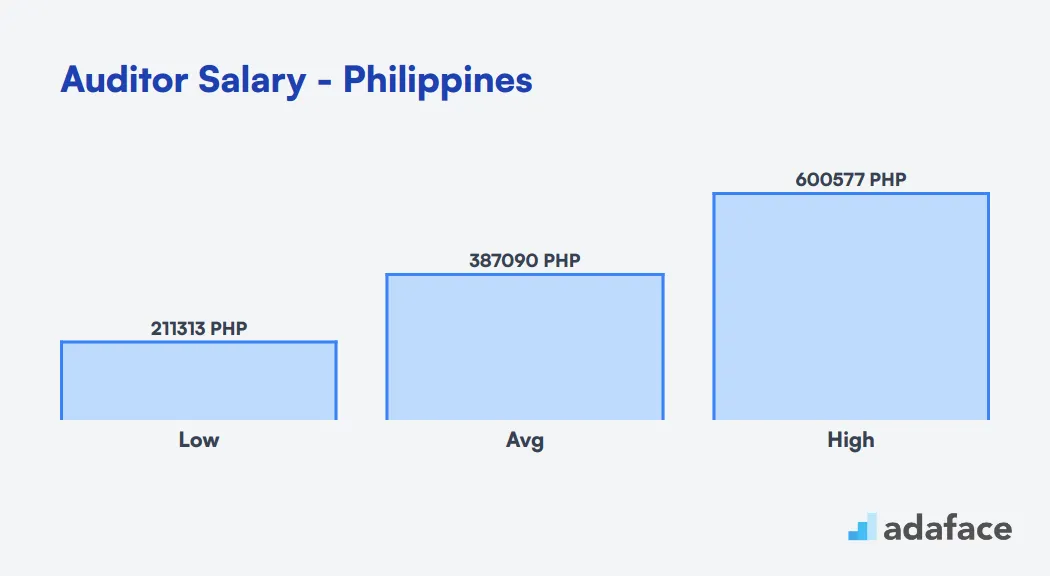
In other countries, such as the Philippines, the salary range is different. Filipino auditors earn an average of PHP 387,091 annually, with salaries ranging from PHP 211,314 to PHP 600,578. Remember that these figures are just averages, and actual costs may differ based on your specific requirements and market conditions.
Auditor Salary United States
In the United States, the average salary for auditors is approximately $72,701 per year. Depending on the location, this can vary significantly. For instance, auditors in New York City can earn between $50,298 and $184,300, while those in Tampa, Florida might see salaries ranging from $38,294 to $99,023. This represents the dynamic nature of auditor salaries across different regions.
Auditor Salary in the United Kingdom
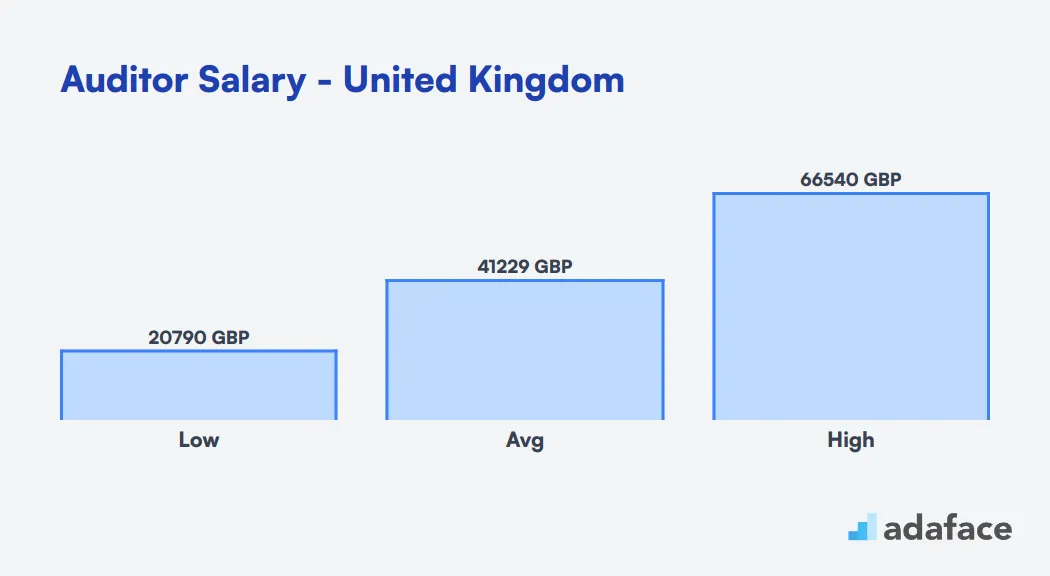
In the United Kingdom, auditor salaries vary based on experience and location. The average salary for auditors in the UK ranges from £30,000 to £65,000 per year. Entry-level positions typically start around £25,000, while senior auditors with extensive experience can earn upwards of £80,000 annually.
London-based auditors generally command higher salaries due to the higher cost of living. Big Four accounting firms often offer competitive packages, which can include bonuses and benefits on top of the base salary.
Auditor Salary Philippines
The average salary for an auditor in the Philippines is approximately PHP 387,091 annually. Salaries can range from PHP 211,314 to PHP 600,578 depending on factors like location and experience. In cities like Taguig and Cebu City, auditors may expect higher salaries compared to locations like Caloocan or Parañaque.
What are the ranks of Auditors?
Navigating the ranks of auditors can sometimes be challenging due to the varying titles and responsibilities across organizations. However, understanding these ranks helps in identifying the right candidate for the role you need. Here are some common ranks in the auditing profession:
- Junior Auditor: This entry-level position involves assisting senior auditors in examining financial statements and reports for accuracy. Junior auditors often perform routine audits and help prepare audit findings.
- Internal Auditor: Internal auditors are responsible for assessing the financial and operational processes within an organization. They ensure compliance with internal policies and identify areas for improvement. You can find more details in this auditor job description.
- Senior Auditor: A senior auditor supervises junior staff and leads audit projects. They review the work of junior auditors and provide insights into audit findings, ensuring that procedures comply with standards and regulations.
- Audit Manager: This role involves overseeing the entire audit process within an organization. Audit managers develop audit plans, manage teams, and communicate audit results to senior management.
- Director of Internal Audit: At the top of the hierarchy, the director of internal audit sets the audit strategy and ensures that the audit department effectively assesses risk management and control processes.
Aptitude Test for Auditors
FAQs
When hiring an auditor, look for candidates with a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, or a related field. Professional certifications such as Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) are highly valuable. Additionally, seek candidates with experience in auditing, strong analytical skills, and knowledge of relevant regulations and standards.
To assess an auditor's technical skills, consider using accounting and finance tests that cover areas such as financial reporting, auditing procedures, and regulatory compliance. Case studies or practical exercises can also help evaluate a candidate's ability to apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios.
Important soft skills for auditors include excellent communication, both written and verbal, strong attention to detail, critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and integrity. Auditors should also possess good interpersonal skills to interact effectively with clients and team members.
Structure auditor interviews by combining behavioral questions, technical inquiries, and scenario-based problems. Start with questions about the candidate's experience and background, then move on to specific auditing scenarios. Include questions that assess their knowledge of auditing standards and their approach to ethical dilemmas. Consider using auditor interview questions to guide your process.
Certifications such as CPA, CIA, or Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) demonstrate a candidate's commitment to the profession and their expertise in specific areas of auditing. While not always mandatory, these certifications can be strong indicators of an auditor's knowledge and professional standing.
To evaluate an auditor's attention to detail, use attention to detail tests or provide sample financial statements with intentional errors for them to identify. You can also ask candidates to describe their process for reviewing documents and catching discrepancies during previous audits.
When hiring an auditor for a specific industry, look for candidates with relevant experience or knowledge in that sector. They should be familiar with industry-specific regulations, accounting practices, and common risks. Consider asking about their experience with similar clients or their understanding of the unique challenges faced by businesses in your industry.

40 min skill tests.
No trick questions.
Accurate shortlisting.
We make it easy for you to find the best candidates in your pipeline with a 40 min skills test.
Try for freeRelated posts
Free resources



